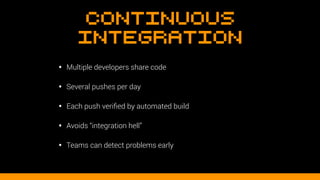
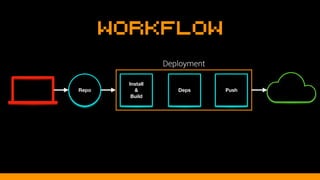
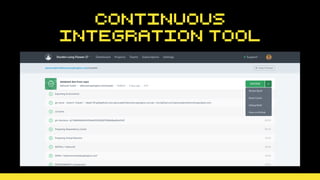
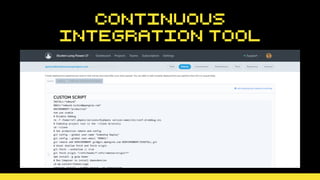
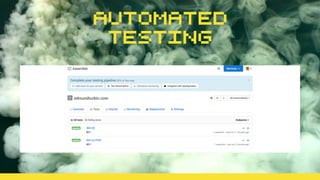
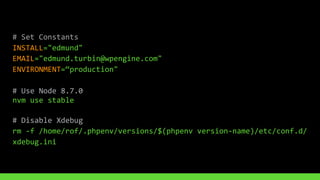
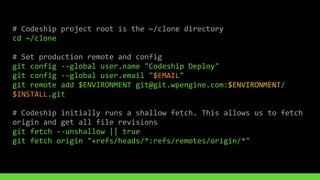
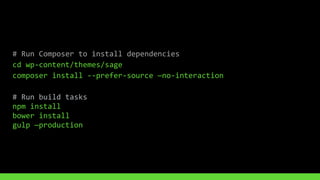
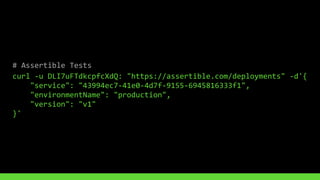
This document discusses using version control and continuous integration to deploy code. It recommends developing code locally, using distributed version control like Git, and deploying to a testing environment before production. The continuous integration workflow involves multiple developers sharing code through a central version control repository. Each code push is verified by automated builds to avoid integration issues and catch problems early. The document provides an example deployment script for Codeship that checks out code, installs dependencies, builds assets, commits changes, and pushes to the production remote. It also discusses testing deployments using Assertible and lessons learned around caching packages, installing dependencies, and using forceful Git pushes for deployment.