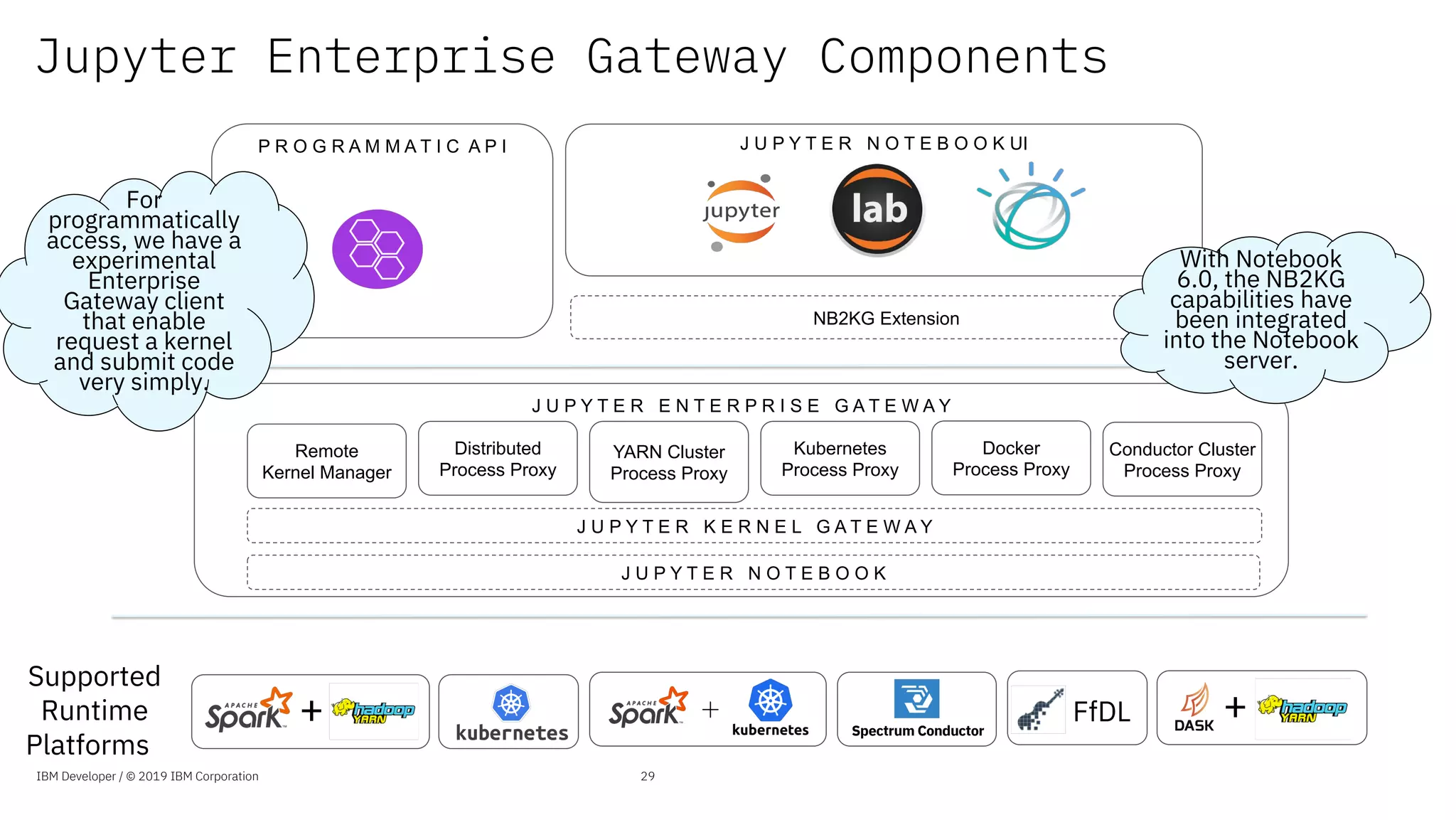
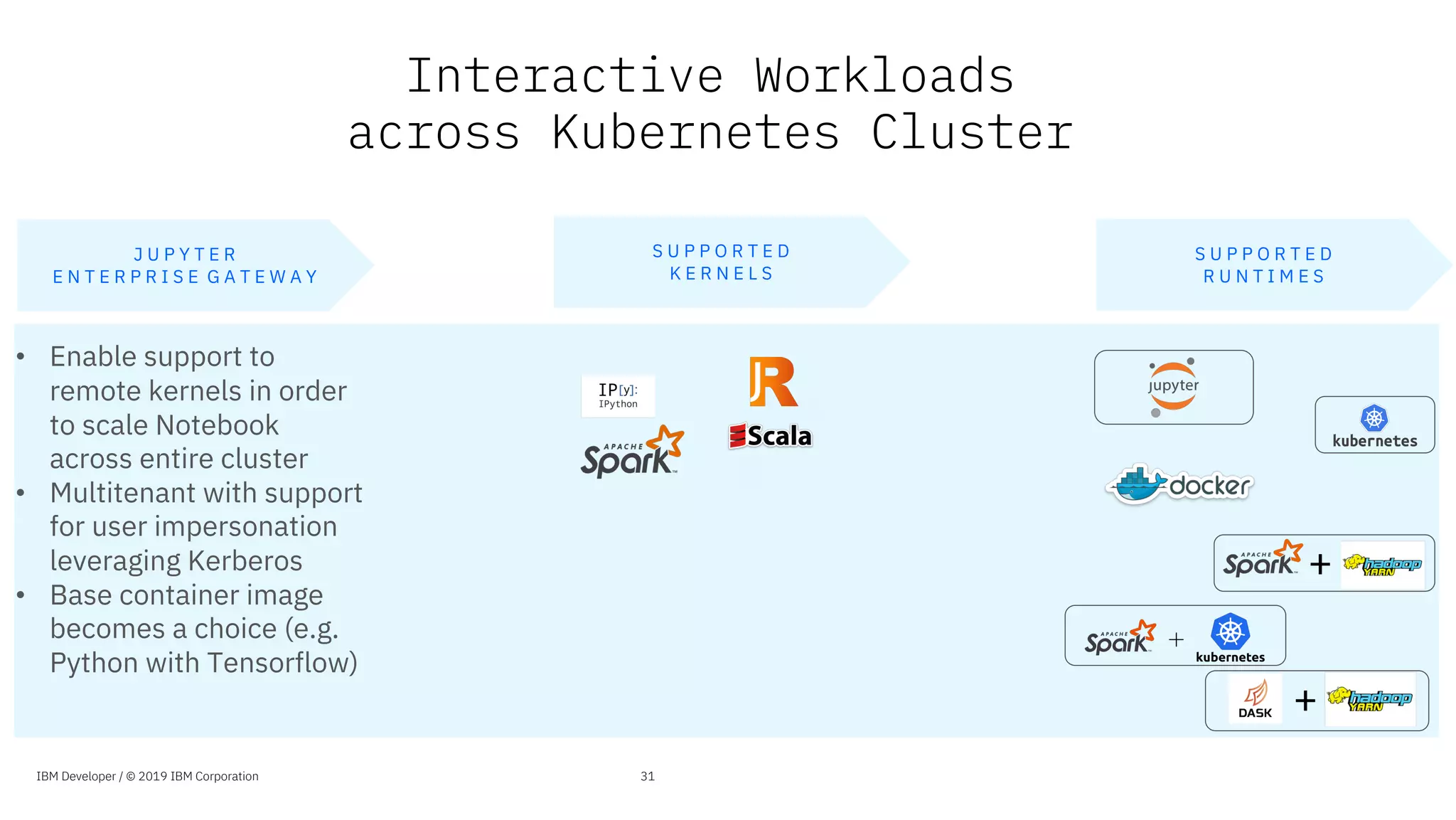
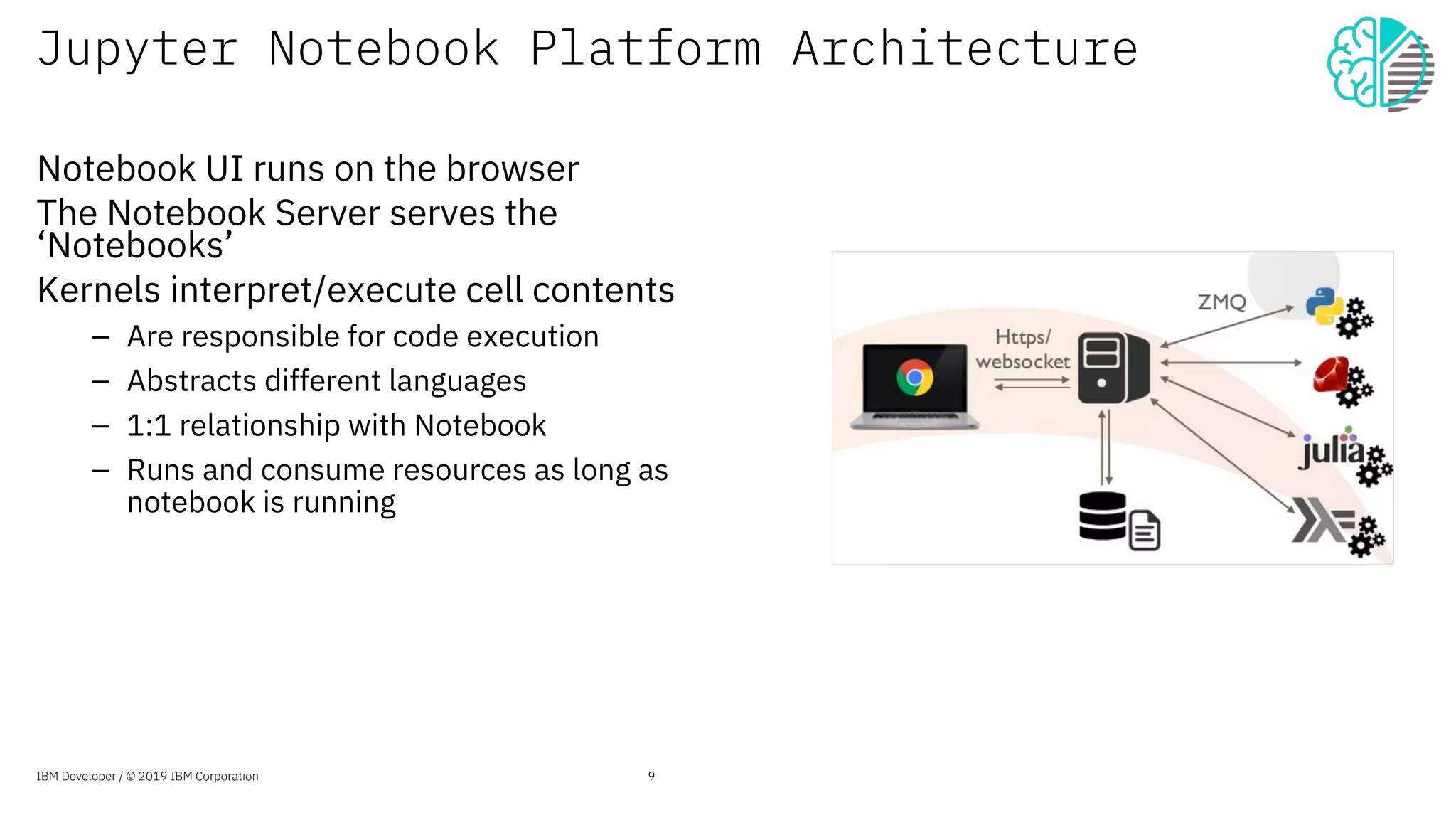
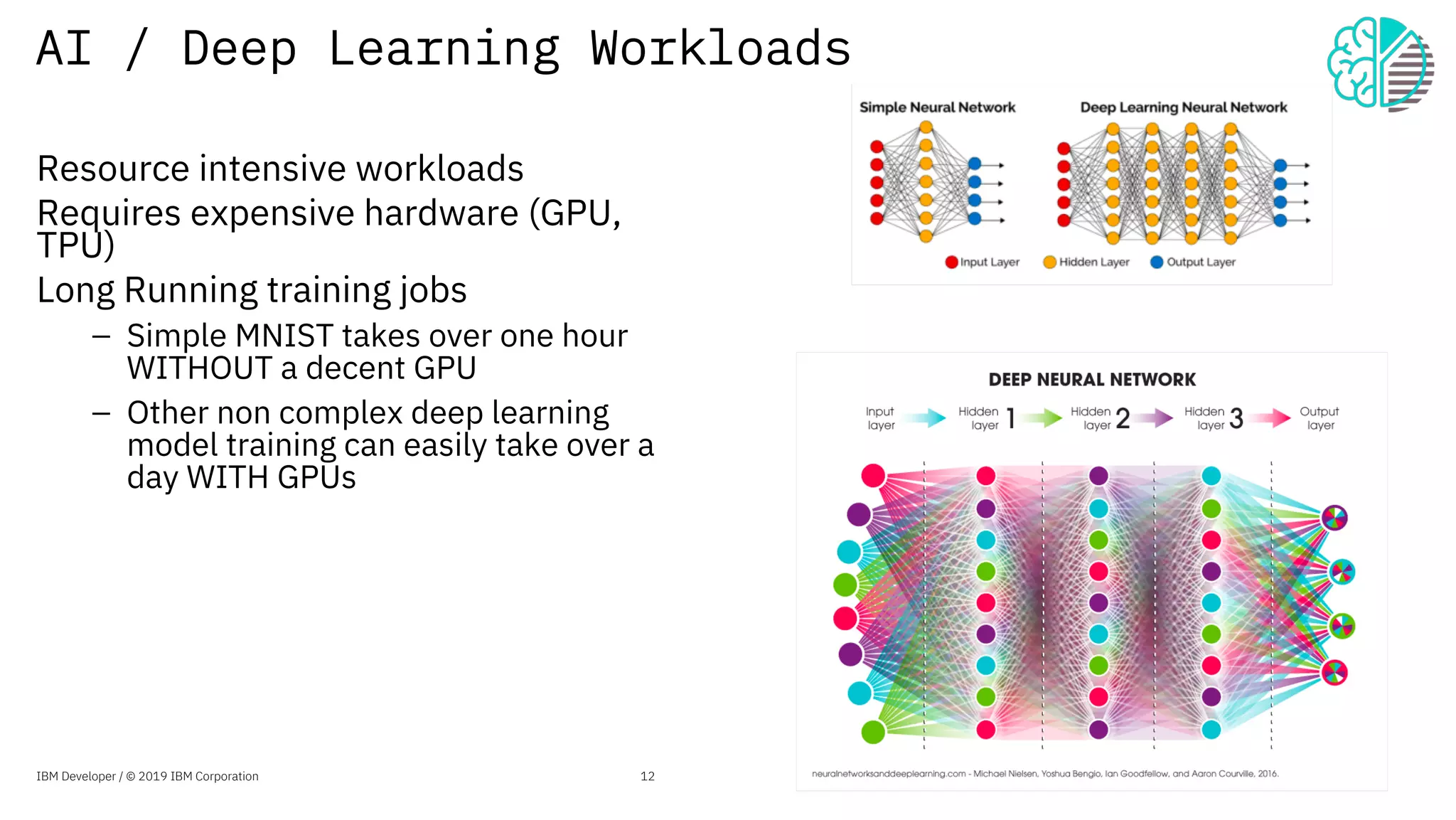
