Normal occlusion (2)
- 2. Normal occlusionNormal occlusion OcclusionOcclusion Oc-upOc-up Clusion: closingClusion: closing Thus occlusion means closingThus occlusion means closing up.up. The definition of the termThe definition of the term occlusion in many dictionariesocclusion in many dictionaries only states that it is the act ofonly states that it is the act of closure or being closedclosure or being closed.. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 3. Definitions:Definitions: Angle:Angle: AngleAngle defines occlusion as the normaldefines occlusion as the normal relation of the occlusal inclined planes ofrelation of the occlusal inclined planes of the teeth when the jaws are closed.the teeth when the jaws are closed. Wheeler’s:Wheeler’s: It may be defined as the contact relationshipIt may be defined as the contact relationship of the teeth in function or parafunction.of the teeth in function or parafunction. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 4. Occlusion is a complex phenomenon involvingOcclusion is a complex phenomenon involving the teeth, periodontal ligaments the jaws thethe teeth, periodontal ligaments the jaws the temporomandibular joint, the muscles and thetemporomandibular joint, the muscles and the nervous system.nervous system. When the jaws are closed and the heads of theWhen the jaws are closed and the heads of the condyles are in the resting position in thecondyles are in the resting position in the glenoid fossa the cusps , fossae and incisalglenoid fossa the cusps , fossae and incisal edges of individual teeth of the upper andedges of individual teeth of the upper and lower arches comes into contact with onelower arches comes into contact with one another, the sum of these relations make upanother, the sum of these relations make up the occlusion of the dentition.the occlusion of the dentition. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 5. AspectsAspects of occlusionof occlusion OCCLUSION STATIC DYNAMIC www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 6. StaticStatic refers to the form, alignment andrefers to the form, alignment and articulation of the teeth within andarticulation of the teeth within and between the arches and the relationship ofbetween the arches and the relationship of teeth to their supporting structure.teeth to their supporting structure. DynamicDynamic refers to the function of therefers to the function of the stomatognathic system as a wholestomatognathic system as a whole comprising teeth , supporting structures ,comprising teeth , supporting structures , TMJ , neuromuscular and nutritiveTMJ , neuromuscular and nutritive systems.systems. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 7. TerminologyTerminology 1.Gnathology1.Gnathology:: It is the science of mandibular movementsIt is the science of mandibular movements and resultant occlusal contacts.and resultant occlusal contacts. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 8. 2. Ideal Occlusion2. Ideal Occlusion:-:- It is a pre-conceived theoretical concept ofIt is a pre-conceived theoretical concept of occlusal structure and functionalocclusal structure and functional relationship that include idealizedrelationship that include idealized principles of characteristics that anprinciples of characteristics that an occlusion should have.occlusion should have. This concept refers to both to an aestheticThis concept refers to both to an aesthetic and a physiologic ideal. Important aspectand a physiologic ideal. Important aspect of ideal occlusion includes functionalof ideal occlusion includes functional harmony and stability of masticatoryharmony and stability of masticatory system and neuromuscular harmony in thesystem and neuromuscular harmony in the masticatory system.masticatory system. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 9. 3. Physiologic occlusion3. Physiologic occlusion:-:- It refers to an occlusion that deviates in oneIt refers to an occlusion that deviates in one or more ways from ideal, yet it is wellor more ways from ideal, yet it is well adapted to that particular environment, isadapted to that particular environment, is esthetic and shows no pathologicesthetic and shows no pathologic manifestations or dysfunction.manifestations or dysfunction. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 10. 4. Balanced occlusion4. Balanced occlusion:-:- Balanced occlusion is said to exist whenBalanced occlusion is said to exist when there exist a simultaneous contact ofthere exist a simultaneous contact of maxillary and mandibular teeth on rightmaxillary and mandibular teeth on right and left , in the anterior and posteriorand left , in the anterior and posterior occlusal areas when the jaws are either inocclusal areas when the jaws are either in centric or eccentric occlusion.centric or eccentric occlusion. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 11. 5. Functional occlusion5. Functional occlusion:-:- It is defined as an arrangement of teethIt is defined as an arrangement of teeth which will provide the highest efficiencywhich will provide the highest efficiency during all the excessive movements of theduring all the excessive movements of the mandible which are necessary duringmandible which are necessary during function.function. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 12. 