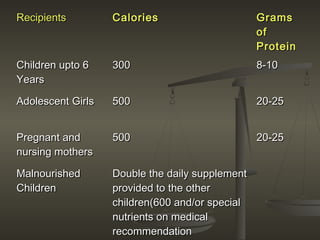
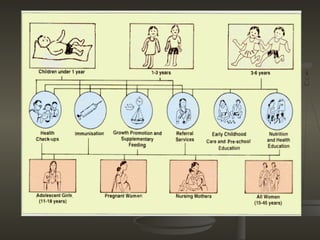
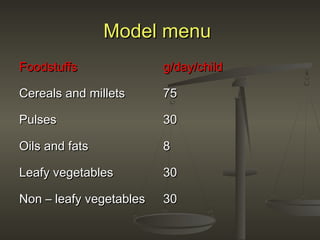
The document discusses several community nutrition programmes in India that aim to improve nutrition among vulnerable groups. It describes the objectives and services provided by key programmes like the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) programme and Mid-Day Meal Scheme. ICDS provides supplementary nutrition, immunization, health check-ups and education to children under 6, pregnant/nursing mothers. It has shown positive impacts like reduced malnutrition and school dropout rates. The Mid-Day Meal Scheme provides free lunches to over 100 million school-going children, improving nutrition and increasing school attendance and completion.