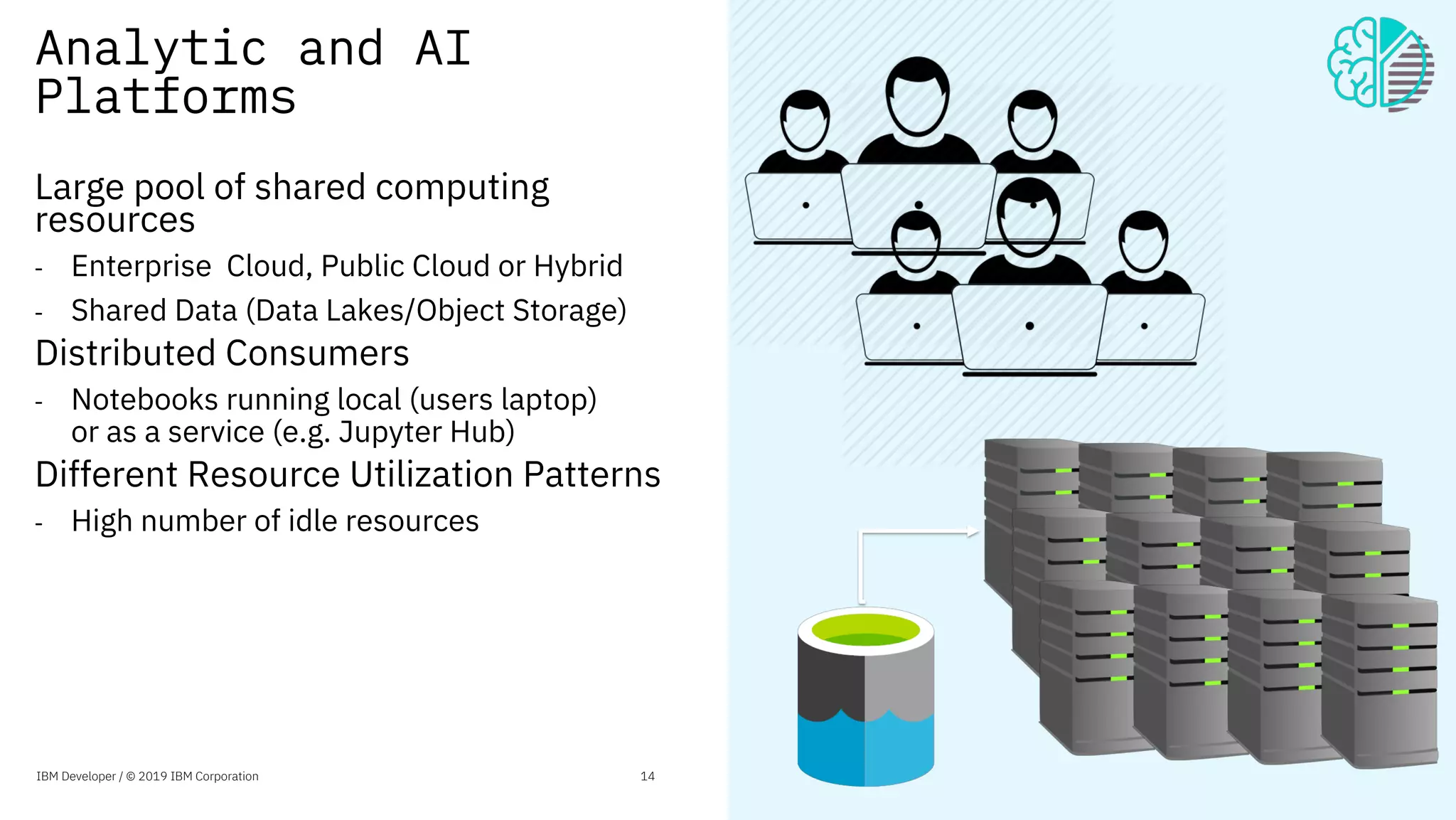
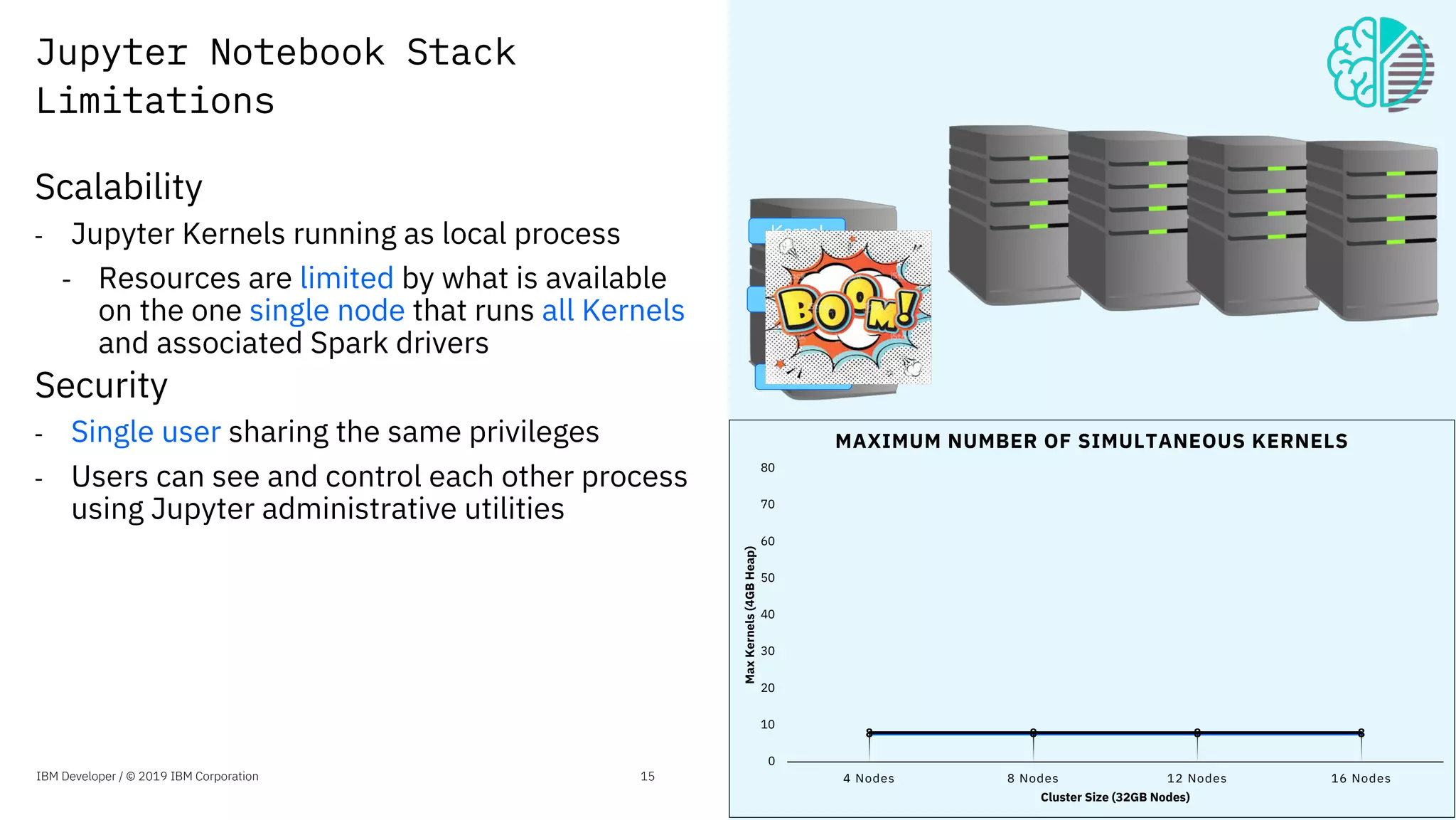
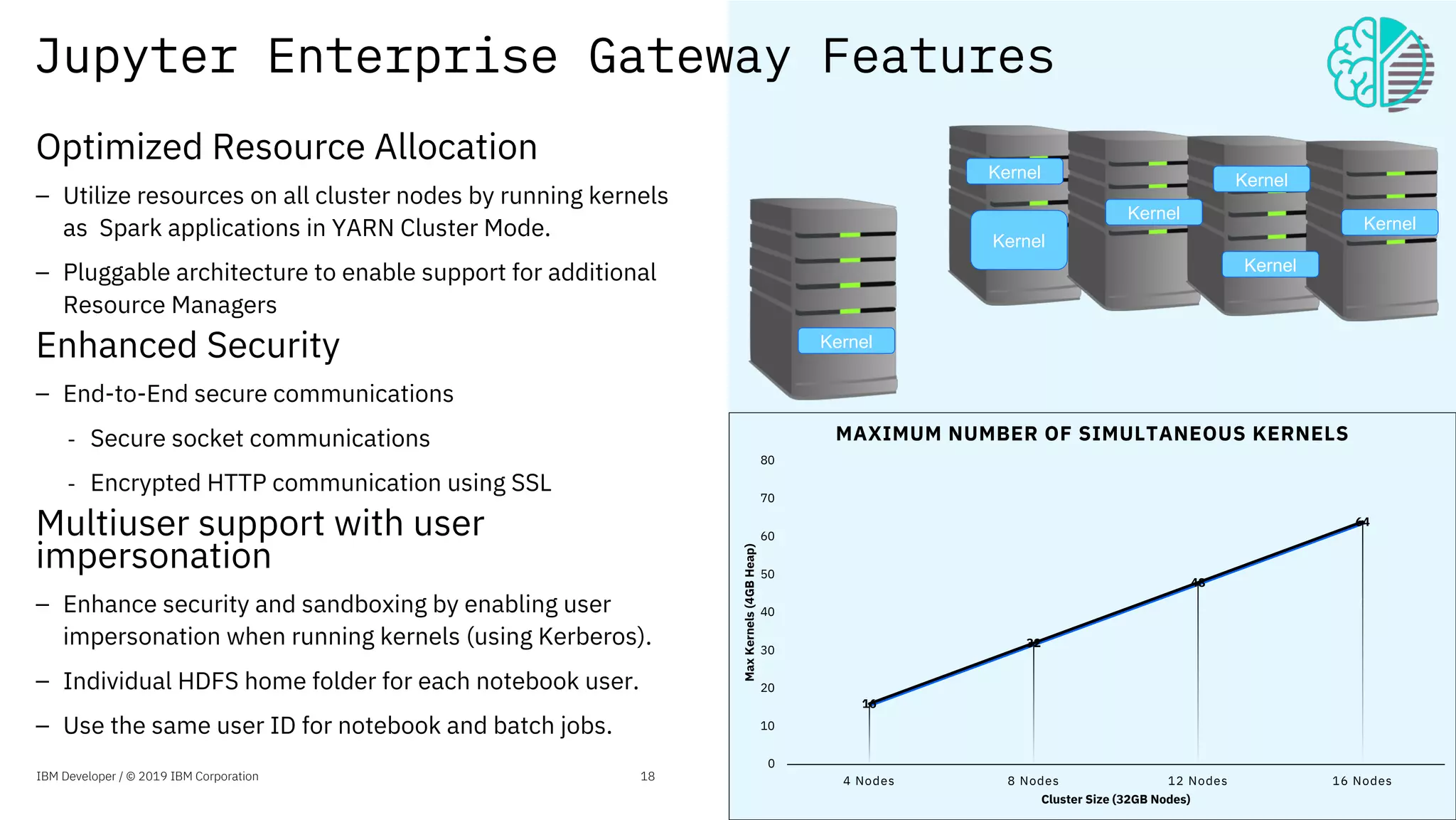