6.Therapeutic occlusion6.Therapeutic occlusion:-:- An occlusion that has been modified byAn occlusion that has been modified by appropriate therapeutic modalities in orderappropriate therapeutic modalities in order to change a non physiological occlusion toto change a non physiological occlusion to one that is at least physiologic if not ideal.one that is at least physiologic if not ideal. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 13. 7.Traumatic occlusion7.Traumatic occlusion:-:- Traumatic occlusion is an abnormal occlusalTraumatic occlusion is an abnormal occlusal stress which is capable of producing orstress which is capable of producing or has produced an injury to thehas produced an injury to the periodontiumperiodontium www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 14. CUSPS SUPPORTING CUSPS OR CENTRIC HOLDING CUSPS OR STAMP CUSPS NON SUPPORTING CUSPS OR SHEARING CUSPS OR GUIDING CUSPS www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 15. Supporting cusps /Centric holding cups/stamp cupsSupporting cusps /Centric holding cups/stamp cups The buccal cusps of mandibular and palatal cups ofThe buccal cusps of mandibular and palatal cups of maxillary posterior teeth are called stamp cusps.maxillary posterior teeth are called stamp cusps. They occlude into the central fossae and marginalThey occlude into the central fossae and marginal ridges of opposing teeth.ridges of opposing teeth. Non-supporting cusps/Shearing cusps or guidingNon-supporting cusps/Shearing cusps or guiding cuspscusps The maxillary buccal and mandibular lingual cuspsThe maxillary buccal and mandibular lingual cusps are called non-supporting, shearing or guidingare called non-supporting, shearing or guiding cusps. They contact and guide the mandiblecusps. They contact and guide the mandible during lateral excursion and shear food duringduring lateral excursion and shear food during mastication.mastication. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 16. Imaginary occlusal planesImaginary occlusal planes and curvesand curves 1. Curve of Spee1. Curve of Spee:-:- It refers to the anterior-It refers to the anterior- posterior curvature of theposterior curvature of the occlusal surface beginningocclusal surface beginning at the tip of the lowerat the tip of the lower cuspid and following thecuspid and following the cusps tip of the bicuspidscusps tip of the bicuspids and molars continuing asand molars continuing as an arc through thean arc through the condyle. If the curve iscondyle. If the curve is extended, it would form aextended, it would form a circle of about 4 inchcircle of about 4 inch diameter.diameter. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 17. The curve results fromThe curve results from variations in axialvariations in axial alignment of lower teeth.alignment of lower teeth. The long axis of eachThe long axis of each lower tooth is alignedlower tooth is aligned nearly parallel to itsnearly parallel to its individual arc of closureindividual arc of closure around the condylar axis.around the condylar axis. This requires a gradualThis requires a gradual progressive increasedprogressive increased mesial tilting of teethmesial tilting of teeth towards molars whichtowards molars which creates the curve ofcreates the curve of Spee.Spee. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 18. 2. Curve of Wilson2. Curve of Wilson:-:- This is a curve thatThis is a curve that contacts the buccal andcontacts the buccal and lingual cusps tips oflingual cusps tips of the mandibularthe mandibular posterior teeth. Theposterior teeth. The curve of Wilson iscurve of Wilson is medio-lateral on eachmedio-lateral on each side of the arch. Itside of the arch. It results from the inwardresults from the inward inclination of lowerinclination of lower posterior teeth.posterior teeth. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 19. This curve helps in twoThis curve helps in two ways:-ways:- A) Teeth are alignedA) Teeth are aligned parallel to the directionparallel to the direction of medial pterygoid forof medial pterygoid for optimum resistance tooptimum resistance to masticatory forces.masticatory forces. B) The elevated buccalB) The elevated buccal cusps prevent food fromcusps prevent food from going past the occlusalgoing past the occlusal table.table. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 20. 3. Curve of Monson3. Curve of Monson:-:- It is obtained by extending the Curve ofIt is obtained by extending the Curve of Spee and Curve of Wilson to all cuspsSpee and Curve of Wilson to all cusps and incisal edges.and incisal edges. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 21. Centric RelationCentric Relation Centric relationCentric relation is the relationis the relation of the mandible to theof the mandible to the maxilla when themaxilla when the mandibular condyles are inmandibular condyles are in most superior and retrudedmost superior and retruded position in their glenoidposition in their glenoid fossa with the articular discfossa with the articular disc properly interposed. Centricproperly interposed. Centric relation is also called asrelation is also called as ligamentous positionligamentous position oror terminal hinge position.terminal hinge position. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 22. Centric OcclusionCentric Occlusion Centric occlusionCentric occlusion is thatis that position of mandibularposition of mandibular condyle when jaws arecondyle when jaws are closed and the teeth areclosed and the teeth are in maximumin maximum intercuspation. Centricintercuspation. Centric occlusion is also calledocclusion is also called asas Inter-cuspal positionInter-cuspal position oror convenienceconvenience occlusionocclusion.. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 23. Centric relation and centric occlusion shouldCentric relation and centric occlusion should coincide in order to have perfect harmonycoincide in order to have perfect harmony between the teeth, the temporo mandibular jointbetween the teeth, the temporo mandibular joint and neuromuscular system. Studies have shownand neuromuscular system. Studies have shown that majority of the population have a maximumthat majority of the population have a maximum intercuspation 1-2 mm forwards of centricintercuspation 1-2 mm forwards of centric relation.relation. Maximum intercuspation can also occur withoutMaximum intercuspation can also occur without the condyles being in centric relation. This isthe condyles being in centric relation. This is calledcalled habitual occlusionhabitual occlusion oror acquired occlusionacquired occlusion.. In such cases, the movement from theIn such cases, the movement from the premature contact in centric relation to centricpremature contact in centric relation to centric occlusion is calledocclusion is called a slide in centric.a slide in centric. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 24. Physiologic Rest PositionPhysiologic Rest Position This position is obtained when all the jaw musclesThis position is obtained when all the jaw muscles are at rest. This position depends on restingare at rest. This position depends on resting muscle tone, in this position the upper and lowermuscle tone, in this position the upper and lower jaws are not in contact and the space betweenjaws are not in contact and the space between the upper and lower teeth is called as thethe upper and lower teeth is called as the freeway spacefreeway space . This measures on average 2-5. This measures on average 2-5 mm at the incisal area. The lips are generallymm at the incisal area. The lips are generally closed during this position. It is constantclosed during this position. It is constant throughout life and is not dependent on thethroughout life and is not dependent on the presence or absence of teeth. All functionalpresence or absence of teeth. All functional movements begin and end with rest position.movements begin and end with rest position. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 25. Centric ContactCentric Contact They are the areas of the teeth that contact theThey are the areas of the teeth that contact the opposing teeth.opposing teeth. There are two types of centric contacts:There are two types of centric contacts: Posterior centric contactsPosterior centric contacts:-:- Posterior centric contacts consists of the facial range ofPosterior centric contacts consists of the facial range of contacts and lingual range or contacts.contacts and lingual range or contacts. Facial range of posterior centric contactFacial range of posterior centric contact involveinvolve mandibular facial cusps tips contacting centralmandibular facial cusps tips contacting central fossae and mesial marginal ridges of the opposingfossae and mesial marginal ridges of the opposing maxillary teeth.maxillary teeth. Lingual range of posterior centric contactLingual range of posterior centric contact involvesinvolves the maxillary lingual cusps tips contacting thethe maxillary lingual cusps tips contacting the central fossae and distal marginal ridges of thecentral fossae and distal marginal ridges of the opposing mandibular teeth.opposing mandibular teeth. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 26. Anterior centric contact sAnterior centric contact s:-:- Anterior teeth have only one range of centricAnterior teeth have only one range of centric contacts and are in line with the facial range ofcontacts and are in line with the facial range of posterior centric contacts.posterior centric contacts. Centric contacts often occurs on inclines ofCentric contacts often occurs on inclines of posterior teeth. These contacts that occurs onposterior teeth. These contacts that occurs on one incline are calledone incline are called poded centric contactpoded centric contact. If. If contact occurs between two inclines the contactcontact occurs between two inclines the contact is termed bipoded contact. If contact occurs on 3is termed bipoded contact. If contact occurs on 3 inclines it is called tripoded contacts and Ifinclines it is called tripoded contacts and If contact occurs on 4 inclines it is calledcontact occurs on 4 inclines it is called quadrapoded contacts.quadrapoded contacts. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 28. Eccentric occlusionEccentric occlusion This refers to contact of teeth that occursThis refers to contact of teeth that occurs during movements of the mandible.during movements of the mandible. It is of two types:It is of two types: a)a) Functional occlusion.Functional occlusion. b)b) Non functional occlusion.Non functional occlusion. