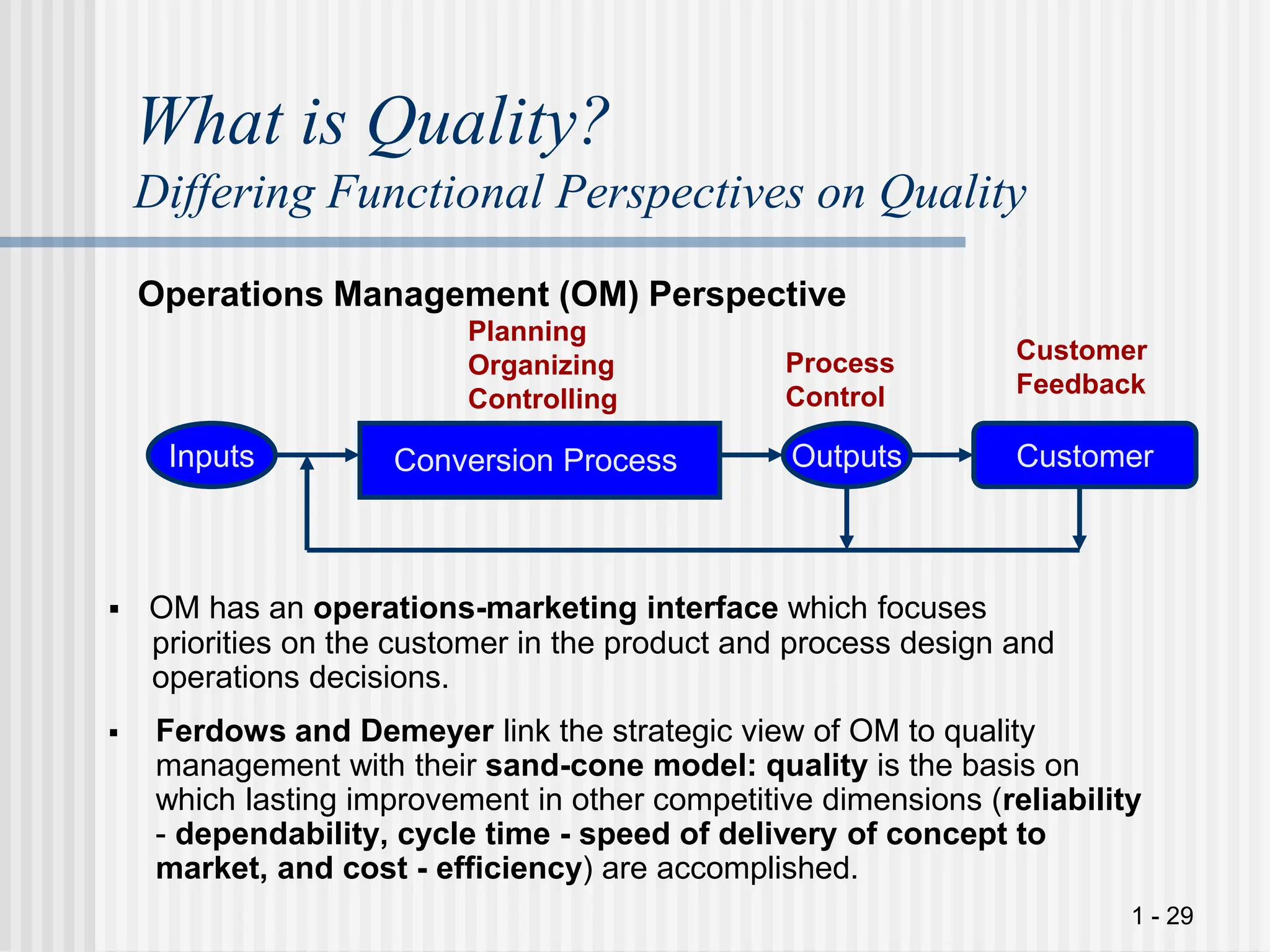
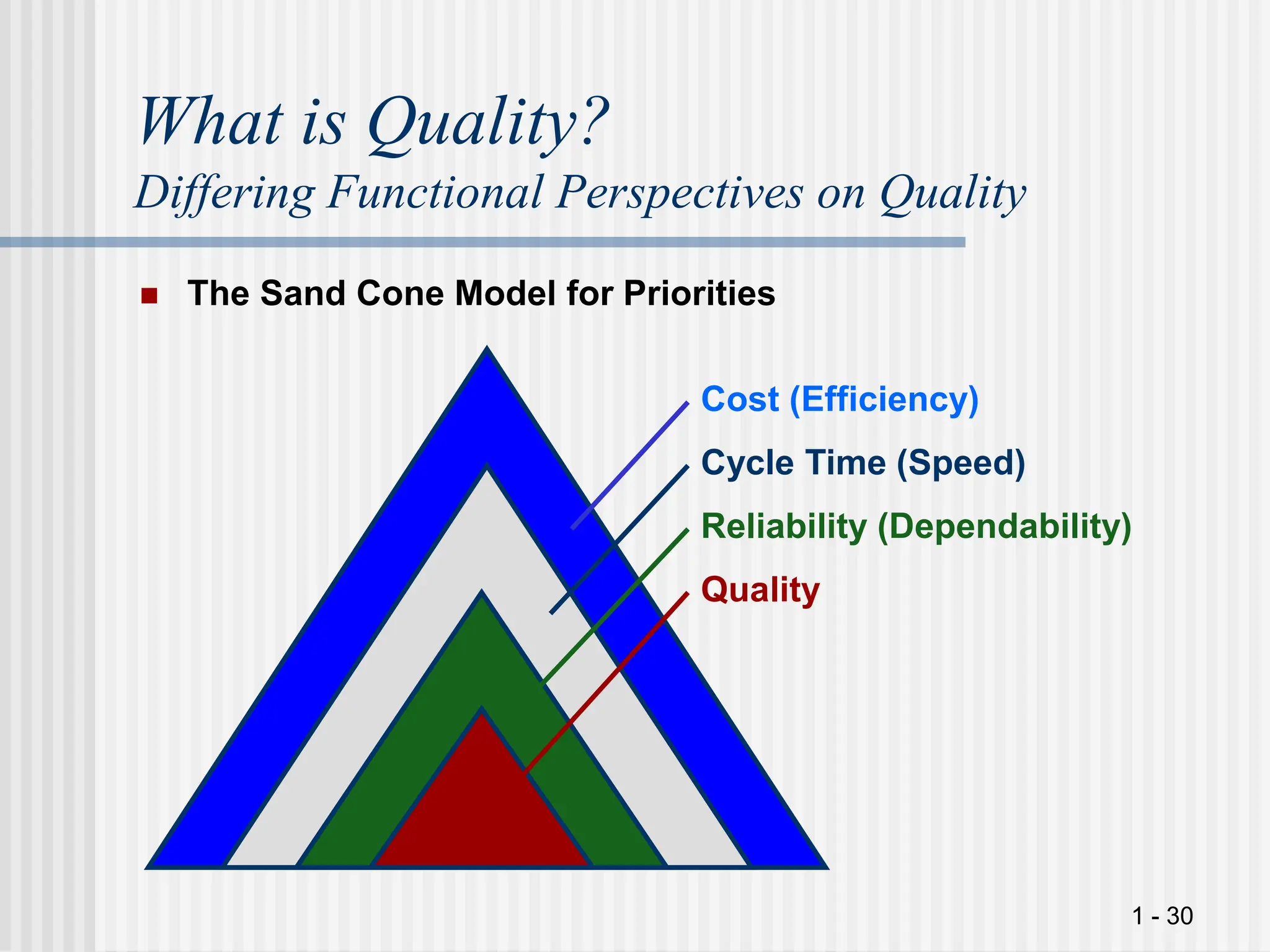
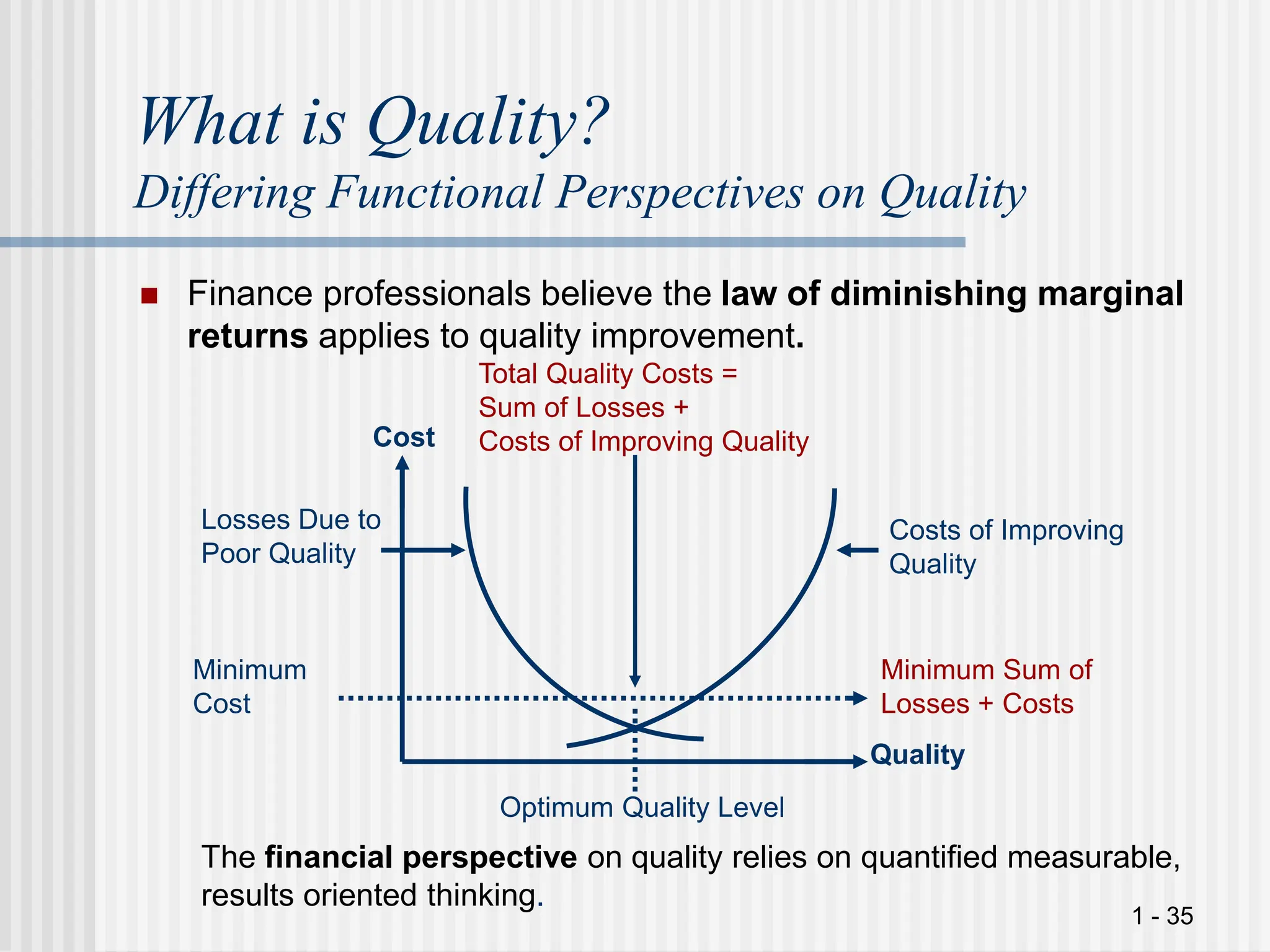
El documento aborda la importancia de la gestión de la calidad en la cadena de suministro, destacando que todas las áreas funcionales deben ser responsables de sus procesos de gestión de calidad. Se presentan diferentes perspectivas sobre la calidad, incluyendo la importancia de una definición común en equipos interfuncionales, y se discuten dimensiones de calidad tanto para productos como para servicios. Además, se enfatiza en la necesidad de adoptar un enfoque contingente para la mejora de la calidad, considerando diversas variables operativas en la empresa.