Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX
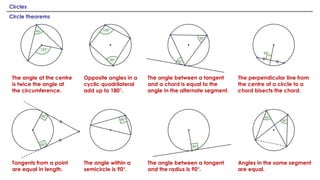
This document discusses several theorems related to circles. It states that the angle at the center of a circle is twice the angle at the circumference. The angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle in the alternate segment. Opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral add up to 180 degrees. Tangents from a point are equal in length and the angle between a tangent and the radius is 90 degrees. The perpendicular line from the center of a circle to a chord bisects the chord. Angles in the same segment are equal and the angle within a semicircle is 90 degrees.
