Positive Externalities vs Negative Externalities.docx
•Download as DOCX, PDF•
0 likes•77 views
it is a managerial economics
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Essay for the Course: Public Economics.
Essay: How Does the Presence of Externalities Explain Government Intervention in Health Care Production and Financing?.
It is showed 12 out of 27 pages.
Más Información en: https://www.linkedin.com/profile/preview?vpa=pub&locale=es_ES
http://www.blogmisproyetosuniversitarios-carlos.blogspot.com.es/Ec386. how does the presence of externalities explain government intervention...

Ec386. how does the presence of externalities explain government intervention...Carlos Alonso Rodríguez ☁
Recommended
Essay for the Course: Public Economics.
Essay: How Does the Presence of Externalities Explain Government Intervention in Health Care Production and Financing?.
It is showed 12 out of 27 pages.
Más Información en: https://www.linkedin.com/profile/preview?vpa=pub&locale=es_ES
http://www.blogmisproyetosuniversitarios-carlos.blogspot.com.es/Ec386. how does the presence of externalities explain government intervention...

Ec386. how does the presence of externalities explain government intervention...Carlos Alonso Rodríguez ☁
More Related Content
Similar to Positive Externalities vs Negative Externalities.docx
Similar to Positive Externalities vs Negative Externalities.docx (20)
Extra Credit1. A natural monopoly” exists whenA .docx

Extra Credit1. A natural monopoly” exists whenA .docx
Negative Externalities and Positive Externalities Notes - A-level & IB economics

Negative Externalities and Positive Externalities Notes - A-level & IB economics
2011: Externalities and Solutions (by Joyce and Vicky)

2011: Externalities and Solutions (by Joyce and Vicky)
The Social Responsibility of Business is to Increase its Pro.docx

The Social Responsibility of Business is to Increase its Pro.docx
Module 3 Lecture (Ch. 15) Jobs & UnemploymentWHAT IS ‘UNEMPLOYM.docx

Module 3 Lecture (Ch. 15) Jobs & UnemploymentWHAT IS ‘UNEMPLOYM.docx
More from Viraja Kanawally
More from Viraja Kanawally (9)
Recently uploaded
Saudi Arabia [ Abortion pills) Jeddah/riaydh/dammam/+966572737505☎️] cytotec tablets uses abortion pills 💊💊
How effective is the abortion pill? 💊💊 +966572737505) "Abortion pills in Jeddah" how to get cytotec tablets in Riyadh " Abortion pills in dammam*💊💊
The abortion pill is very effective. If you’re taking mifepristone and misoprostol, it depends on how far along the pregnancy is, and how many doses of medicine you take:💊💊 +966572737505) how to buy cytotec pills
At 8 weeks pregnant or less, it works about 94-98% of the time. +966572737505[ 💊💊💊
At 8-9 weeks pregnant, it works about 94-96% of the time. +966572737505)
At 9-10 weeks pregnant, it works about 91-93% of the time. +966572737505)💊💊
If you take an extra dose of misoprostol, it works about 99% of the time.
At 10-11 weeks pregnant, it works about 87% of the time. +966572737505)
If you take an extra dose of misoprostol, it works about 98% of the time.
In general, taking both mifepristone and+966572737505 misoprostol works a bit better than taking misoprostol only.
+966572737505
Taking misoprostol alone works to end the+966572737505 pregnancy about 85-95% of the time — depending on how far along the+966572737505 pregnancy is and how you take the medicine.
+966572737505
The abortion pill usually works, but if it doesn’t, you can take more medicine or have an in-clinic abortion.
+966572737505
When can I take the abortion pill?+966572737505
In general, you can have a medication abortion up to 77 days (11 weeks)+966572737505 after the first day of your last period. If it’s been 78 days or more since the first day of your last+966572737505 period, you can have an in-clinic abortion to end your pregnancy.+966572737505
Why do people choose the abortion pill?
Which kind of abortion you choose all depends on your personal+966572737505 preference and situation. With+966572737505 medication+966572737505 abortion, some people like that you don’t need to have a procedure in a doctor’s office. You can have your medication abortion on your own+966572737505 schedule, at home or in another comfortable place that you choose.+966572737505 You get to decide who you want to be with during your abortion, or you can go it alone. Because+966572737505 medication abortion is similar to a miscarriage, many people feel like it’s more “natural” and less invasive. And some+966572737505 people may not have an in-clinic abortion provider close by, so abortion pills are more available to+966572737505 them.
+966572737505
Your doctor, nurse, or health center staff can help you decide which kind of abortion is best for you.
+966572737505
More questions from patients:
Saudi Arabia+966572737505
CYTOTEC Misoprostol Tablets. Misoprostol is a medication that can prevent stomach ulcers if you also take NSAID medications. It reduces the amount of acid in your stomach, which protects your stomach lining. The brand name of this medication is Cytotec®.+966573737505)
Unwanted Kit is a combination of two medicines, whiAbortion pills in Jeddah |• +966572737505 ] GET CYTOTEC![Abortion pills in Jeddah |• +966572737505 ] GET CYTOTEC](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Abortion pills in Jeddah |• +966572737505 ] GET CYTOTEC](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
Abortion pills in Jeddah |• +966572737505 ] GET CYTOTECAbortion pills in Riyadh +966572737505 get cytotec
Recently uploaded (15)
Abortion pills in Jeddah |• +966572737505 ] GET CYTOTEC![Abortion pills in Jeddah |• +966572737505 ] GET CYTOTEC](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Abortion pills in Jeddah |• +966572737505 ] GET CYTOTEC](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
Abortion pills in Jeddah |• +966572737505 ] GET CYTOTEC
Independent Escorts Vikaspuri / 9899900591 High Profile Escort Service in Delhi

