Embed presentation
Download to read offline




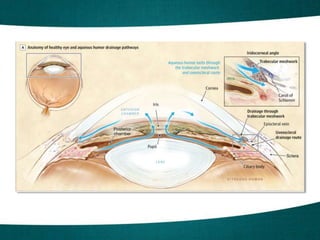














The document discusses the prevalence and risk factors of narrow angles in different populations, noting a general prevalence of 3.8% in the US and significantly higher rates in other groups. Symptoms of acute angle closure include decreased vision, halos, headaches, and eye pain, with signs such as conjunctival congestion and mid-dilated pupils. Treatment options include a combination of medications like pilocarpine, brimonidine, acetazolamide, and timolol, with definitive treatment requiring careful angle estimation.

















