Customer Centric Cross Selling Strategies
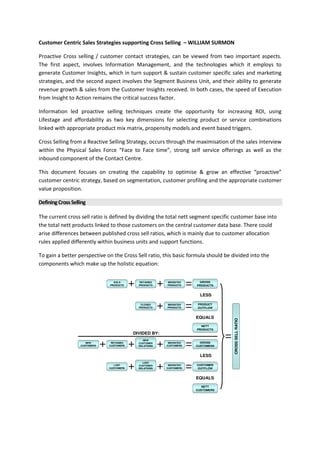
- 1. Customer Centric Sales Strategies supporting Cross Selling – WILLIAM SURMON Proactive Cross selling / customer contact strategies, can be viewed from two important aspects. The first aspect, involves Information Management, and the technologies which it employs to generate Customer Insights, which in turn support & sustain customer specific sales and marketing strategies, and the second aspect involves the Segment Business Unit, and their ability to generate revenue growth & sales from the Customer Insights received. In both cases, the speed of Execution from Insight to Action remains the critical success factor. Information led proactive selling techniques create the opportunity for increasing ROI, using Lifestage and affordability as two key dimensions for selecting product or service combinations linked with appropriate product mix matrix, propensity models and event based triggers. Cross Selling from a Reactive Selling Strategy, occurs through the maximisation of the sales interview within the Physical Sales Force “Face to Face time”, strong self service offerings as well as the inbound component of the Contact Centre. This document focuses on creating the capability to optimise & grow an effective “proactive” customer centric strategy, based on segmentation, customer profiling and the appropriate customer value proposition. DefiningCrossSelling The current cross sell ratio is defined by dividing the total nett segment specific customer base into the total nett products linked to those customers on the central customer data base. There could arise differences between published cross sell ratios, which is mainly due to customer allocation rules applied differently within business units and support functions. To gain a better perspective on the Cross Sell ratio, this basic formula should be divided into the components which make up the holistic equation: SOLD PRODUCTS RETAINED PRODUCTS MIGRATED PRODUCTS GROSS PRODUCTS LESS CLOSED PRODUCTS MIGRATED PRODUCTS PRODUCT OUTFLOW EQUALS NETT PRODUCTS NEW CUSTOMERS RETAINED CUSTOMERS NEW CUSTOMER RELATIONS MIGRATED CUSTOMERS GROSS CUSTOMERS LESS LOST CUSTOMERS LOST CUSTOMER RELATIONS MIGRATED CUSTOMERS CUSTOMER OUTFLOW EQUALS NETT CUSTOMERS DIVIDED BY: CROSSSELLRATIO
- 2. The application of this ratio is flawed due to the following: • Customer allocation rules ( Segment vs Product business units ) • It is not Strategy Sensitive: • Profitability vs Market Share Growth • Customer Growth, Retention strategies • Operating model customer allocation rules • Seasonal & Economic Cycles. • It is not Sub Segment focused PROITABILITY FINANCIAL PERSPECTIVE CUSTOMER PERSPECTIVE INTERNAL PERSPECTIVE RESOURCE PERSPECTIVE MARKET SHARE FINANCIAL PERSPECTIVE CUSTOMER PERSPECTIVE INTERNAL PERSPECTIVE RESOURCE PERSPECTIVE C U R R E N T V I E W D E S I R E D S T A T E Reflecting on the ratio calculation, it becomes evident that the Cross Sell Ratio, could be impacted by a host of factors, not only through expanding a customer’s existing account portfolio with additional product sales or service offerings. It also implies that in order to positively impact the Cross sell ratio, there is a need to: • Cross sell & product bundle at the source of customer acquisition. • Retain existing customers, especially those who have multiple product / service portfolios. • Take note of customers that are migrated to other Segment or Product SBUs in line with their current Operating Model and Segmentation / Migration rules. It is important to understand that the Cross Sell ratio will drop, with every new customer that is acquired, who does not have a Cross Sell ratio larger than 1:1. i.e. The ratio drops with every new stand alone customer acquired. In addition, this is also impacted by the affordability of the lower end of the segmented customer base. To summarise, the basic customer strategies impacting the Cross Sell ratio are: (UCARE) • Acquisition - New customer acquisition
