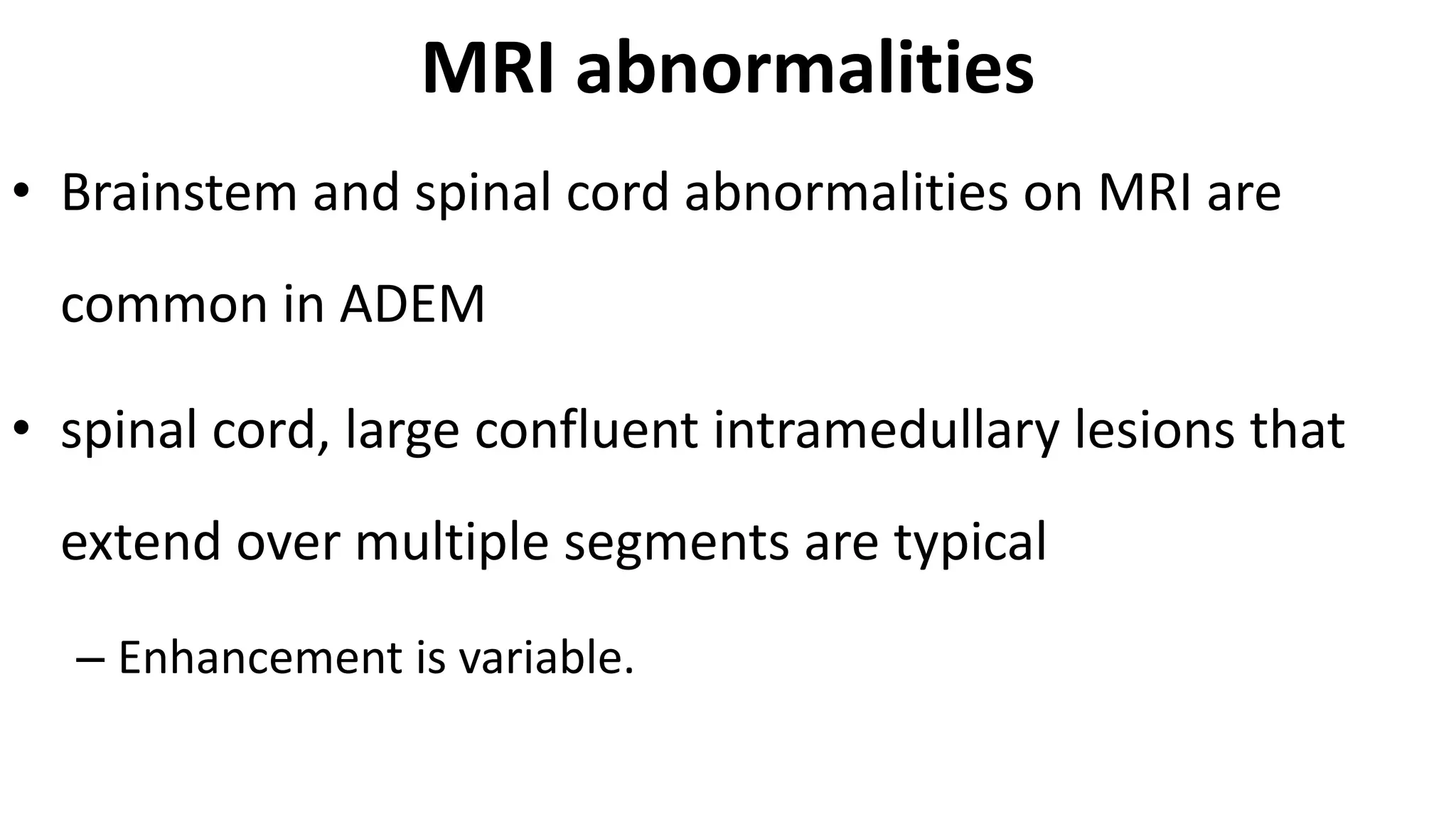
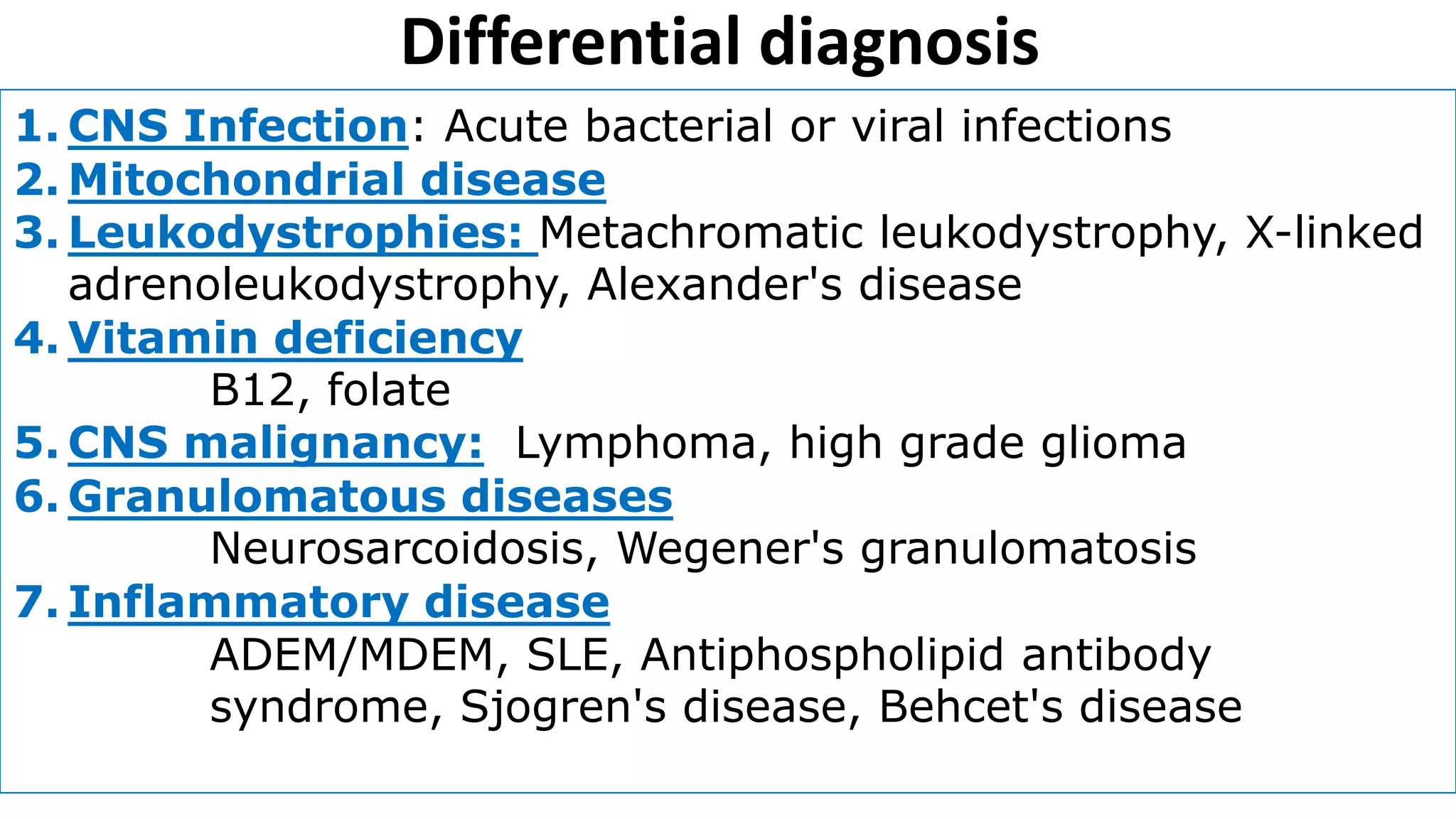
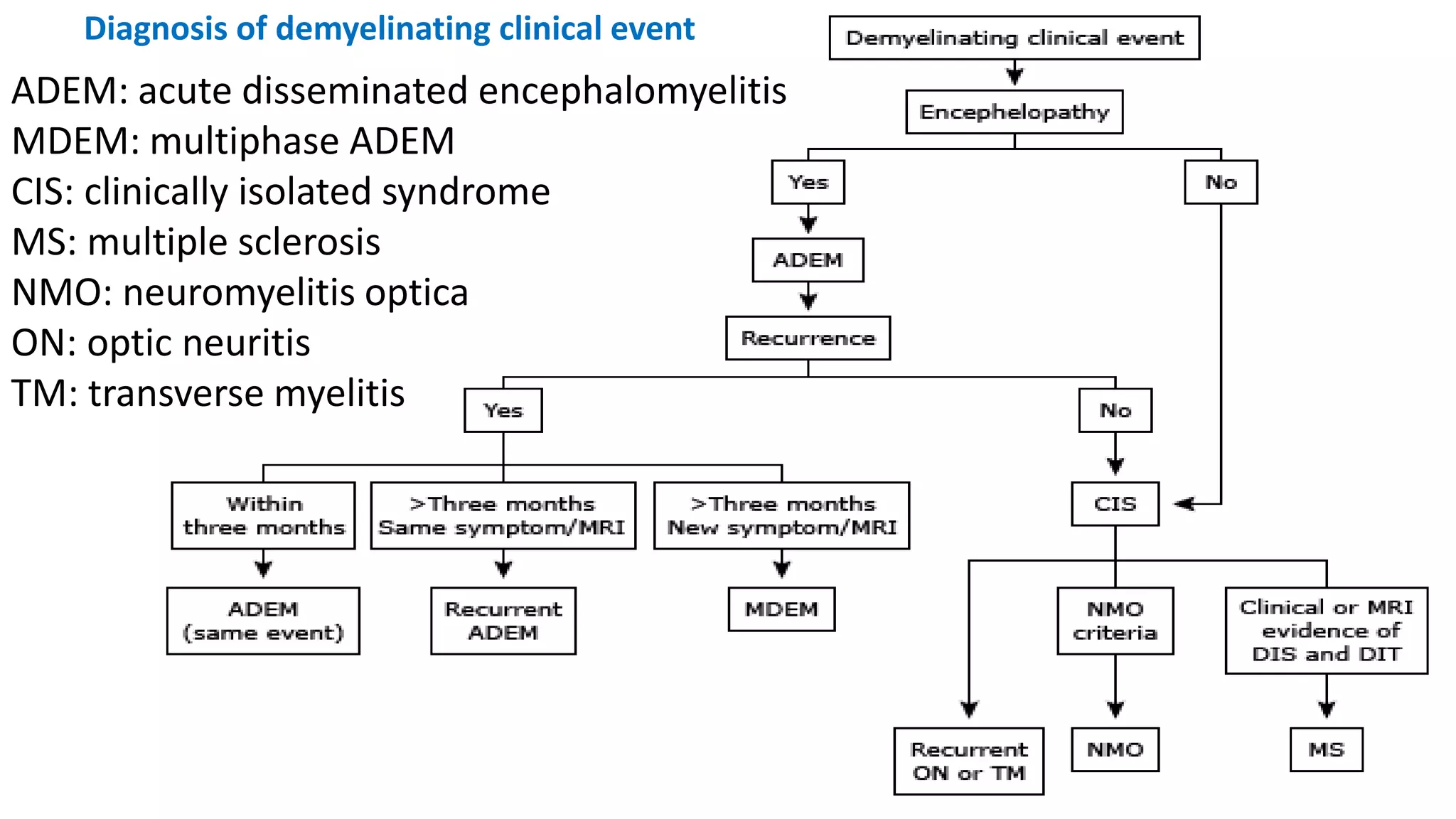
