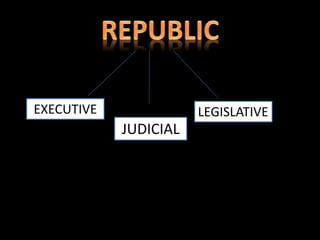
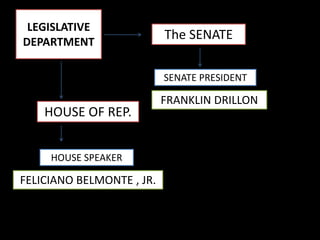
This document outlines the three branches of government in the Philippines: executive, judicial, and legislative. It provides details on the executive departments that comprise the largest part of the country's bureaucracy. It then summarizes that the legislative power is vested in the bicameral Congress of the Philippines, consisting of the Senate and House of Representatives. The Senate has 24 members elected to six-year terms, while the House has a maximum of 250 members.