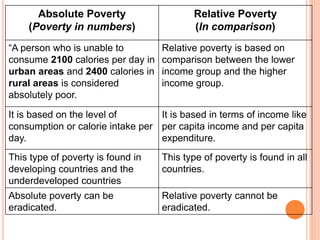
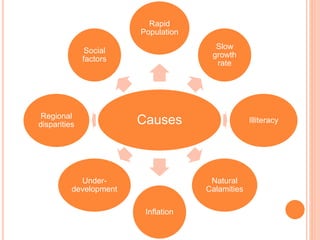
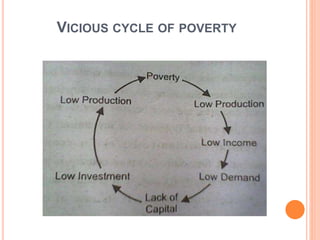
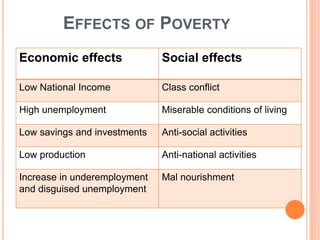
This document discusses poverty in India. It defines poverty as the inability to afford basic human needs like food, shelter and education. Poverty has been a long-standing problem in India and was intense during the colonial era. There are two concepts of poverty - absolute poverty refers to inability to consume a minimum number of calories, while relative poverty compares income levels. Rural poverty affects agricultural laborers and the landless, while urban poverty affects slum dwellers. Government measures to reduce poverty include rural employment programs, training for self-employment, subsidized food and loans for small businesses.