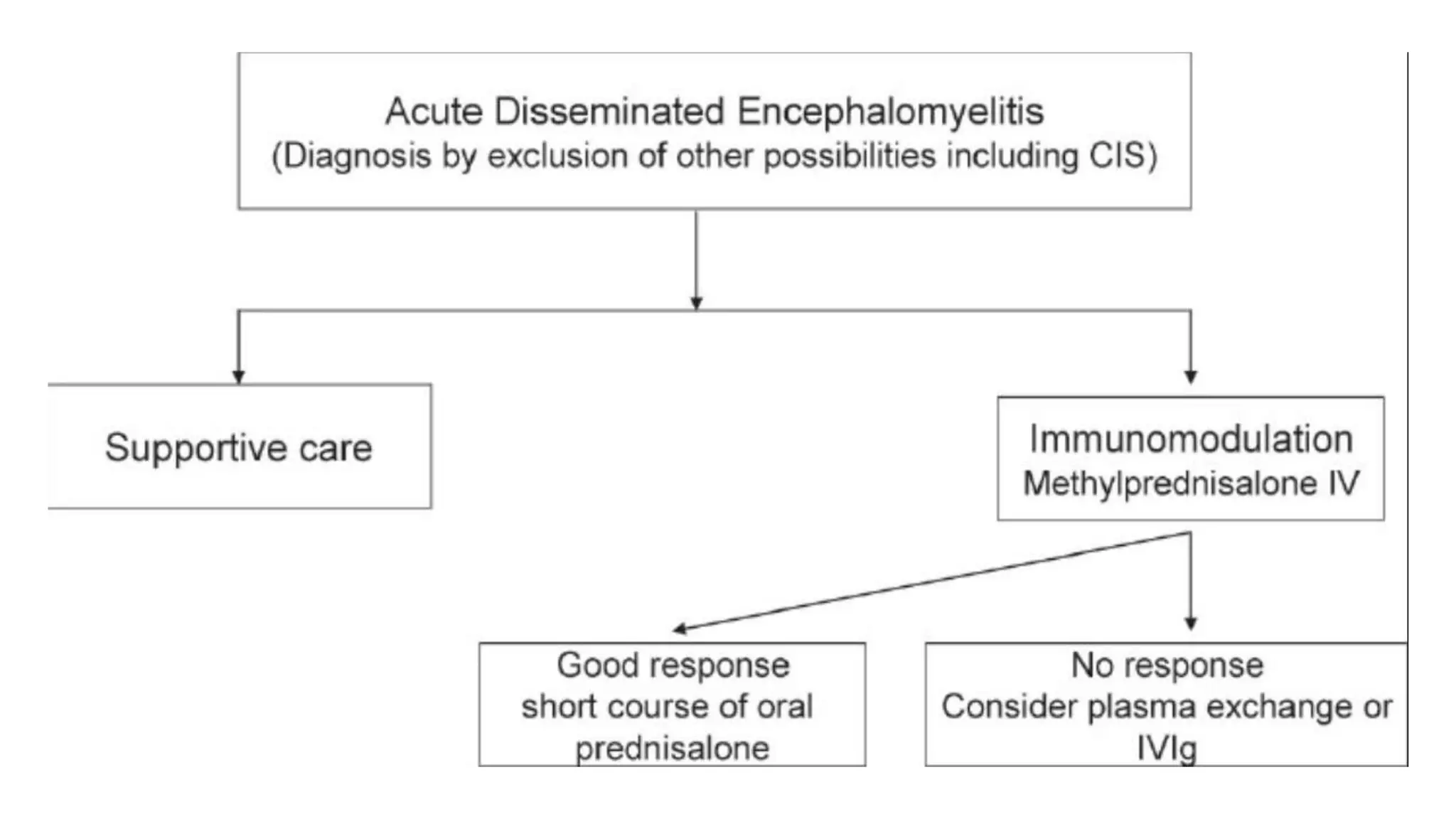
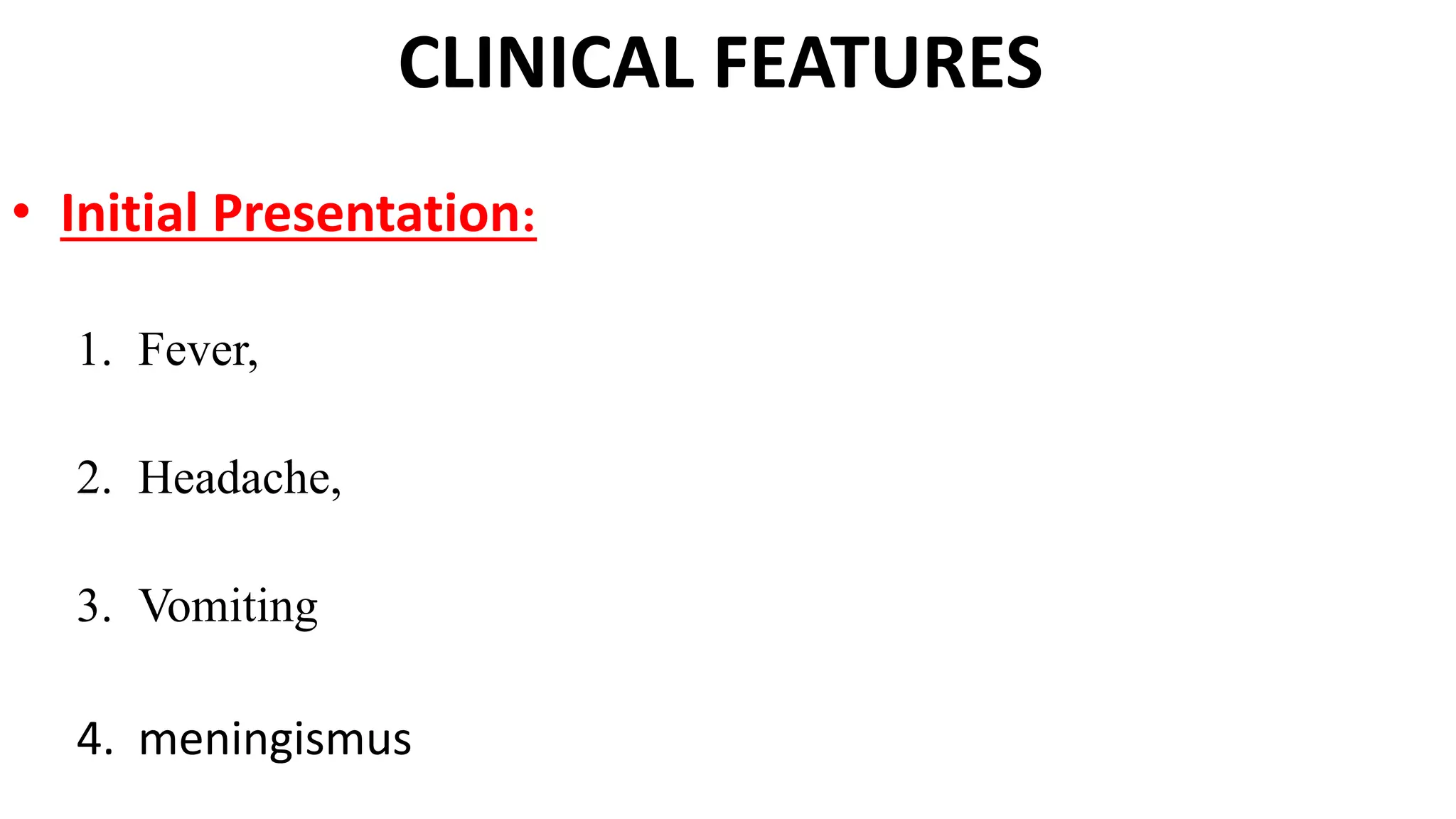
This document provides information about acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM). It defines ADEM as a demyelinating disease of the central nervous system that typically presents as a monophasic disorder with encephalopathy and multifocal neurological symptoms. The document discusses the pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment of ADEM. It states that ADEM is usually treated initially with high-dose intravenous corticosteroids over 3-5 days.































