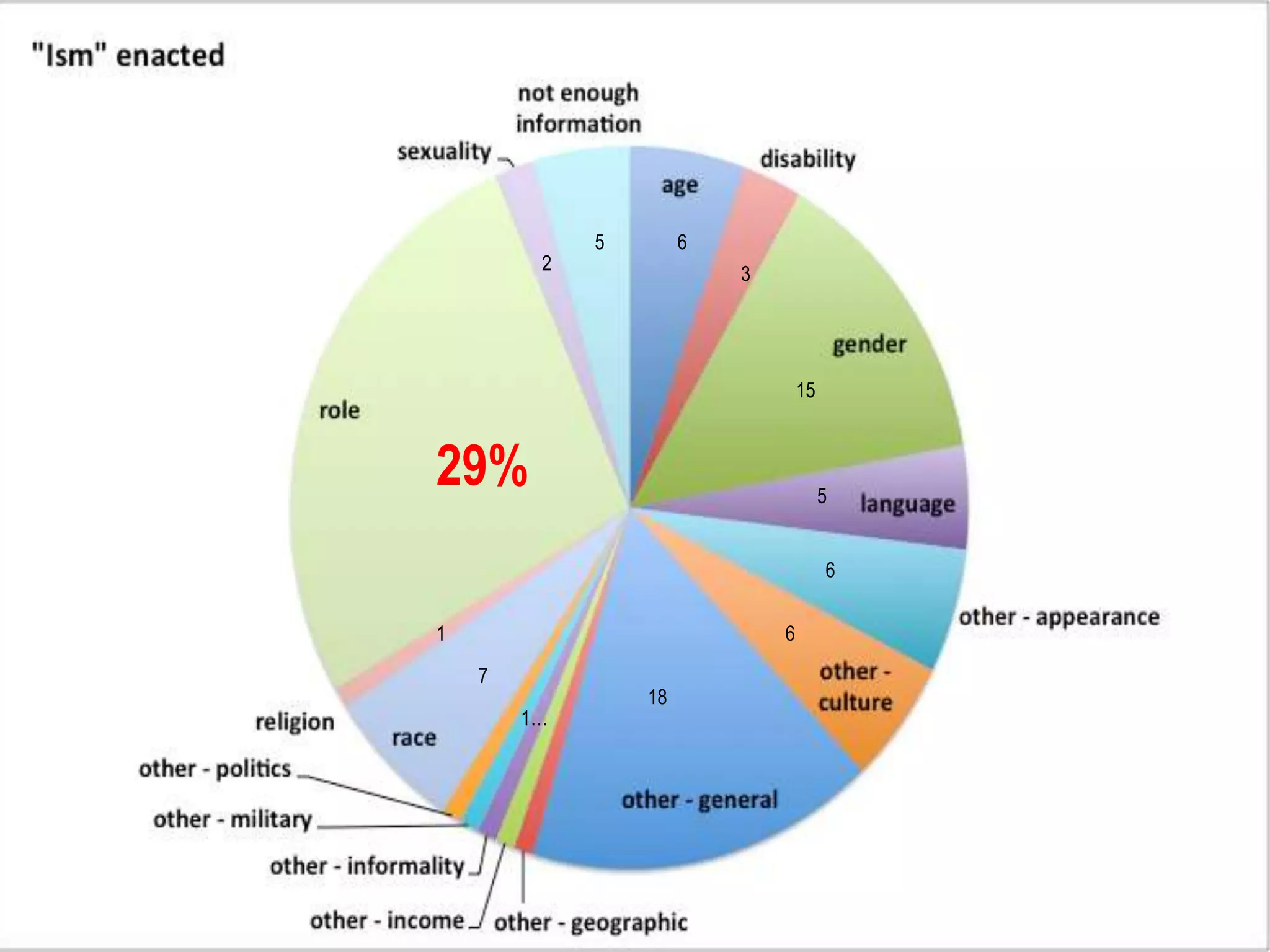
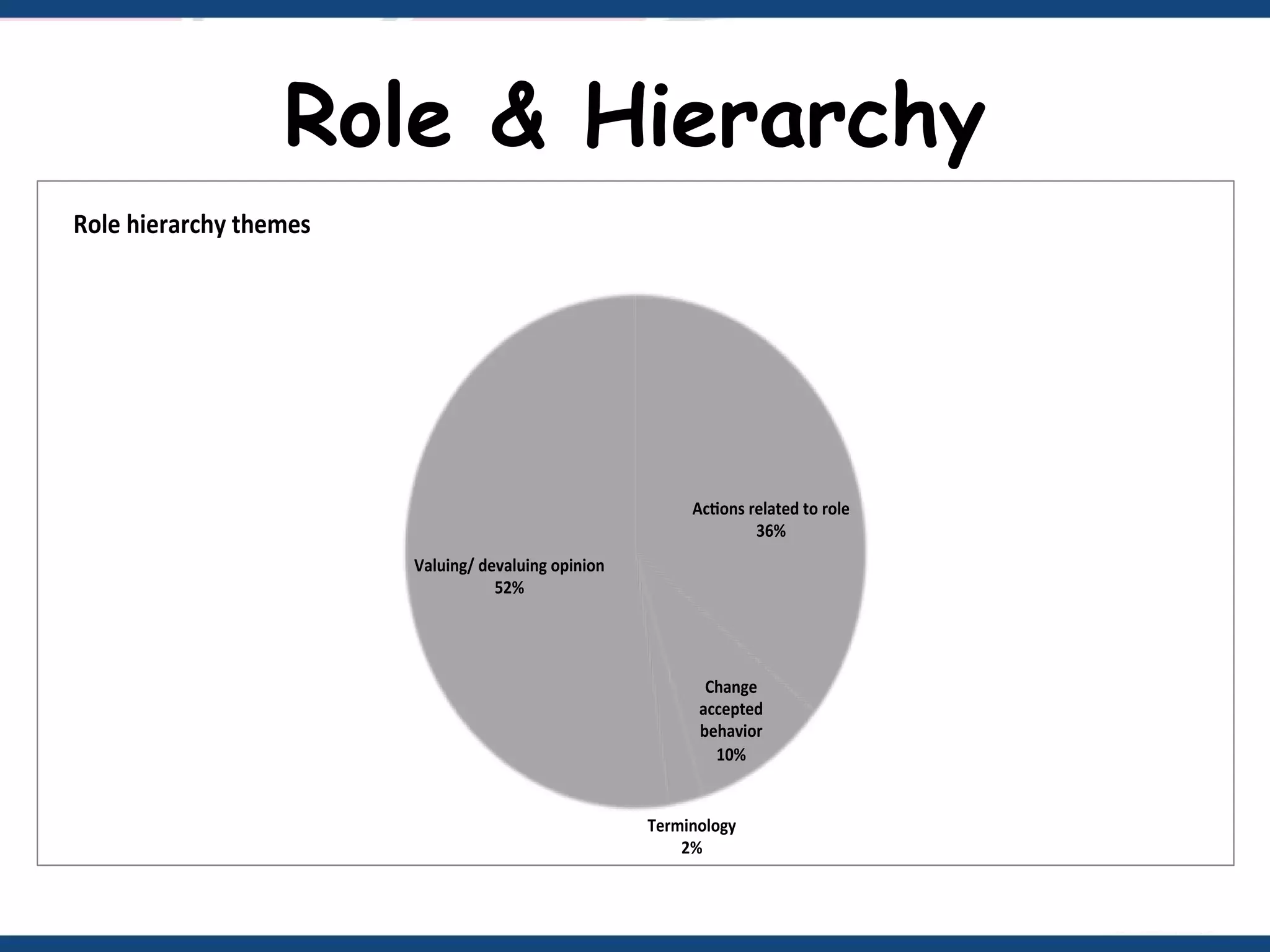
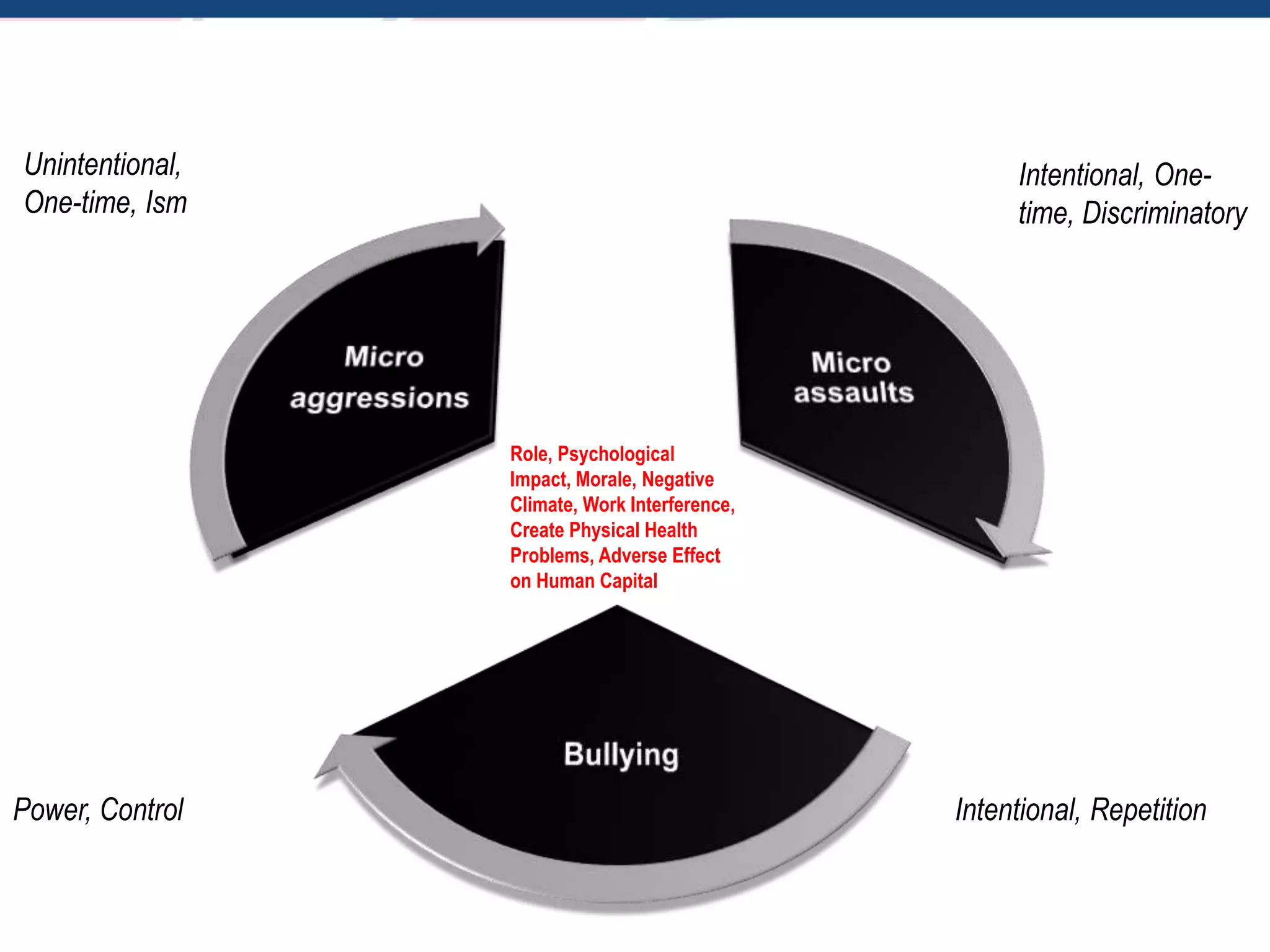
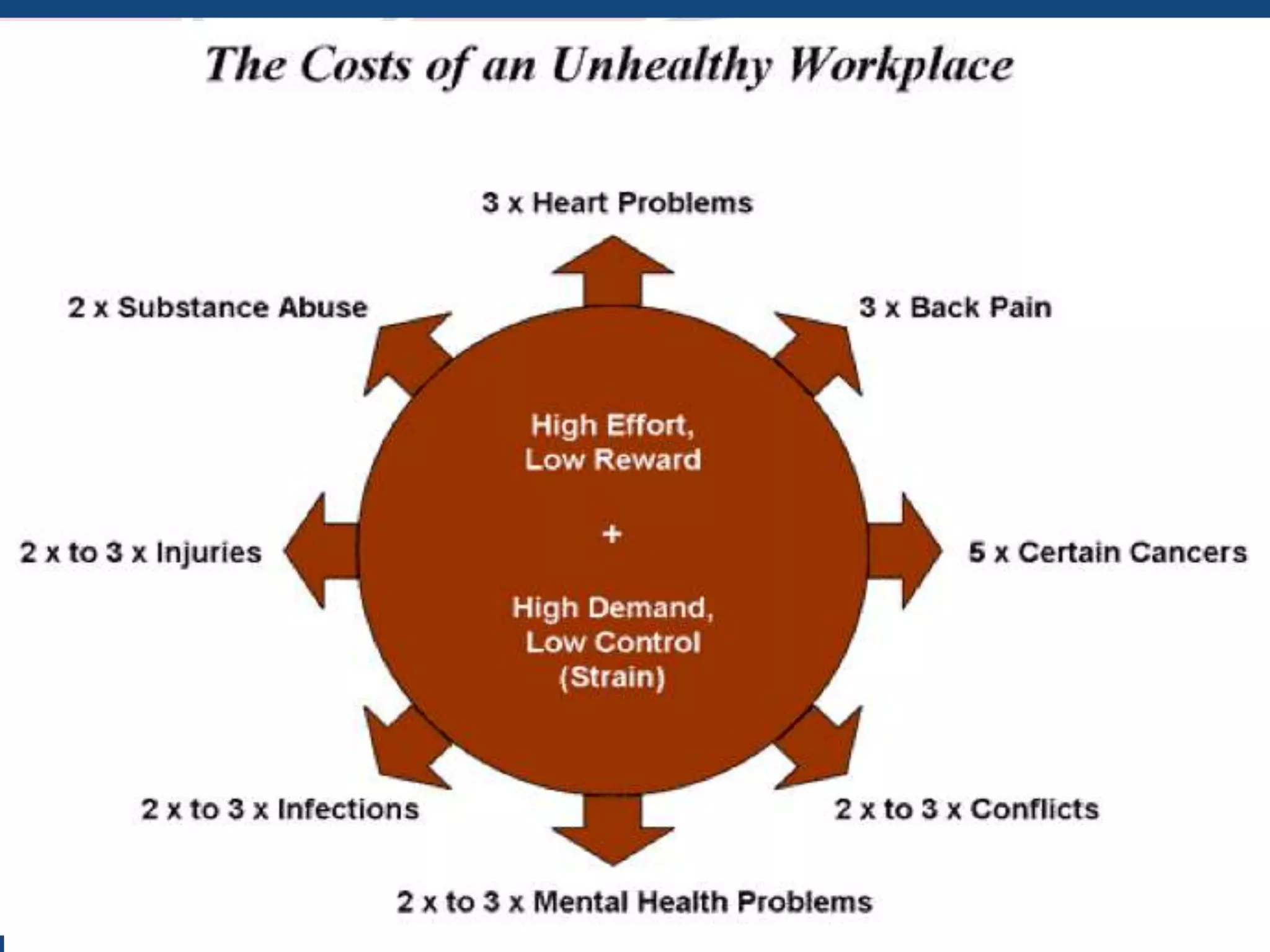
The document discusses microaggressions, which are subtle, often unintentional indignities that can negatively affect psychological well-being and perpetuate systemic disparities in various sectors like education and healthcare. It also differentiates between microassaults and workplace bullying, highlighting their respective impacts on individuals and organizational climate. Strategies to address these issues include active listening, recognizing biases, and taking actions against bullying.