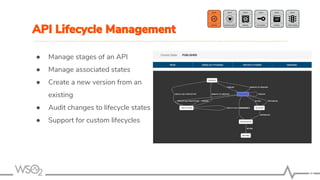
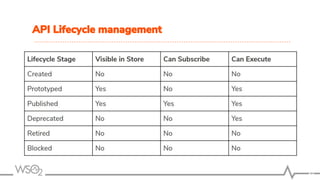
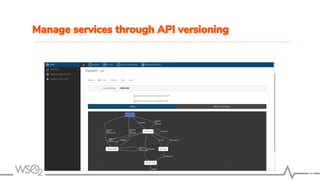
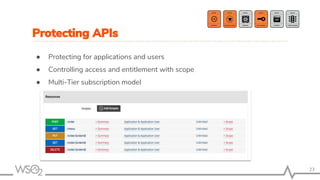
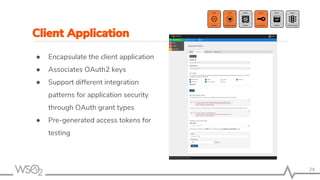
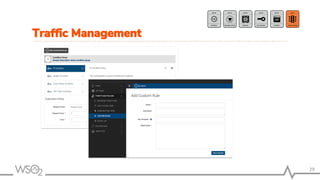
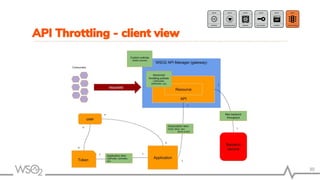
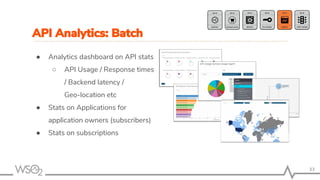
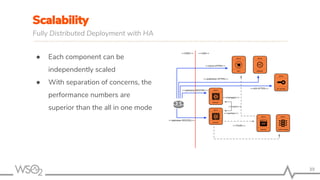
The document outlines best practices for API management using WSO2 API Manager, focusing on an API-first design approach, lifecycle management, versioning services, securing APIs, rate limiting, and monitoring. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining high-quality APIs through proper design, security mechanisms, and analytics for performance tracking. Additionally, it discusses strategies for promoting APIs and ensuring scalability in a distributed architecture.