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 29. Functional occlusionFunctional occlusion:-:- Functional occlusionFunctional occlusion also called working side occlusionalso called working side occlusion refers to tooth contact that occur in the segment of therefers to tooth contact that occur in the segment of the arch towards which the mandible moves.arch towards which the mandible moves. Two typesTwo types:: I)I) Lateral functional occlusionLateral functional occlusion:-:- It includes tooth contacts that occur on canine andIt includes tooth contacts that occur on canine and posterior teeth on the side towards which the mandibleposterior teeth on the side towards which the mandible moves. It is also of two types:moves. It is also of two types: i)i) Canine guided occlusionCanine guided occlusion:-:- During the lateral mandibular movements, the opposingDuring the lateral mandibular movements, the opposing upper and lower canines of working side contact therebyupper and lower canines of working side contact thereby causing disclusion of all posterior teeth on the workingcausing disclusion of all posterior teeth on the working and balancing sides. Canine guided occlusion is usuallyand balancing sides. Canine guided occlusion is usually seen in young individual with unworn dentition.seen in young individual with unworn dentition. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 30. Canine guidance in right and left laterotrusion www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 31. ii)ii) Grouped lateral occlusionGrouped lateral occlusion:-:- In addition to canine guidance, certainIn addition to canine guidance, certain other posterior teeth on the workingother posterior teeth on the working side also contact during lateralside also contact during lateral movement of mandible, such type ofmovement of mandible, such type of contact during lateral movement iscontact during lateral movement is called grouped lateral occlusion.called grouped lateral occlusion. II)II) Protrusive functional occlusionProtrusive functional occlusion:-:- Includes eccentric contacts that occursIncludes eccentric contacts that occurs when the mandible moves forward.when the mandible moves forward. Ideally six mandibular anterior teethIdeally six mandibular anterior teeth contact along the lingual inclines ofcontact along the lingual inclines of the maxillary anterior teeth while thethe maxillary anterior teeth while the posterior disocclude.posterior disocclude. b)b) Non functional occlusionNon functional occlusion:-:- They are tooth contact that occur in theThey are tooth contact that occur in the segment away from which thesegment away from which the mandible moves.mandible moves. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 32. DisclusionDisclusion:-:- Term is used to describe disocclusion orTerm is used to describe disocclusion or separation of non functional posteriorseparation of non functional posterior teeth during eccentric motions of the jaw .teeth during eccentric motions of the jaw . Disclusion of posterior teeth is broughtDisclusion of posterior teeth is brought about byabout by condylar guidancecondylar guidance andand incisalincisal guidance.guidance. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 33. Condylar guidanceCondylar guidance refers to the downwardrefers to the downward movement of both the condyles along themovement of both the condyles along the slopes of the articular eminence duringslopes of the articular eminence during protrusive movements leading toprotrusive movements leading to separation of the posteriors. In case ofseparation of the posteriors. In case of lateral movements, the condyles on thelateral movements, the condyles on the non-functioning side translates forwardnon-functioning side translates forward along the eminence while the condyle onalong the eminence while the condyle on the functioning side pivots in its fossathe functioning side pivots in its fossa leading to disclusion of posterior teeth onleading to disclusion of posterior teeth on the non-functional side.the non-functional side. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 34. Anterior guidance/IncisalAnterior guidance/Incisal guidanceguidance refers to anteriorrefers to anterior tooth functions whichtooth functions which separates the posteriorseparates the posterior teeth during eccentricteeth during eccentric motions of the jaw. Duringmotions of the jaw. During protrusive and lateralprotrusive and lateral movement of themovement of the mandible, the lowermandible, the lower anterior teeth tracesanterior teeth traces downward from their areadownward from their area of centric contact towardsof centric contact towards the incisal edges ofthe incisal edges of maxillary teeth whilemaxillary teeth while disoccluding the non-disoccluding the non- functional posterior teeth.functional posterior teeth. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 35. Canine and central incisor guidance contacts in centric relation www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 36. Condylar guidance has its greatest influenceCondylar guidance has its greatest influence on discluding the most distal posterioron discluding the most distal posterior teeth while incisal guidance providesteeth while incisal guidance provides discluding effect on the more mesial teeth.discluding effect on the more mesial teeth. The condylar guidance is a fixed anatomicThe condylar guidance is a fixed anatomic factor that can not be controlled by thefactor that can not be controlled by the dentist while the incisal guidance can bedentist while the incisal guidance can be controlled by modifying the form andcontrolled by modifying the form and arrangement of the anterior teeth.arrangement of the anterior teeth. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 37. Arrangement of teeth inArrangement of teeth in humanshumans Human dentition exhibits two types of toothHuman dentition exhibits two types of tooth arrangement when upper and lowerarrangement when upper and lower teeth occlude with one another:teeth occlude with one another: 1.1. Cups-fossa occlusionCups-fossa occlusion 2.2. Cusp-embrasure occlusionCusp-embrasure occlusion www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 38. Cusp fossa occlusion/ toothCusp fossa occlusion/ tooth to tooth arrangement:to tooth arrangement: In this type of occlusion theIn this type of occlusion the stamp cusp of one toothstamp cusp of one tooth occludes in a single fossaoccludes in a single fossa of a single opponent. Theof a single opponent. The upper stamp cusps fit intoupper stamp cusps fit into all except the mesialall except the mesial fossa of the lower teethfossa of the lower teeth while lower stamp cuspswhile lower stamp cusps fit into all the upper fossafit into all the upper fossa except the distal ones ofexcept the distal ones of bicuspids.bicuspids. This kind of arrangementThis kind of arrangement where contact occurswhere contact occurs between single opposingbetween single opposing teeth is calledteeth is called a cuspa cusp fossa occlusion or a toothfossa occlusion or a tooth to tooth arrangementto tooth arrangement.. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 39. Cusp-embrasure occlusionCusp-embrasure occlusion or tooth to two teethor tooth to two teeth occlusionocclusion This type of occlusionThis type of occlusion results in fitting of oneresults in fitting of one stamp cusp into a fossastamp cusp into a fossa and the fitting of anotherand the fitting of another cusp of the same toothcusp of the same tooth into the embrasure areainto the embrasure area of two opposing teeth.of two opposing teeth. In this type of arrangementIn this type of arrangement each tooth occludes witheach tooth occludes with two opposing teethtwo opposing teeth www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 40. Advantages of cusp-fossa arrangementAdvantages of cusp-fossa arrangement:: 1.1. Forces are directed more towards theForces are directed more towards the long axis of the teeth.long axis of the teeth. 2.2. The arrangement leads to greaterThe arrangement leads to greater stability of the arch, decreasing thestability of the arch, decreasing the tendency towards tooth movement.tendency towards tooth movement. 3.3. The chances of food impacting in theThe chances of food impacting in the embrasures is lessembrasures is less www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
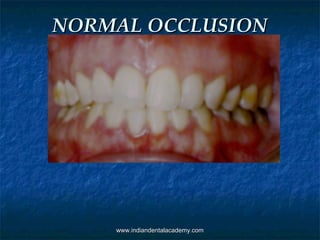
- 41. Normal occlusionNormal occlusion ““ Normal” means absence of any disease withNormal” means absence of any disease with functional adaptability and capability of thefunctional adaptability and capability of the masticatory system to compensate for anymasticatory system to compensate for any deviation within the range of tolerance.deviation within the range of tolerance. AA normal occlusionnormal occlusion considers occlusal contacts,considers occlusal contacts, alignment of teeth, overbite , overjet,alignment of teeth, overbite , overjet, arrangement and relationship of teeth withinarrangement and relationship of teeth within and between the arches, relationship of theand between the arches, relationship of the teeth to osseous structures and relations of theteeth to osseous structures and relations of the neuromuscular mechanism to the occlusion.neuromuscular mechanism to the occlusion. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 42. Primary occlusionPrimary occlusion The normal occlusion of theThe normal occlusion of the primary teeth at the age ofprimary teeth at the age of three years is as follows:three years is as follows: 1.1. Mesial surfaces of maxillaryMesial surfaces of maxillary and mandibular centraland mandibular central incisors are in line with eachincisors are in line with each other at the median line.other at the median line. 2.2. The maxillary central incisorThe maxillary central incisor occludes with the mandibularoccludes with the mandibular central incisor and mesial thirdcentral incisor and mesial third of the mandibular lateralof the mandibular lateral incisor. The mandibularincisor. The mandibular anterior teeth strike theanterior teeth strike the maxillary anterior teethmaxillary anterior teeth lingually above the level of thelingually above the level of the incisal ridges.incisal ridges. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 43. 3. The maxillary lateral incisor occludes with3. The maxillary lateral incisor occludes with the distal two third of the mandibularthe distal two third of the mandibular lateral incisors and that portion of thelateral incisors and that portion of the mandibular canine which is mesial to themandibular canine which is mesial to the point of its cusp.point of its cusp. 4. The maxillary canine occludes with that4. The maxillary canine occludes with that portion of the mandibular canine distal toportion of the mandibular canine distal to its cusp tip and the mesial third ofits cusp tip and the mesial third of mandibular first molar.mandibular first molar. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 44. 5. The maxillary first molar occludes with the5. The maxillary first molar occludes with the distal two third of the mandibular firstdistal two third of the mandibular first molar and the mesial portion ofmolar and the mesial portion of mandibular second molar which portion ismandibular second molar which portion is represented by the mesial marginal ridgerepresented by the mesial marginal ridge and the mesial triangular ridge.and the mesial triangular ridge. 6. The maxillary second molar occludes with6. The maxillary second molar occludes with the remainder if the mandibular secondthe remainder if the mandibular second molar, the distal surface of maxillary molarmolar, the distal surface of maxillary molar projecting slightly over the distal portion ofprojecting slightly over the distal portion of the mandibular second molar.the mandibular second molar. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 45. Permanent occlusionPermanent occlusion It can be discussed under following pointIt can be discussed under following point 1.1. Dental arch form.Dental arch form. 2.2. Compensating curvatures of dental arches.Compensating curvatures of dental arches. 3.3. Compensating curvatures of individual teeth .Compensating curvatures of individual teeth . 4.4. Angulations and inclination of teeth in relationAngulations and inclination of teeth in relation to various planes.to various planes. 5.5. Functional form of teeth at their incisal orFunctional form of teeth at their incisal or occlusal thirdocclusal third www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 46. 6. Facial and lingual relations of each tooth in one6. Facial and lingual relations of each tooth in one arch to its antagonist or antagonists in thearch to its antagonist or antagonists in the opposing arch in centric occlusion.opposing arch in centric occlusion. 7. Occlusal contacts and intercuspal relations of all7. Occlusal contacts and intercuspal relations of all the teeth of one arch with those in thethe teeth of one arch with those in the opposing arch in centric occlusion.opposing arch in centric occlusion. 8. Occlusal contacts and intercuspal relations of all8. Occlusal contacts and intercuspal relations of all the teeth of one arch with those in thethe teeth of one arch with those in the opposing arch in various mandibularopposing arch in various mandibular movements.movements. 9. Neuromuscular aspect of occlusion.9. Neuromuscular aspect of occlusion. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 47. Dental arch formDental arch form From occlusal aspect theFrom occlusal aspect the dental arches aredental arches are parabolic in shape. Theparabolic in shape. The shape is determined byshape is determined by underlying basal bone.underlying basal bone. Maxillary arch >Maxillary arch > Mandibular arch.Mandibular arch. AdvantagesAdvantages:: 1.1. Protects lips , cheek andProtects lips , cheek and tongue during the openingtongue during the opening and closing movements.and closing movements. 2.2. Provides stability therebyProvides stability thereby preventing tooth migration.preventing tooth migration. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 48. Compensating curvatures of dentalCompensating curvatures of dental archesarches Mandibular archMandibular arch conforms to aconforms to a curved plane whichcurved plane which appears concaveappears concave and maxillary archand maxillary arch appears convex.appears convex. i)i) Curve of Spee.Curve of Spee. ii)ii) Curve of Wilson.Curve of Wilson. iii)iii) Curve of Manson.Curve of Manson. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 49. Compensating curvatures ofCompensating curvatures of individual teethindividual teeth Vertical section of the jaws with the teeth inVertical section of the jaws with the teeth in centric occlusion demonstrates the fact thatcentric occlusion demonstrates the fact that axes of the posterior teeth approach alignmentaxes of the posterior teeth approach alignment with each other but these axes are notwith each other but these axes are not perpendicular to the horizontal plane.perpendicular to the horizontal plane. Any line which bisects crown and root of toothAny line which bisects crown and root of tooth from any aspect exhibits some curvature. Thisfrom any aspect exhibits some curvature. This was termedwas termed spherical congruencyspherical congruency byby MaxwellMaxwell.. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 50. Angulations and inclination of teethAngulations and inclination of teeth in relation to various planesin relation to various planes The mesiodistal and the faciolingual axialThe mesiodistal and the faciolingual axial inclinations of the teeth are usually described ininclinations of the teeth are usually described in terms of the angles between the long axes of aterms of the angles between the long axes of a tooth and a line drawn perpendicular to thetooth and a line drawn perpendicular to the horizontal plane or the median plane.horizontal plane or the median plane. MesioMesio distaldistal 88 1414 1010 1010 55 99 99 66 1717 66 77 00 22 22 FacioFacio linguallingual 1010 2020 88 2020 66 99 55 99 1616 1212 2626 2323 2828 2222www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 54. Functional Form Of Teeth At TheirFunctional Form Of Teeth At Their Incisal Or Occlusal ThirdIncisal Or Occlusal Third The incisal and occlusal thirds of the toothThe incisal and occlusal thirds of the tooth crowns present convex or concavecrowns present convex or concave surfaces at all contacting occlusal areas.surfaces at all contacting occlusal areas. When the teeth of one jaw come intoWhen the teeth of one jaw come into contact with their antagonist in thecontact with their antagonist in the opposite jaw during various mandibularopposite jaw during various mandibular movements. Curved surfaces come intomovements. Curved surfaces come into contact with curved surfaces.contact with curved surfaces. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 55. Facial And Lingual Relations Of Each ToothFacial And Lingual Relations Of Each Tooth In One Arch To Its Antagonist OrIn One Arch To Its Antagonist Or Antagonists In The Opposing Arch InAntagonists In The Opposing Arch In Centric OcclusionCentric Occlusion.. In ICP, each tooth of one arch is inIn ICP, each tooth of one arch is in occlusion with portions of two other teethocclusion with portions of two other teeth in the opposing arch except mandibularin the opposing arch except mandibular central incisor and maxillary third molar.central incisor and maxillary third molar. This helps to equalize the forces of impact inThis helps to equalize the forces of impact in occlusion and to distribute the work ofocclusion and to distribute the work of teeth evenly thereby preserving theteeth evenly thereby preserving the integrity of the arch.integrity of the arch. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 56. Occlusal Contacts And IntercuspalOcclusal Contacts And Intercuspal Relations Of All The Teeth Of One ArchRelations Of All The Teeth Of One Arch With Those In The Opposing Arch InWith Those In The Opposing Arch In Centric OcclusionCentric Occlusion The areas of occlusal contact that supportingThe areas of occlusal contact that supporting cusps make with opposing teeth in centriccusps make with opposing teeth in centric occlusion are called centric stops. The areas ofocclusion are called centric stops. The areas of occlusal contact on the supporting cusps thatocclusal contact on the supporting cusps that makes contact with opposing tooth in centricmakes contact with opposing tooth in centric occlusion is also called centric stops. It providesocclusion is also called centric stops. It provides occlusal stability.occlusal stability. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 57. Lingual surface of maxillary incisors and caninesLingual surface of maxillary incisors and canines 66 Labial surface of mandibular incisors andLabial surface of mandibular incisors and caninescanines 66 Triangular ridges of maxillary buccal cusps ofTriangular ridges of maxillary buccal cusps of premolars and molarspremolars and molars 1616 Triangular ridges of lingual cusps of mandibularTriangular ridges of lingual cusps of mandibular premolars and molarspremolars and molars 1616 Buccal embrasure of mandibular premolars andBuccal embrasure of mandibular premolars and molarsmolars 88 Lingual embrasures of maxillary premolars andLingual embrasures of maxillary premolars and molarsmolars 1010 Concept Of 138 Points Of Occlusal Contact) www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 58. Lingual cusp points of maxillary premolarsLingual cusp points of maxillary premolars and molarsand molars 1616 buccal cusp points of mandibular premolarsbuccal cusp points of mandibular premolars and molarsand molars 1616 Distal fossae of premolarsDistal fossae of premolars 88 Central fossae of molarsCentral fossae of molars 1212 Mesial fossae of mandibular molarsMesial fossae of mandibular molars 66 Distal fossae of maxillary molarsDistal fossae of maxillary molars 66 Lingual grooves of maxillary molarsLingual grooves of maxillary molars 66 Buccal grooves of mandibular molarsBuccal grooves of mandibular molars 66 www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 60. Occlusal Contacts And Intercuspal RelationsOcclusal Contacts And Intercuspal Relations Of All The Teeth Of One Arch With Those InOf All The Teeth Of One Arch With Those In The Opposing Arch In Various MandibularThe Opposing Arch In Various Mandibular MovementsMovements There are 4 types of mandibularThere are 4 types of mandibular movements:movements: 1.1. Laterotrusion ( working side movements)Laterotrusion ( working side movements) 2.2. Mediotrusion ( non working sideMediotrusion ( non working side movements)movements) 3.3. Protrusive movementsProtrusive movements 4.4. Lateroprotrusive movements.Lateroprotrusive movements. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 65. Neuromuscular Aspect OfNeuromuscular Aspect Of OcclusionOcclusion It includes function and parafunction of theIt includes function and parafunction of the stomatognathic system.stomatognathic system. FunctionFunction includes chewing, sucking, swallowing,includes chewing, sucking, swallowing, speech and respiration.speech and respiration. ParafunctionParafunction includes bruxism ( clenching andincludes bruxism ( clenching and grinding )grinding ) All these function involve a greater coordinationAll these function involve a greater coordination that is ultimately controlled by the centralthat is ultimately controlled by the central nervous system.nervous system. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 66. Occlusal stabilityOcclusal stability It refers to tendency of the teeth , jaws joints andIt refers to tendency of the teeth , jaws joints and muscles to remain in an optimal functional state.muscles to remain in an optimal functional state. The stability of the occlusion and the maintenanceThe stability of the occlusion and the maintenance of the tooth position are dependent on all theof the tooth position are dependent on all the forces that acts on the teeth.forces that acts on the teeth. Occlusal forces, eruptive forces, lip and cheekOcclusal forces, eruptive forces, lip and cheek pressure , periodontal support and the tonguepressure , periodontal support and the tongue pressure are all involved in maintaining thepressure are all involved in maintaining the position of the teethposition of the teeth www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 67. Andrews six keys to normal occlusion:-Andrews six keys to normal occlusion:- 1.1. Molar interarch relationship,Molar interarch relationship, 2.2. Mesio-distal crown angulation,Mesio-distal crown angulation, 3.3. Labio-lingual crown inclination,Labio-lingual crown inclination, 4.4. Absence of rotation,Absence of rotation, 5.5. Tight contacts,Tight contacts, 6.6. Curve of spee.Curve of spee. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 68. 1) MOLAR INTERARCH RELATIONSHIP:-1) MOLAR INTERARCH RELATIONSHIP:- Mesio –buccal cusp of upper first molar shouldMesio –buccal cusp of upper first molar should occlude in the buccal groove between the mesial andocclude in the buccal groove between the mesial and medial buccal cusp of the lower first molar.medial buccal cusp of the lower first molar. The mesio-lingual cusp of the upper first molar shouldThe mesio-lingual cusp of the upper first molar should occlude In the central fossa of lower first molar.occlude In the central fossa of lower first molar. The crown of upper first molar must be angulated soThe crown of upper first molar must be angulated so that the distal marginal ridge occlude with mesialthat the distal marginal ridge occlude with mesial marginal ridge of the lower second molar.marginal ridge of the lower second molar. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 69. 2) MESO-DISTAL CROWN ANGULATION:-2) MESO-DISTAL CROWN ANGULATION:- A line that passes alonght the long axis of theA line that passes alonght the long axis of the crown through the most prominent part in thecrown through the most prominent part in the center of the labial or buccal surface is calledcenter of the labial or buccal surface is called the long axis of the clinical crown.the long axis of the clinical crown. For the normal occlusion the gingival part of theFor the normal occlusion the gingival part of the long axis the crown must be distal to occlusallong axis the crown must be distal to occlusal part of the line.part of the line. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 70. LABIO-LINGUAL CROWN INCLINATION :-LABIO-LINGUAL CROWN INCLINATION :- The crown inclination is determined from a Mesial orThe crown inclination is determined from a Mesial or distal view.distal view. If the gingival area of the crown is more linguallyIf the gingival area of the crown is more lingually placed than the occlusal area, it is referred to asplaced than the occlusal area, it is referred to as positive crown inclination.positive crown inclination. In the case the gingival area of the crown is moreIn the case the gingival area of the crown is more labially or buccally placed than the occlusal area , itlabially or buccally placed than the occlusal area , it is referred to asis referred to as negative crown inclination.negative crown inclination. The maxillary incisor exhibits a positive crownThe maxillary incisor exhibits a positive crown inclination, while the mandibular incisors show ainclination, while the mandibular incisors show a very mild negative crown inclination.very mild negative crown inclination. All the maxillary and mandibular posterior have aAll the maxillary and mandibular posterior have a negative crown inclination.negative crown inclination. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 71. 4)ABSENCE OF ROTATION:-4)ABSENCE OF ROTATION:- Normal occlusal is characterized by theNormal occlusal is characterized by the absence of any rotation.absence of any rotation. Rotated posterior teeth occupy more space inRotated posterior teeth occupy more space in dental arch while rotated incisors occupy lessdental arch while rotated incisors occupy less space.space. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 72. 5) TIGHT CONTACTS:-5) TIGHT CONTACTS:- To consider a occlusion as normal there shouldTo consider a occlusion as normal there should be tight contacts between adjacent teeth.be tight contacts between adjacent teeth. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 73. 6) CURVE OF SPEE:-6) CURVE OF SPEE:- A normal occlusal plane according to Andrew'sA normal occlusal plane according to Andrew's should be flat , with the curve of SPEE notshould be flat , with the curve of SPEE not exceeding 1.5mm.exceeding 1.5mm. www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com