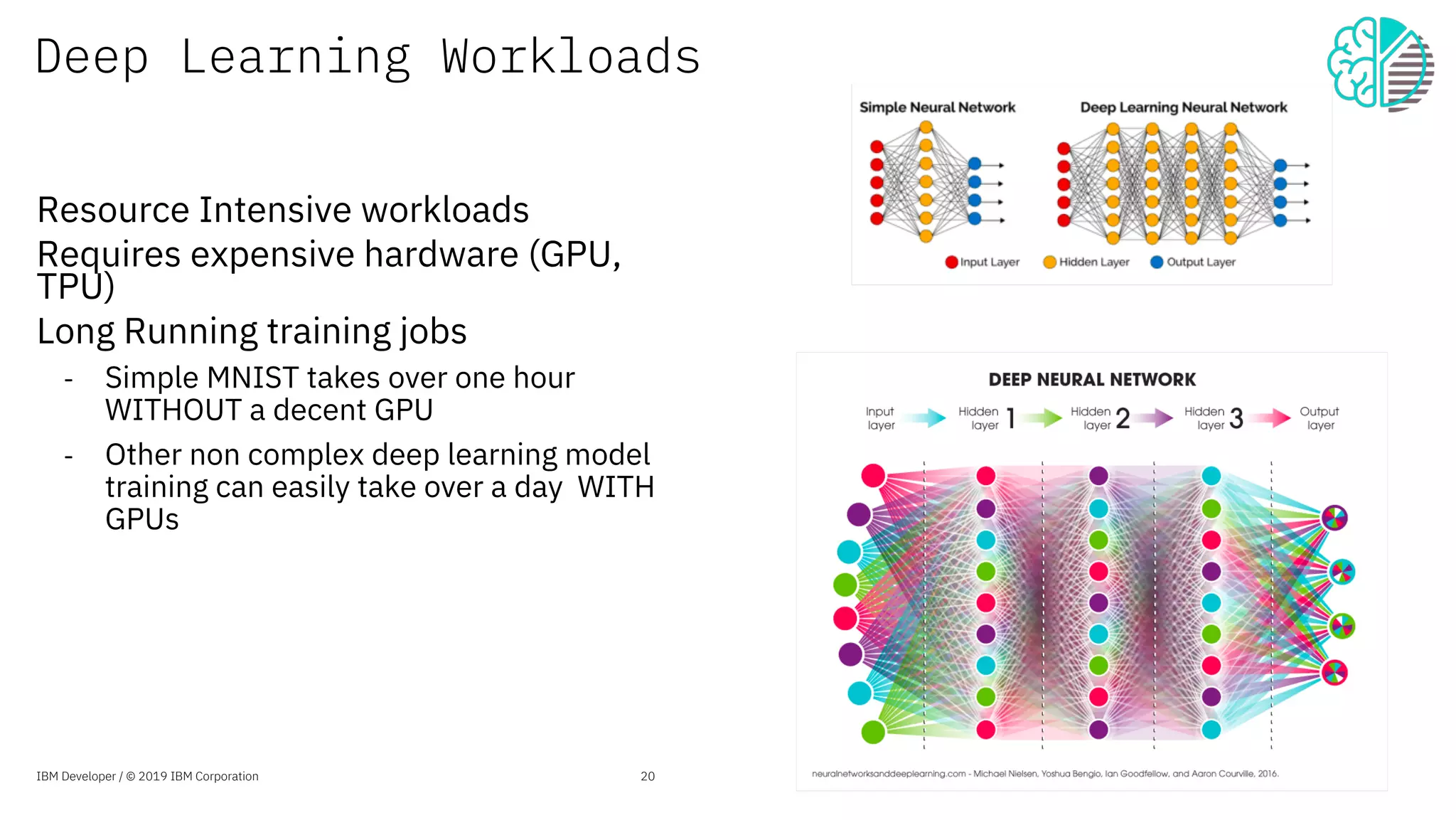
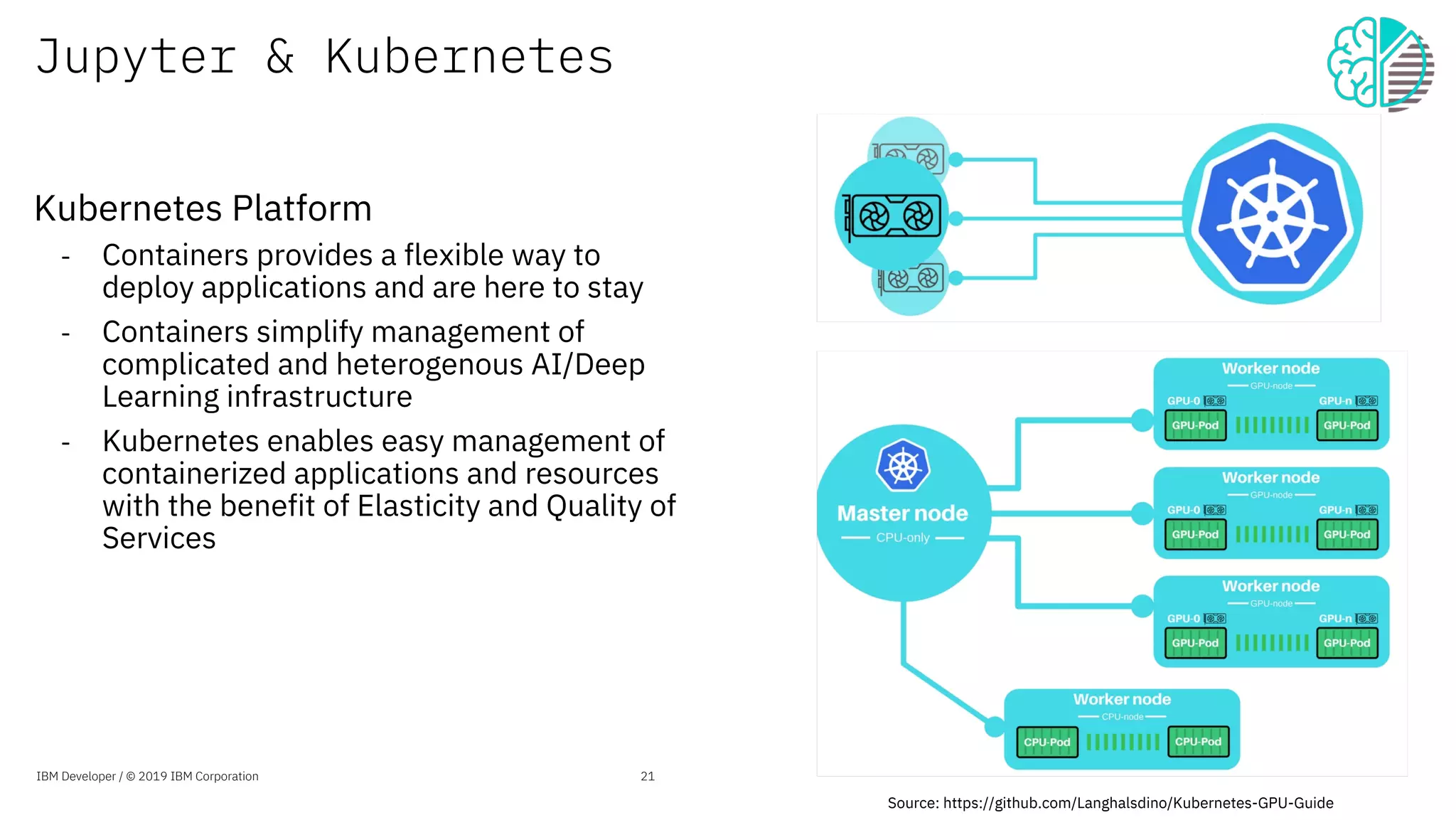
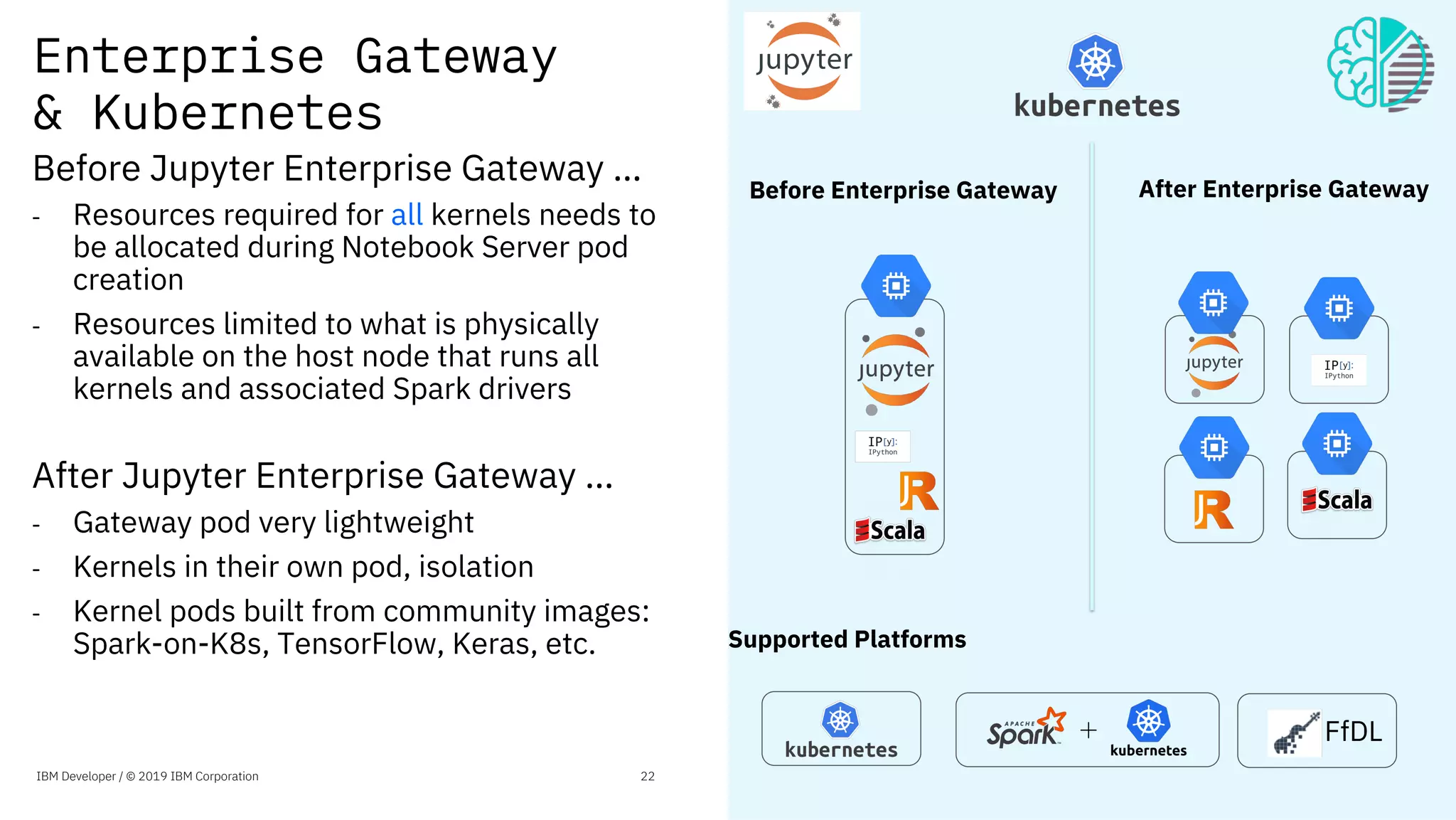
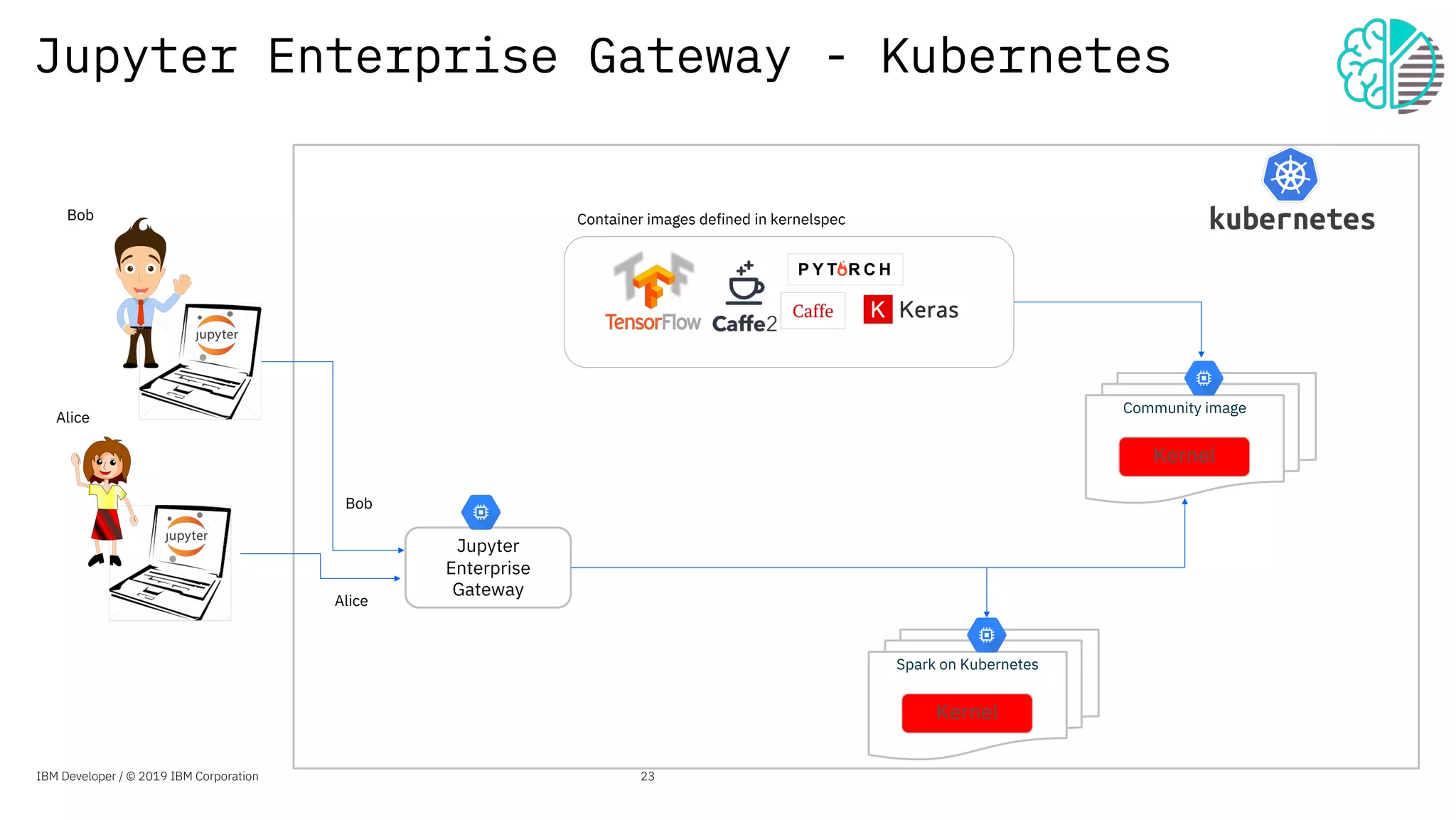
