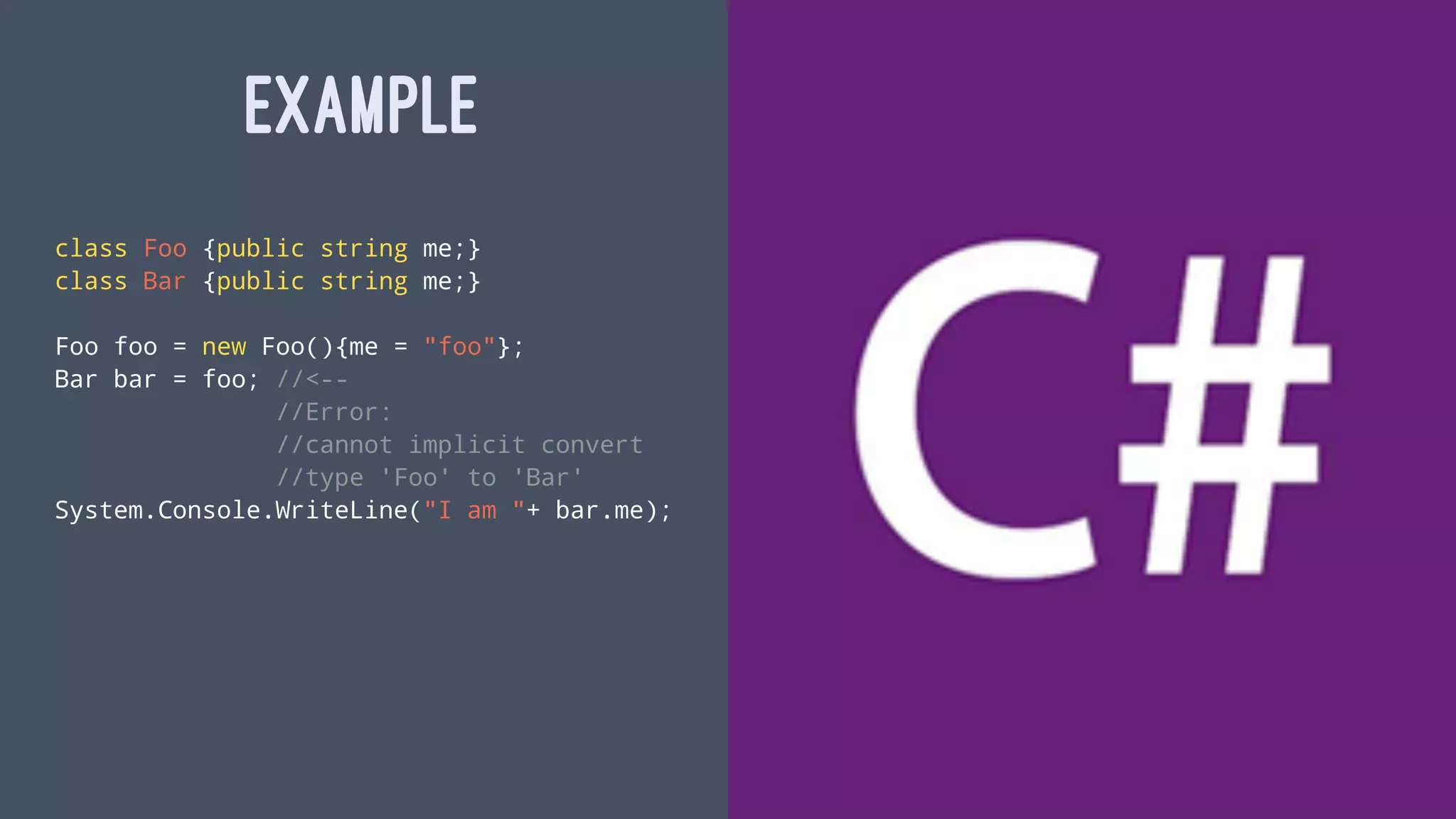
This document discusses TypeScript design goals and features. It begins by explaining that TypeScript aims to use JavaScript behavior and programmer intentions to guide its design rather than mimicking existing languages. It then lists goals of aligning with ECMAScript proposals and using a consistent, fully erasable structural type system. The document provides examples of TypeScript types, unions, intersections, and discriminated unions. It also discusses using functional programming with algebraic data types, functors, and monads to implement validation in TypeScript. Homework suggestions are provided at the end.
