- 3. • Retention - Existing customer retention • Cost / Profitability Management - Customer migration / allocation within segments related to CVPs • Expansion - Customer relationship expansion • Utilisation - Account Utilisation This understanding of the various Cross Sell factors, supports the view that all Product and Segment SBUs are either directly or indirectly responsible for the resultant Cross Sell Ratio. This responsibility is linked to their value proposition, product offering and the manner in which customers are acquired and retained. Furthermore, it is pertinent to understand the impact of the following additional factors, on the ability to ‘Cross Sell’ and the effectiveness of it: • Affordability ( Customers ability to pay for additional products) • Life Stage ( A customers need for a product ) • Customer Profitability ( Usage of the product - Fair Value ) • Product Offering ( Most appropriate product ) • Legislation ( FAIS, NCA etc ) • Dormancies / Closures ( Usage vs start up & admin costs ) • Enablement within the Value Chain - Fulfilment process and the impact thereof on the success of the ‘Sale’ ( End to End virtual fulfilment ) and policy / governance / compliance interpretations and applications. Cross Selling can therefore be defined as: • ‘A proactive, customer centric, additional offering / solution to an existing or new customer, which results in a mutually beneficial commercial relationship’. The Cross Selling ratio should be defined as: • ‘A strategically sensitive ratio, applied to a specific sub segment, with the intention of positively influencing the overall profitability or market share of the identified sub segment’, while enhancing the customers financial situation and service experience. Accordingly, any customer focused activity initiated by a segment SBU towards the specific customer segment, has operational and commercial consequences for the remainder of the product SBUs within the corporate entity, and the Cross Sell ratio for the customer segment involved. It is therefore crucial, for a collaborative, segment customer Value Proposition and contact strategy to be established throughout the corporate entity. In addition, the segment will need to identify at least 4 or more separate cross sell ratios, against which it can measure related performance and get consensus for these with all stakeholders.
- 4. Importance of Cross Selling Cross selling alone will not achieve substantial revenue growth if viewed in isolation. Revenue growth is achieved through a blend of Acquisition, Retention, Expansion, Cost Management / profitability, and Utilisation strategies. However, ‘Cross Selling’ to the existing customer base, will, if conducted responsibly, result in a substantial contribution to the overall segment revenue growth. So what is a responsible approach to ‘Cross Selling’, and what potential value can it contribute? In order to define a responsible approach, it is important to understand the existing Customer Market, both from an internal as well as an external perspective. Using statistics from ‘Census 2001’, ‘AMPS 2001’,‘Consumer Research’ conducted in 2001, and Customer Insights gained from, the current market is depicted as follows: 24% 42% 34% UNEMPLOYED NOT ECONOMICALLY ACTIVE EMPLOYED 15,1 Mil 10,7 Mil 18,9 Mil 91% 8% 1% R0 < R3 999 R4 000 < R29 999 R30 000 < Above SOURCE – AMPS 2001 SOURCE – CENSUS 2001 92% 6% 2% Lower R4k - R13,9k Middle R14k - R19,9k Upper R20k - R29,9K SOURCE – CONSUMER RESEARCH 92% OF MIDDLE MARKET CUSTOMERS FALL WITHIN THE LOWER INCOME SEGMENT. INCOME DRIVES USAGE, WHICH IN TURN DRIVES REVENUE ( AFFORDABILITY TO TAKE ON ADDITIONAL PRODUCTS ? ) Reflecting on the above graphs, the important factors that stand out are: • 34% of the total population is employed, and the current trend, compared to 1996 Census information, is that the Unemployment Ratio is deteriorating. • The majority ( 91% ) of the population, have an income below R4 000 per month. • 8% Of the population receiving a higher than R4000 income, have 92% falling within the Lower earning Sub segment.
- 5. Current Customer Growth trends are emphasising the need for focused Retention, Expansion and Profitability strategies. Sufficient volumes of new customers, which will be required to dramatically impact on Revenue growth are not, according to market statistics, unlimited. If viewed in collaboration with the current market share dynamics and the cost on new customer acquisition, then new customer acquisition strategies should take second priority to focused and meaningful customer retention and cross sell activities, which support profitable growth. To understand the potential revenue growth within a Financial Services existing customer base, it is important to understand the various revenue streams. This includes: • Nett Interest Income • Non Interest Income o Transaction & Service Fees o Commissions o Profit Share The segment products can also be grouped to four broad categories: • Transactional products • Investment products • Lending products • Insurance products Cross selling a second transactional account to a customer, could potentially result in the same transaction volumes being distributed between two products, thereby potentially lowering the overall profitability of the customer due to increased account maintenance costs. Product usage is core to certain product’s profitability, and the importance of selling the right product to the right customer, based on affordability, is imperative A segment’s transactional book ( Savings and Cheque Accounts ), and the profitability thereof can be viewed according to the following table: R 0 - R 4,000 R 4,001 - R 8,000 R 8,001 - R 12,000 R 12,001 - R 16,000 R 16,001 - R 20,000 R 20,000 + 0101 0202 0303 0404 04 +04 + NumberofProducts Monthly Turnover TRANSACTIONAL SEGMENTATION LIFE CYCLE BUYING CYCLE CULTURE AFFORDABILITY USAGE TRANSACTIONAL VOLUME TICKET VALUE
- 6. The above table, represents segment Transactional Account customers. These customers have been allocated into sectors based on credit turnover ( income eg, salaries ) and products held. This Transactional account matrix, showed that customer profitability can be influenced by increasing product take up, as well as increasing the usage of the existing product. Further analysis, was undertaken in selected groups, including the Stand Alone product customers, to understand the sub segment composition and product mix, as well as the next most likely product take up based on propensity modelling. The findings were as follows: • In the single product category, profitability is directly related to transaction volume. The greater the turnover, the higher the transaction volume. • Next product take up within the 2nd product in a retail segment customer base indicates the following preferences: o Cheque Accounts Credit Card Personal Loan Savings Account o Savings Accounts Investments Credit Cards Personal Loans ( Including Short Loans ) A responsible ‘Cross Sell’ strategy for the Transactional Customer base, should include a blend of Lending and Investment products, and self service related offerings Further analysis of the stand alone customer base indicates the following: • High number of scholars and unemployed customers. From a cross selling perspective, these customers should not be included in the cross sell calculation, as it would be not be a priority to increase their product holding due to affordability factors, which could either result in account dormancies.
- 7. To summarise the above Stand Alone Customer base using Propensity Potential: STAND ALONE POTENTIAL – PROPENSITY BASED % Tar to Convers. % Tar to Contacts % Tar to Prospect ANNUAL TARGT TOTAL CARD VAF HL SAV INV P/L CHQ TOTALCARDAVAFAHLSAVINVP/LCHQPROSPECTS SALES POTENTIAL WITHIN THE STAND ALONE SEGMENT CUSTOMER BASE, USING PROPENSITY MODELS TO DETERMINE 1ST PRODUCT TAKE UP. THE ABOVE FIGURES EXCLUDE PRODUCTS THAT WOULD BE CROSS SOLD AGAINST THE PRIMARY PRODUCT SALE ( 2:1 = …………x 2 = …………. +………… = ………….. potential product sales – Cross Sell Ratio for the Stand Alone ……….. base will move from 1 to 1,…. ) The ‘Stand Alone’ analysis can also be applied to 2 product customers, in order to correctly target and cross sell a 3rd product. This ‘cross sell’ technique can be systemised into the data warehouse, to provide a continuous flow of cross sell leads to be actioned by the various SBUs and Distribution Channels. Further analysis to be completed on the segment customer base. This analysis, is aimed at identifying: • The current composition of segments in terms of Sub Segments, Profitability, Usage, Product Mix & Channel Mix. • The potential of future Cross Selling & Usage initiatives aimed at the existing segment customer base. • The impact of customer & account attrition on profitability and to highlight some of the underlying reasons. The analytic process, which is based on the following method: Product Potential This is determined by grouping the segment Customer base into 3 specific customer groupings: • Transactional, Lending & Investing Each group is further sub divided into sectors according to Product numbers and Turnover, Average Balance or Initial Loan Balance. Each sector will be further sub divided into the Sub Segments, which is based on age ( Life stage ), and will indicate the number of customers in the Sub Segment, as well as their average profitability. Each Sub Segment will be further divided into the Product Mix, which will also reflect numbers and percentage.