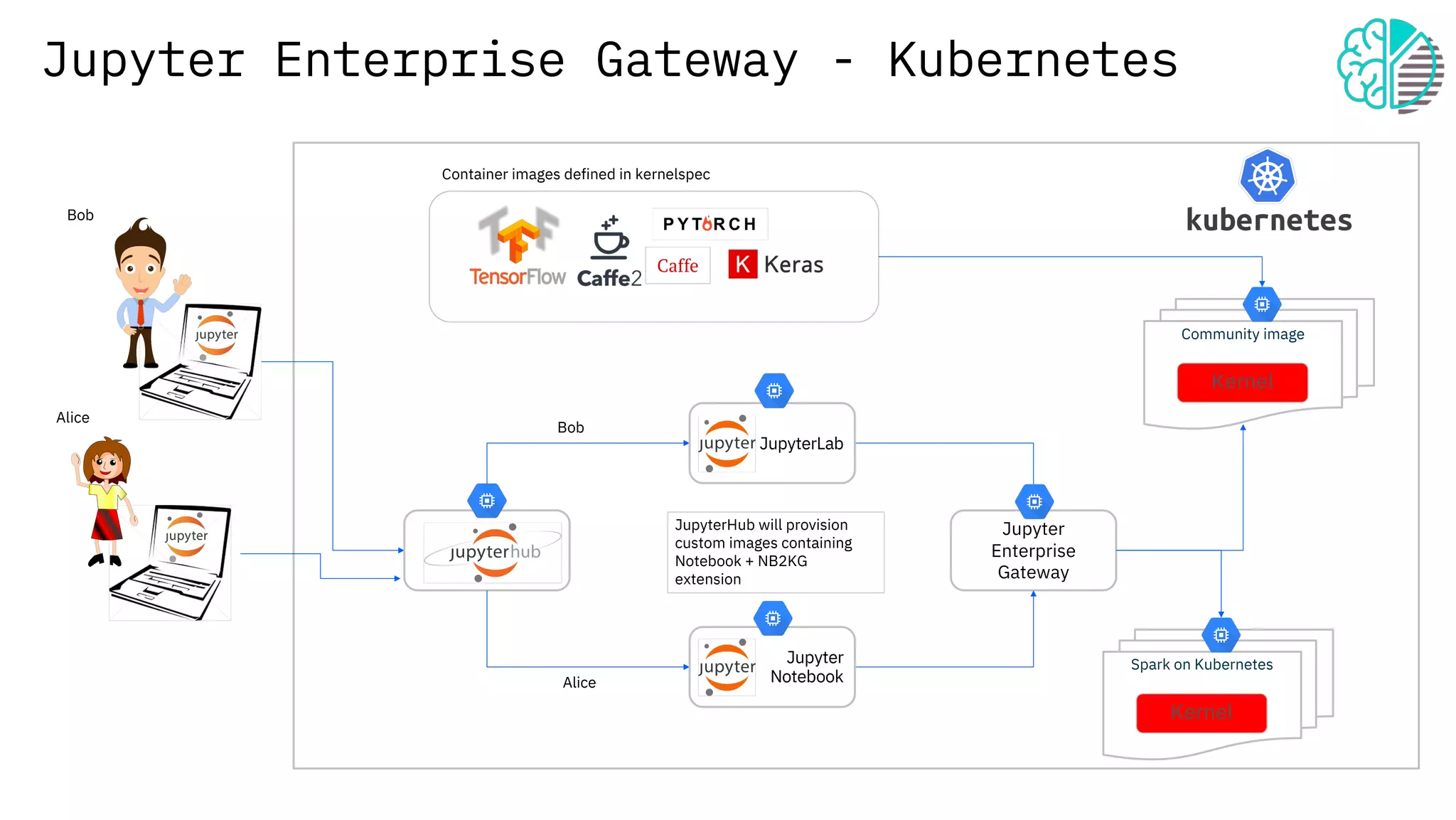
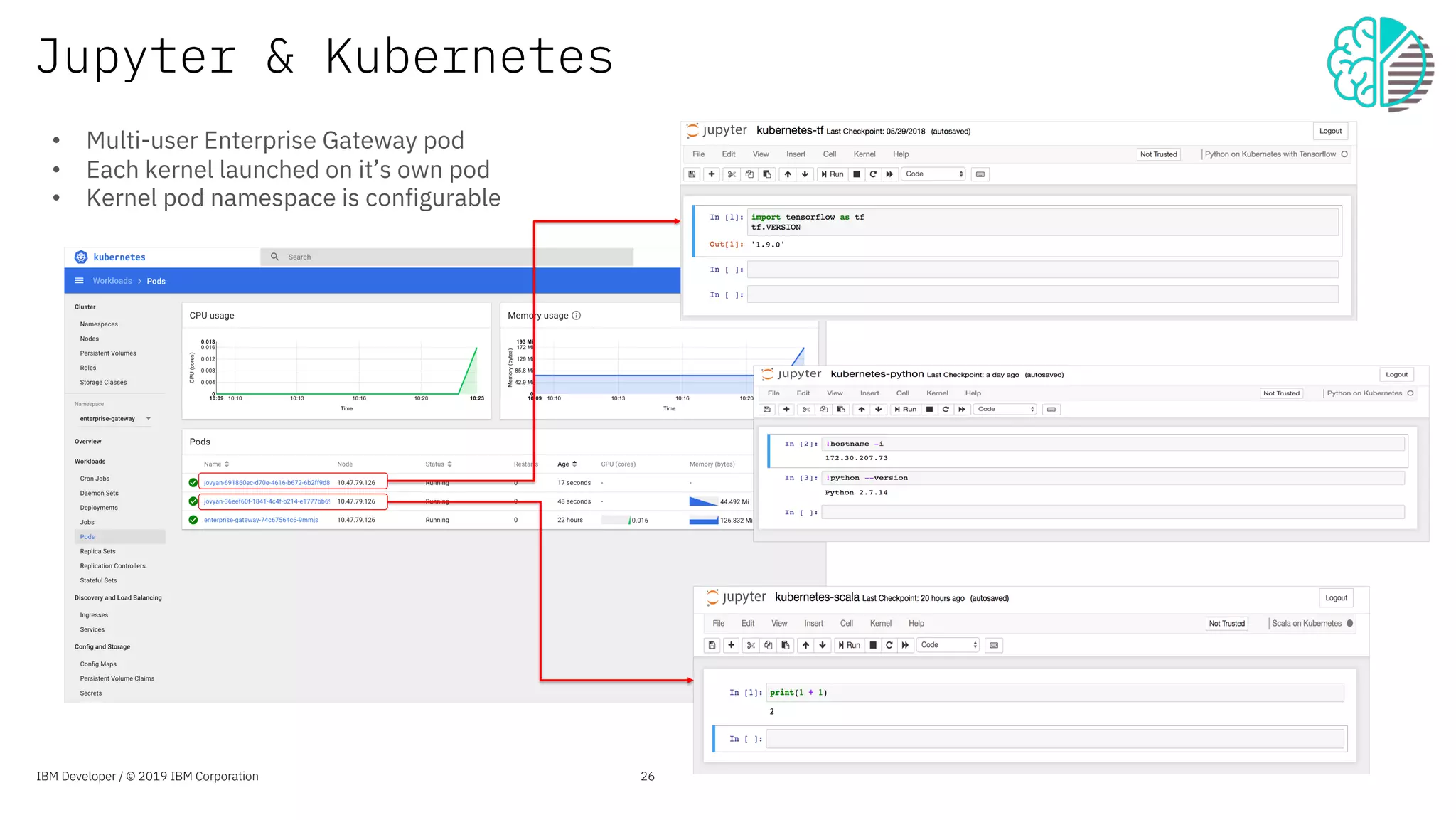
The document presents an overview of the Jupyter Enterprise Gateway, emphasizing its capabilities to enhance the performance and scalability of Jupyter notebooks in enterprise environments. It details the architecture, features, and benefits, including support for multiple users, improved resource allocation, and integration with Kubernetes for managing AI workloads. The document also includes information about the contributions of IBM to open-source technologies and their focus on collaborative innovation in data and AI solutions.










