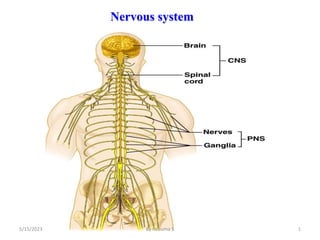
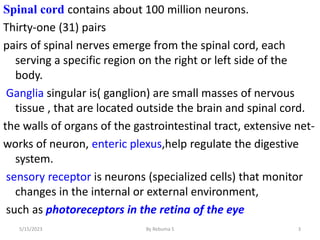
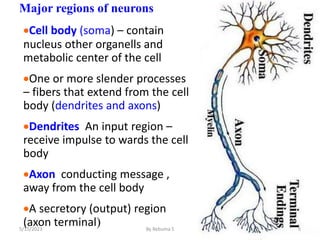
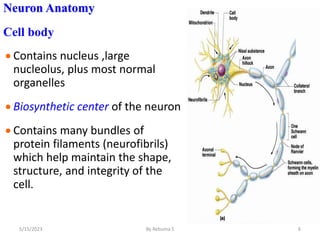
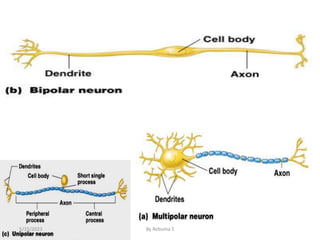
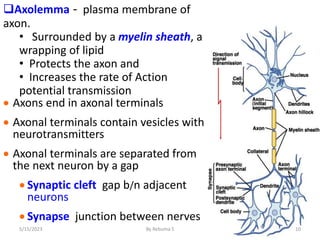
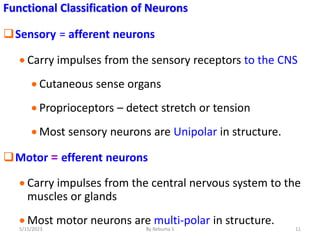
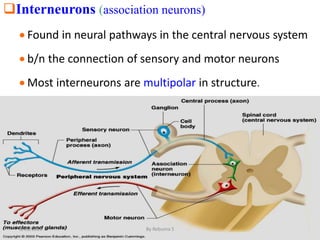
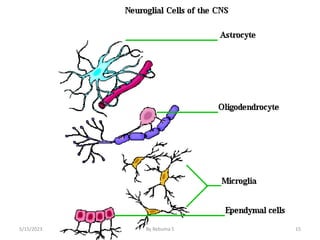
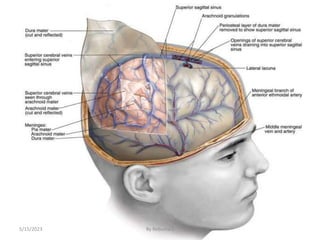
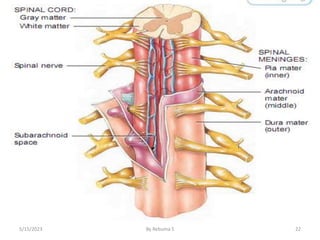
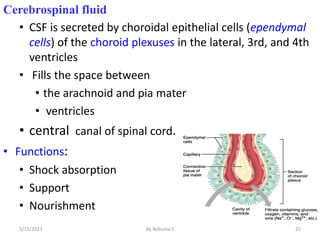
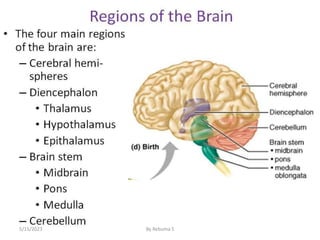
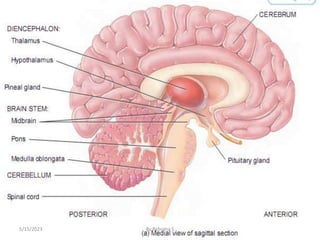
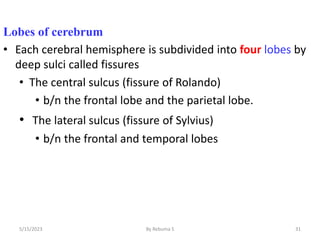
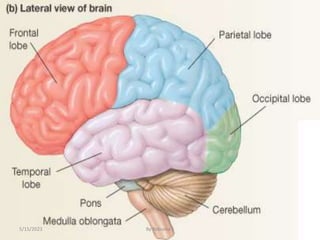
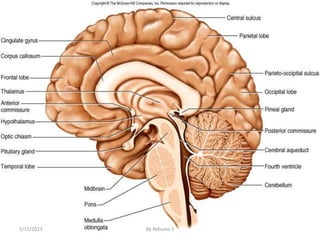
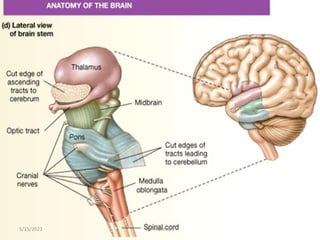
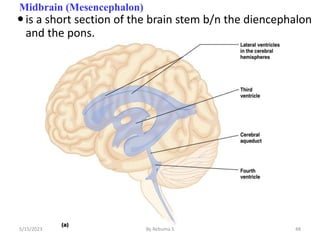
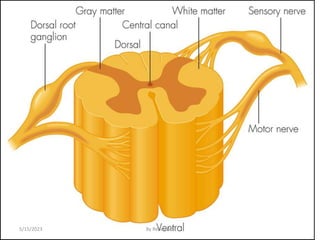
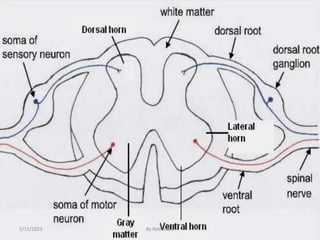
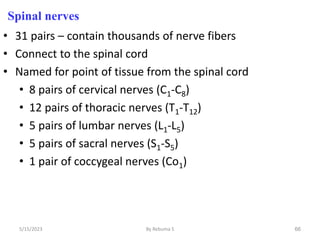
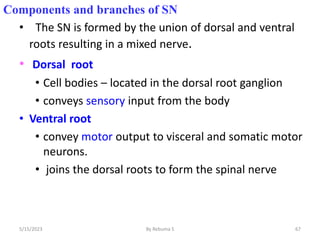
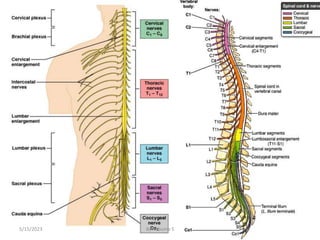
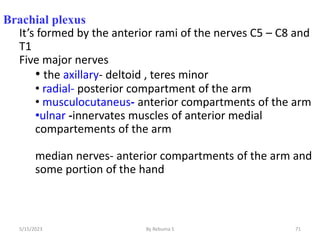
The nervous system is one of the most complex body systems, consisting of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system. The CNS contains billions of neurons and neuroglia that communicate via electrical and chemical signals. The brain is protected by meninges and cerebrospinal fluid. Neurons are specialized cells that conduct electrical signals, while neuroglia provide support. The nervous system is organized into the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The cerebrum controls higher functions and is divided into four lobes. The diencephalon includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus.