Report
Share
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (19)
Lecture 3-4: Exergy, Heating and Cooling, Solar Thermal

Lecture 3-4: Exergy, Heating and Cooling, Solar Thermal
Chemical dynamics, intro,rrk, rrkm theory by dr. y. s. thakare

Chemical dynamics, intro,rrk, rrkm theory by dr. y. s. thakare
On Various Types of Ideals of Gamma Rings and the Corresponding Operator Rings

On Various Types of Ideals of Gamma Rings and the Corresponding Operator Rings
Work energy power 2 reading assignment -revision 2 physics

Work energy power 2 reading assignment -revision 2 physics
BOUND STATE SOLUTION TO SCHRODINGER EQUATION WITH MODIFIED HYLLERAAS PLUS INV...

BOUND STATE SOLUTION TO SCHRODINGER EQUATION WITH MODIFIED HYLLERAAS PLUS INV...
Similar to Energy of block on a spring
Similar to Energy of block on a spring (7)
Energy of block on a spring
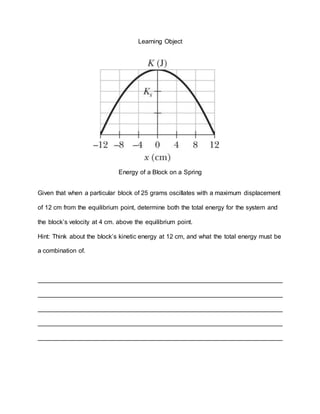
- 1. Learning Object Energy of a Block on a Spring Given that when a particular block of 25 grams oscillates with a maximum displacement of 12 cm from the equilibrium point, determine both the total energy for the system and the block’s velocity at 4 cm. above the equilibrium point. Hint: Think about the block’s kinetic energy at 12 cm, and what the total energy must be a combination of.
- 2. Solution: Since total energy is just a sum of kinetic energy and potential energy, set up the equation with mass as 25, velocity as 0, and 0.12 meters as the height. Then solve for total energy. E = KE + PE E = 0.5mv^2 + mgh E = 0.5(25)(0^2) + 25(9.8)(0.12) E = 29.4 J When the block is 4 cm above the equilibrium height, you substitute 0.04 in for h. The entire equation must always equal 29.4 because of the conservation of energy, so solve for v in the equation. 29.4 = 0.5(25)v^2 + 25(9.8)(.04) 29.4 = 12.5v^2 + 9.8 19.6 = 12.5v^2 v^2 = 1.568 v = 1.252 m/s