- 8. In order to determine Usage potential, the ultimate ( profitable ) channel mix & usage volume, will be determined per sub segment. All customers will be matched against their ultimate channel & usage profile, and areas of potential will be highlighted for customer education on product features or channel cross sell activities TRANSACTIONAL LENDING INVESTING TURNOVER INITIAL LOAN VALUE AVERAGE BALANCE # P R O D U C T S # P R O D U C T S # P R O D U C T S YOUTH 0–18YEARS NUMBER=# AVEPROFIT=(6) STUDENT CIFINDICATOR NUMBER=# AVEPROFIT=(10) YOUNGADULT 19–35YEARS NUMBER=# AVEPROFIT=9 ESTABLISHED MIDDLE 36–54YEARS NUMBER=# AVEPROFIT=15 SENIORS 55+YEARS NUMBER=# AVEPROFIT=7 OTHER NUMBER=# AVEPROFIT=5 SAVINGS 200 26% CHEQUES 100 13% CREDIT CARDS 50 7% INVESTMENTS 150 20% PERS LOANS 150 20% HOME LOANS 70 9% AVAF 20 3% MONEY MARKET 15 2% SUB SEGMENTS PRODUCT TYPE AVERAGEPROFITABILITY NUMBEROFPRODUCTS This approach will be supportive of the company’s view on Customer Centricity, as Cross Selling offers, will be aimed at customers, who are in the right life stage cycle and will benefit from the offering, as well as being in a position to afford the product as to ensure responsible selling practices are maintained. Usage Potential The same analytic approach will be used to determine Usage Potential, the only difference, is that instead of product mix, the channels used, as well as average transaction volume will be reflected. TRANSACTIONAL LENDING INVESTING TURNOVER INITIAL LOAN VALUE AVERAGE BALANCE # P R O D U C T S # P R O D U C T S # P R O D U C T S TELLER 200 26% ENQUIRIES 100 13% ATM 50 7% POS 150 20% SYSTEM 150 20% INTERNET 70 9% TELE BANKING 20 3% CELL BANKING 15 2% SUB SEGMENTS TRANSACTION TYPE AVERAGEPROFITABILITY NUMBEROF TRANSACTIONS YOUTH 0–18YEARS NUMBER=# AVEPROFIT=(6) STUDENT CIFINDICATOR NUMBER=# AVEPROFIT=(10) YOUNGADULT 19–35YEARS NUMBER=# AVEPROFIT=9 ESTABLISHED MIDDLE 36–54YEARS NUMBER=# AVEPROFIT=15 SENIORS 55+YEARS NUMBER=# AVEPROFIT=7 OTHER NUMBER=# AVEPROFIT=5
- 9. Customer Attrition All previous customer/account losses should be analysed to determine the following trends: • Geographical ( Spatial analysis ) • Product Trends ( Investments, Personal Loans, Cheques etc ) • Sub Segment ( Demographic analysis ) • Application Process Issues ( T/A Times & scoring quality etc ) • Account Activation Issues ( New accounts opened / closed no activation ) • Reasons for closure ( Service, Bad debt, Dormancy etc ) The critical factors which will enable this process include: • Quality of Customer Information data. • Quality of the Data Mining Models. • An integrated customer contact management strategy. • Speed of data extraction to sales action. • ‘End to End’ virtual fulfilment of applications. In summarizing the importance of Cross Selling, we can categorise them into two key areas: ‘Lock In’ ( Customer Retention ) • Total needs solutioning • Predicting customer needs • Complexity of Channel Usage Profitability ( Customer Expansion ) • Lifetime value • Pricing • Product mix • Usage Obstacles&Enablers Obstacles Clarification • Uncoordinated and un-integrated marketing, selling and contact strategy towards the segment customer base. • Silo Based Organisational Customer Strategies
- 10. • The quality of our customer information on CIF. • The purer the Customer Information, the greater will be the SBUs ability to contact customers, and predict customer’s propensity to take additional products. • The lack of an ‘End to End’ virtual fulfilment process for customer applications. • Research has shown that 62% of customers visit their branch less than once per month. Without end to end fulfilment in Contact Centres, we will still be reliant on customers going in to branches to finalise applications. • Segmentation could be too complex and static. This inhibits the ability to rapidly respond to changes within the market. • Segmentation should be basic and cater for income & life stage splits. • The lack of an integrated, co-ordinated approach to cross selling through the Distribution Channels. • Various segment strategies when executed, could be directed to the same customer, without prioritising or phasing being applied. • Customer scoring models are product orientated, and may not support multiple product scoring. • A customer approved for a Home Loan, may not necessarily qualify for a Cheque Account. The introduction of a total customer view & multiple product scoring will benefit cross selling. • Data Mining Models • Propensity Models • Event Based Triggers • Next Best Product • Proactive selling techniques developed within the Contact Centre • Focused Selling, Up Selling, Down Selling, Add On Selling, By the Way Selling, Cross Selling, Puppy Dog Selling and Match Selling techniques will up your conversion ratios if aligned to the right campaign. • Potential capacity within t Contact Centres • Optimisation of capacity & the potential for ‘End to End’ processing • Substantial existing Customer Base to support data mining and analytics • Data volumes are required to ensure key commercial drivers linked to Cost of Sale, and Operational Efficiencies. • Highly skilled and tenured sales staff – skilled in multi product lines and services • They need to be able to respond to client needs, questions and responses outside of any call script, but within the compliance and governance framework.