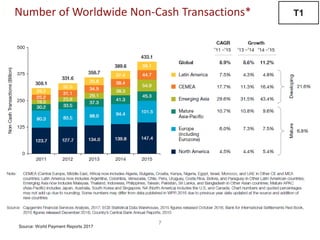
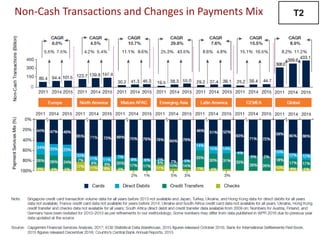
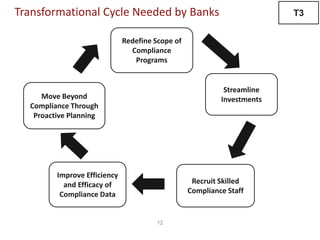
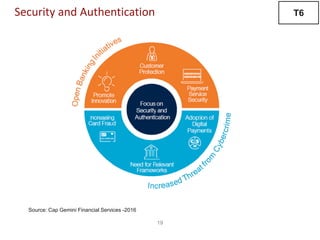
The document discusses recent trends in the payments industry, highlighting the significant rise in digital payments, projected to reach $3.6 trillion globally in 2017, primarily driven by mobile technology and contactless card adoption. It addresses the challenges banks face, including the need for regulatory compliance and innovative operational models, while emphasizing the growing role of fintechs and regtechs. The adoption of open APIs and enhanced security measures are crucial for the future of payment systems and customer satisfaction.