![1. PARAMETRIC POLIMORPHISM2
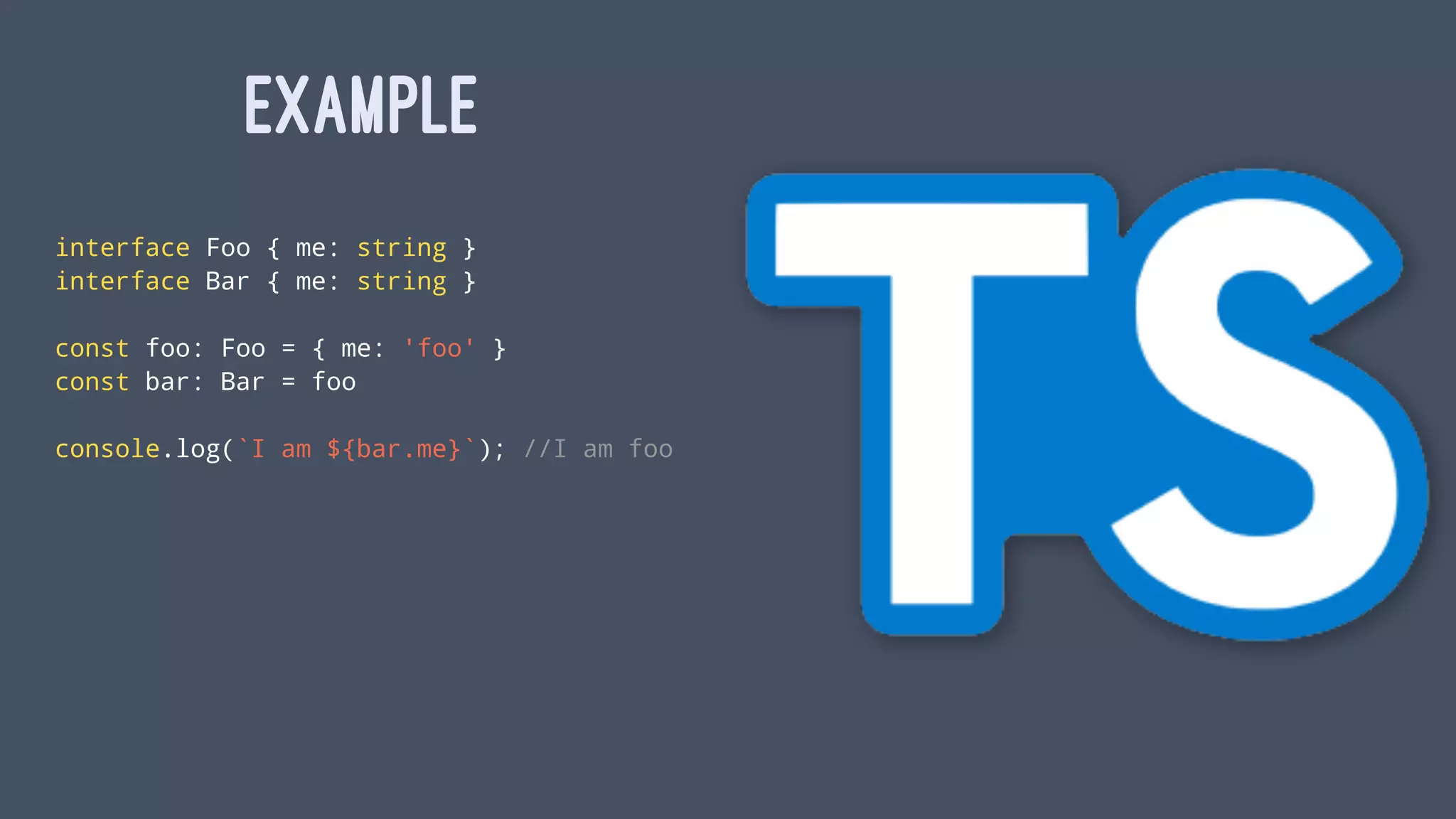
interface Valid<A> { a: A }
interface Invalid<E> { errors: E[] }
function save<A>(data: Valid<A>): void {
alert(`${JSON.stringfy(data.a)} saved!`);
}
function showErrors<E>(data: Invalid<E>): void {
alert(`${JSON.stringfy(data.errors)} :(`);
}
2
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parametric_polymorphism](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-161118115536/75/Ask-The-Expert-Typescript-A-stitch-in-time-saves-nine-24-2048.jpg)