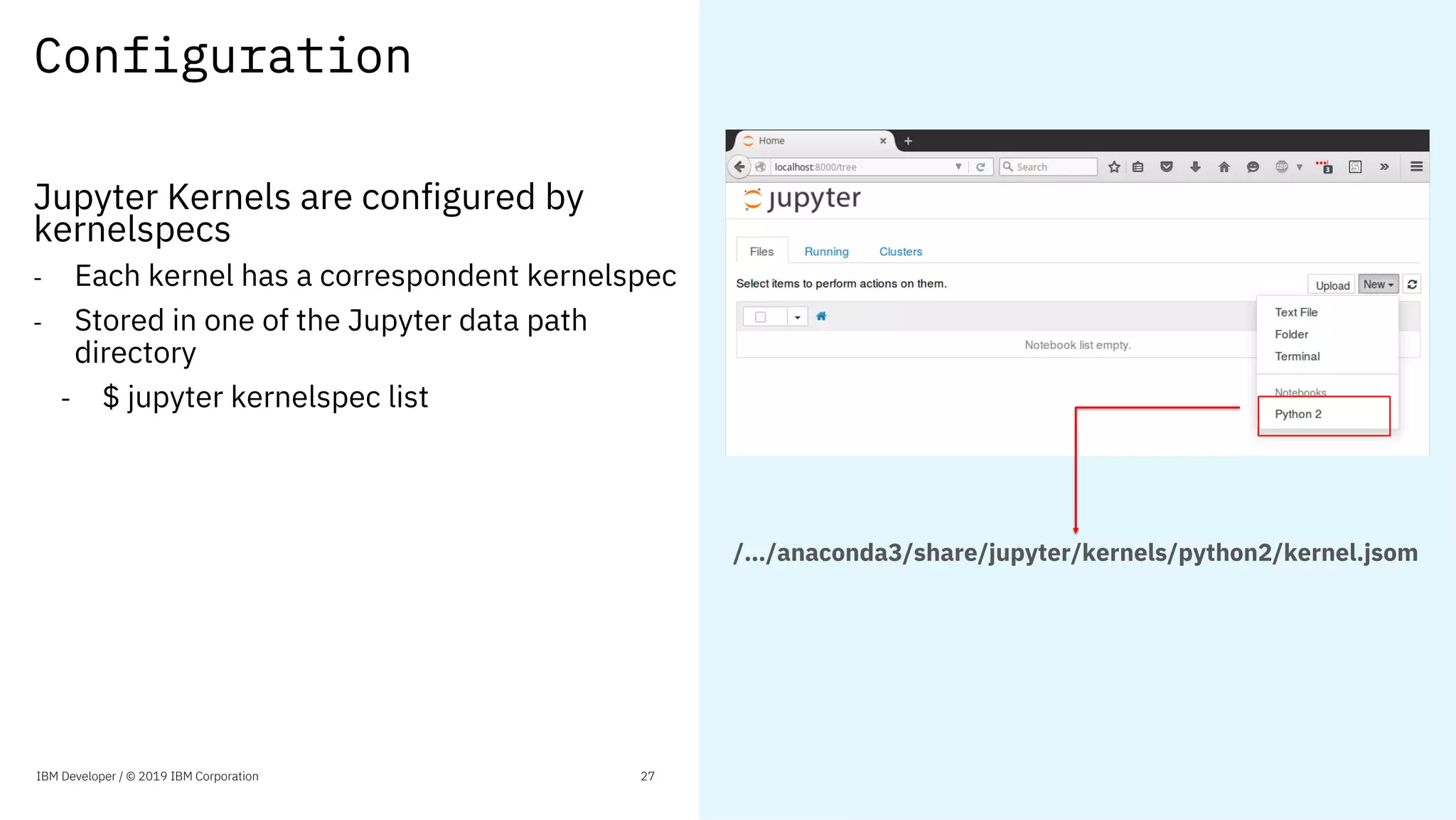
![Configurations
Process Proxy:
• Abstracts kernel process represented by Jupyter
framework
• Pluggable class definition identified in kernelspec
(kernel.json)
• Manages kernel lifecycle
Kernel Launcher:
• Embeds target kernel
• Listens on gateway communication port
• Conveys interrupt requests (via local signal)
• Could be extended for additional communications
{
"language": "python",
"display_name": "Spark - Python (Kubernetes Mode)",
"process_proxy": {
"class_name":
"enterprise_gateway.services.processproxies.k8s.KubernetesProcessProxy",
"config": {
"image_name": "elyra/kubernetes-kernel-py:dev",
"executor_image_name": "elyra/kubernetes-kernel-py:dev”,
"port_range" : "40000..42000"
}
},
"env": {
"SPARK_HOME": "/opt/spark",
"SPARK_OPTS": "--master k8s://https://${KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST --deploy-
mode cluster --name …",
…
},
"argv": [
"/usr/local/share/jupyter/kernels/spark_scala_yarn_cluster/bin/run.sh",
"--RemoteProcessProxy.kernel-id",
"{kernel_id}",
"--RemoteProcessProxy.response-address",
"{response_address}",
"--RemoteProcessProxy.port-range",
"{port_range}",
"--RemoteProcessProxy.spark-context-initialization-mode",
"lazy"
]
}
IBM Developer / © 2019 IBM Corporation 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strata-scalingjupyterwithjupyterenterprisegateway-190330015340/75/Strata-Scaling-Jupyter-with-Jupyter-Enterprise-Gateway-28-2048.jpg)