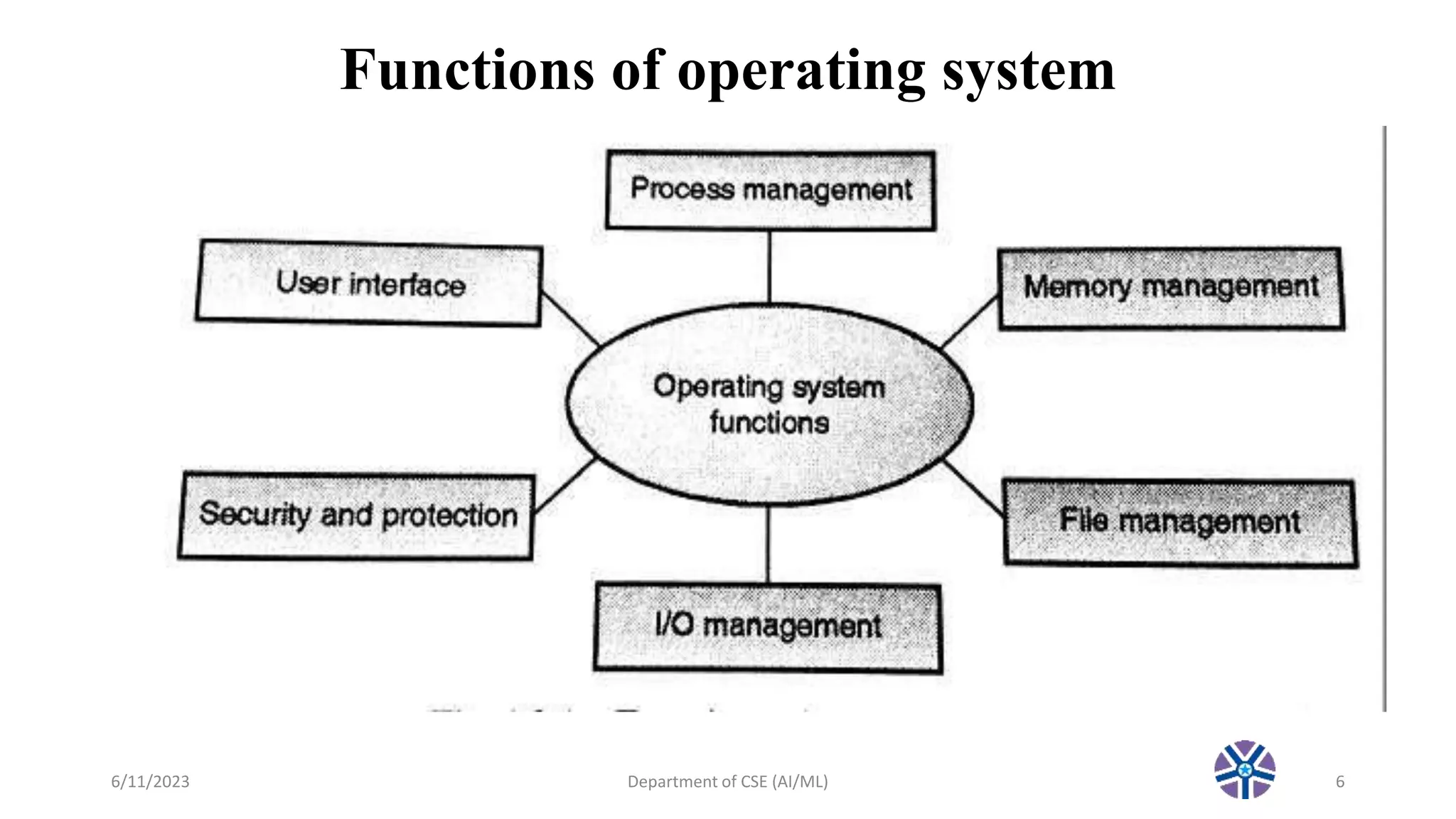
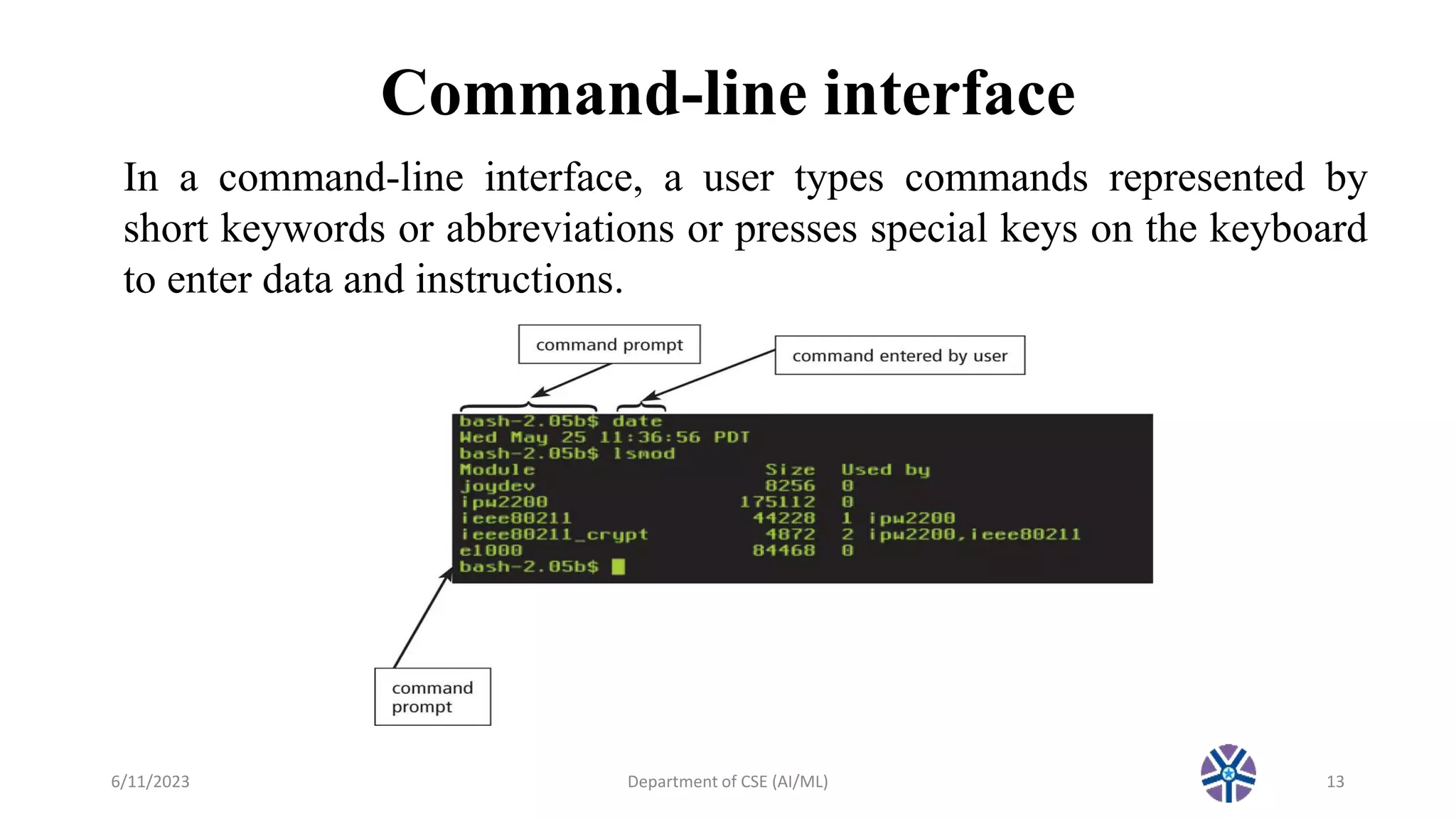
This document outlines the syllabus for an operating systems course. It includes the textbook, references, topics to be covered in lecture 2 such as process management, memory management, file management, and device management. Lecture 2 defines processes, discusses how the operating system manages memory allocation and paging, file systems, I/O devices, security, and user interfaces. Popular operating system classes are also listed, and the topics planned for the next lecture are noted.