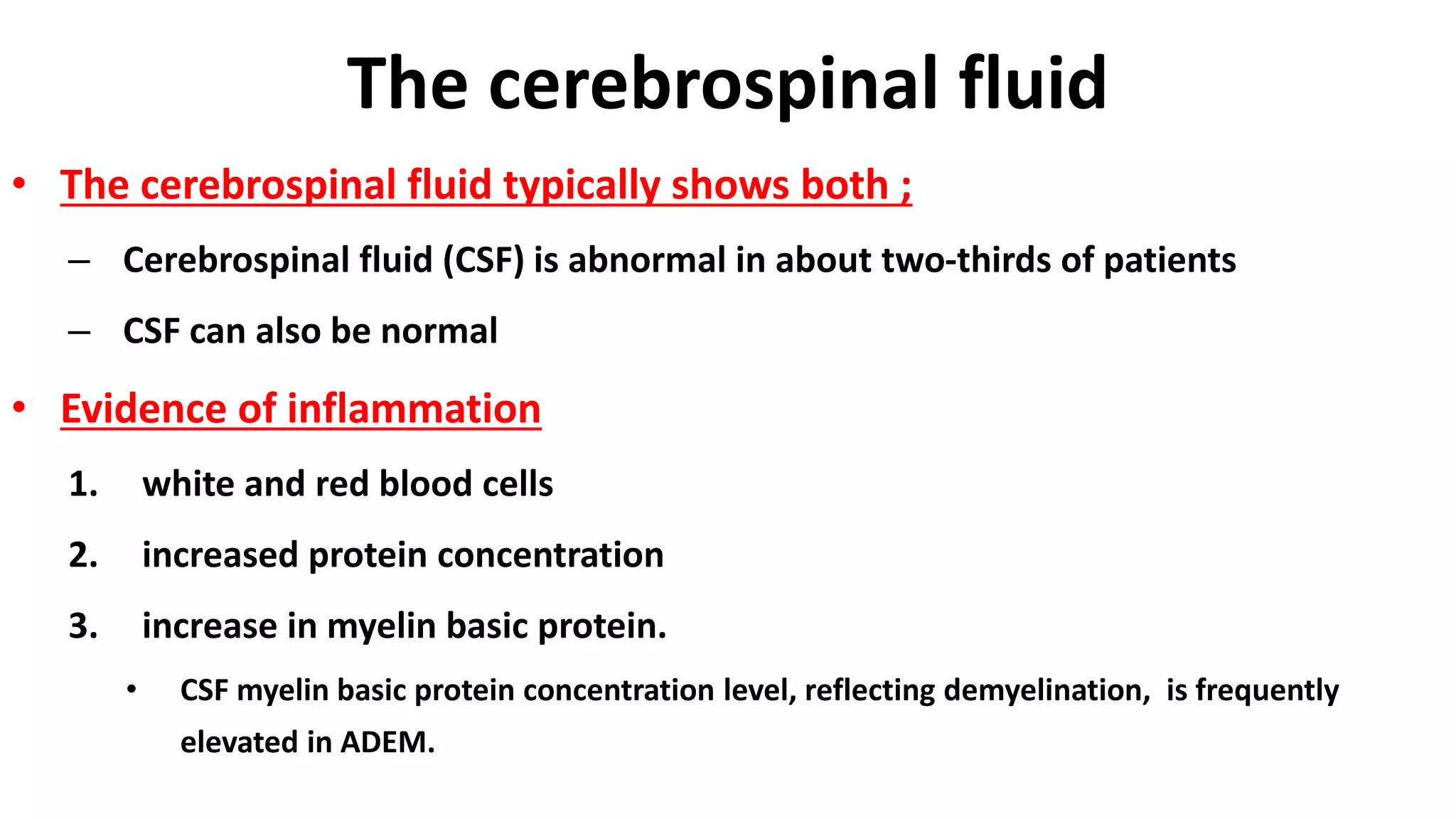

![The cerebrospinal fluid
• Results of CSF immune profile testing (eg, CSF:serum
immunoglobulin G [IgG] index, CNS IgG synthetic rate,
oligoclonality) employing age-appropriate normative data
are positive in fewer than 10% of prepubertal children
with ADEM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutedisseminatedencephalomyelitis-170316222736/75/Acute-disseminated-encephalomyelitis-35-2048.jpg)