GRASS 6.4.0, the new stable release after more than one year of development and testing, brings a number of exciting enhancements to the GIS. Besides the hundreds of new module features, supported data formats, and language translations, GRASS 6.3 brings a number of exciting enhancements to the GIS. A prototype of the new wxPython user interface is debuted, and for the first time since its inception with a port from the VAX 11/780 in 1983, GRASS will run on a non-UNIX based platform: MS-Windows. This is currently still in an experimental state and we hope that widespread testing of 6.3.0 will mean the 6.4 release of WinGRASS will be fully functional and robust. Existing UNIX and Mac users will be happy to know that these new features do not disrupt the base GIS which remains as solid as ever and fully backwards compatible with earlier GRASS 6.0 and GRASS 6.2 releases.
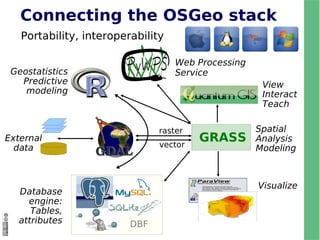
Several infrastructure changes accompany this release with the project becoming a founding member of the Open Source Geospatial Foundation (OSGeo). This includes a new home for the website, the Wiki help system, source code repository, community add-on module repository, integrated bug tracking system, and formal membership for the project in a non-profit legal entity. We hope that these changes will guarantee that the GRASS community will be well supported and vibrant well into the future.