B. ENV. UNIT 2 PART 4.pptx
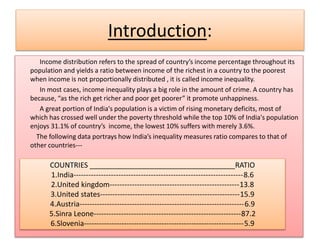
- 1. Introduction: Income distribution refers to the spread of country’s income percentage throughout its population and yields a ratio between income of the richest in a country to the poorest when income is not proportionally distributed , it is called income inequality. In most cases, income inequality plays a big role in the amount of crime. A country has because, “as the rich get richer and poor get poorer” it promote unhappiness. A great portion of India's population is a victim of rising monetary deficits, most of which has crossed well under the poverty threshold while the top 10% of India's population enjoys 31.1% of country’s income, the lowest 10% suffers with merely 3.6%. The following data portrays how India’s inequality measures ratio compares to that of other countries--- COUNTRIES ____________________________________RATIO 1.India--------------------------------------------------------------------8.6 2.United kingdom----------------------------------------------------13.8 3.United states--------------------------------------------------------15.9 4.Austria------------------------------------------------------------------6.9 5.Sinra Leone-----------------------------------------------------------87.2 6.Slovenia----------------------------------------------------------------5.9
- 2. Meaning Of Inequality Of Income Inequality of distribution of wealth and income refers to that situation of an economy in which income of small section of the country is which larger than the average income of the nation and the income of large section is much smaller than the average national income. Indian economy is a mixed economy. Both public and private sectors operate in it. Main objective of the public sector is, “Economic growth with social justice.” On the other hand, the objective of the private sector is to maximize profit. During the period of planning private sector has fully succeeded in achieving its objectives whereas the public sector has largely failed. Consequently inequalities of income and wealth have only been compounded. In this we shall discuss important problems concerning inequalities of income and wealth in India.
- 3. Definition Of Income Inequality The unequal distribution of household or individual income across the various participants in an economy. Income inequality is often presented as the percentage of income to a percentage of population. For example, a statistic may indicate that 70% of country’s income is controlled by 20% of that country’s residents. It is often association with the idea of income “fairness.” It is generally considered “unfair” if the rich have a disproportionally larger portion of a country’s income compared to their population.
- 4. Nature of inequality of income Indian economy reveals several forms of economic inequality. It mains forms are as under: Inequality of income and consumption. Inequality of wealth. Regional inequality. These forms are explain below:-
- 5. 1. Inequality of income and consumption:- There is no official organisation in India to compile data on the personal distribution of income in the country as a whole is not directly available. Some insight into it is provided by the data on distribution of consumption. It is due to this reason that the magnitude of the inequality of income has been estimated from the data regarding the distribution of consumption and income. (a) Inequalities of income. (b) Rural and Urban inequalities. (c) Inequalities of consumption expenditure. (d) Population below poverty line (BPL). 2. Inequalities in the distribution of wealth/Assets:- In India, along with inequality in the distribution of income there also exists inequalities in the distribution of wealth. It can be estimated on the basis of distribution of land holdings, Ownership of building property and ownership of shares of companies. (a) Distribution of landholdings. (b) Ownership of Residential Buildings. (c) Ownership of Shares.
- 6. 3. Regional Inequality:- Regional inequality refers to inequality of economic growth and level of per capita income in different states of the country. Rate of growth and per capita income in some states of the country namely Goa, Haryana, Maharashtra, Punjab, Gujarat etc. is relatively very high. On the other hand, in states like Bihar, Orissa, Madhya Pradesh, U.P., Jharkhand etc. rate of economic growth and per capita income is relatively very low. If regional inequality is not controlled, it may endanger the integration for the nation. Per capita income is consideration to be the best measure to know regional inequality. State Per capita income State Per capita income (high income states) (Rs. P.a.) (low income states) (Rs. P.a.) Goa 70,112 Bihar 7,875 Haryana 38,832 Uttar Pradesh 13,262 Maharashtra 37,081 Madhya Pradesh 15,647 Punjab 34,929 Jharkhand 17,299 Gujarat 34,157 Orissa 19,066
- 7. Causes Of Inequality Of Income In India Inequality in the Ownership of land Private Ownership of Property in Urban Areas Law of Inheritance Inequality of Professional Training Inflation Credit Policy of Financial Institutions More Burden of Indirect Taxes Corruption and Smuggling Unemployment Tax-Evasion
- 8. Government Policy To Reduce Inequalities Of Income And Wealth Land Reforms Extension of Public Sector Encouragement to small-Scale and Cottage Industries Control over Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Employment and Wage Policies Pricing and Distribution Policies Fiscal Policy Measures to correct Regional Imbalances
- 9. CONCLUSION We can conclude that inequalities in the distribution of income and wealth are quite severe in India. The government of India has been endeavouring to reduce inequalities of wealth and income in the country. Several measures have been adopted in this direction but it could not gain much success. Following measures were suggested by the planning commission to minimize inequalities of wealth and income:(i) Agriculture land and urban property should be re-distributed.(ii) Public enterprises should distribute essential goods at subsidised prices to low-income consumers.(iii) More credit facilities be made available to small farmers and cottage and small industries. They should be provided essential raw materials on priority basis.(iv) Rural and Urban poor should be organised. It will be easier for the administration to help them when they are organised.(v) Minimum employment facilities be provided. Emphasis has also been laid on the reduction of inequalities in the distribution of wealth and income during the course of various five plans.