Independent Escorts Vikaspuri / 9899900591 High Profile Escort Service in Delhi
Leaders enhance communication by actively listening, providing constructive f...

Leaders enhance communication by actively listening, providing constructive f...
Reviewing and summarization of university ranking system to.pptx

Reviewing and summarization of university ranking system to.pptx
Strategic Management, Vision Mission, Internal Analsysis

Strategic Management, Vision Mission, Internal Analsysis
Beyond the Codes_Repositioning towards sustainable development

Beyond the Codes_Repositioning towards sustainable development
Marketing Management 16th edition by Philip Kotler test bank.docx

Marketing Management 16th edition by Philip Kotler test bank.docx
Dealing with Poor Performance - get the full picture from 3C Performance Mana...

Dealing with Poor Performance - get the full picture from 3C Performance Mana...
BDSM⚡Call Girls in Sector 99 Noida Escorts >༒8448380779 Escort Service

BDSM⚡Call Girls in Sector 99 Noida Escorts >༒8448380779 Escort Service
How Software Developers Destroy Business Value.pptx

How Software Developers Destroy Business Value.pptx
Positive Externalities vs Negative Externalities.docx
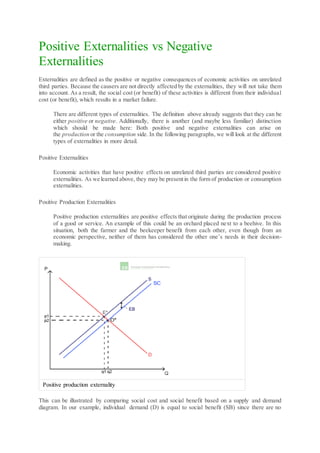
- 1. Positive Externalities vs Negative Externalities Externalities are defined as the positive or negative consequences of economic activities on unrelated third parties. Because the causers are not directly affected by the externalities, they will not take them into account. As a result, the social cost (or benefit) of these activities is different from their individual cost (or benefit), which results in a market failure. There are different types of externalities. The definition above already suggests that they can be either positive or negative. Additionally, there is another (and maybe less familiar) distinction which should be made here: Both positive and negative externalities can arise on the production or the consumption side. In the following paragraphs, we will look at the different types of externalities in more detail. Positive Externalities Economic activities that have positive effects on unrelated third parties are considered positive externalities. As we learned above, they may be presentin the form of production or consumption externalities. Positive Production Externalities Positive production externalities are positive effects that originate during the production process of a good or service. An example of this could be an orchard placed next to a beehive. In this situation, both the farmer and the beekeeper benefit from each other, even though from an economic perspective, neither of them has considered the other one’s needs in their decision- making. Positive production externality This can be illustrated by comparing social cost and social benefit based on a supply and demand diagram. In our example, individual demand (D) is equal to social benefit (SB) since there are no
- 2. externalities on the consumption side. However,social cost (SC) is lower than the individual supply (S) because there is an external benefit (EB) that is not included in the individual supply curve. As a result, the market equilibrium (E*) is different from the optimal market situation (O*) and there is an undersupply of both orchards and beehives. Positive consumption externalities Positive consumption externalities are positive effects on third parties that originate from the consumption of a good or service. A possible example could be your neighbor’s flower garden. She probably cultivates the plants solely for her own pleasure, yet you can still enjoy the beauty of the flowers whenever you walk by. Positive consumption externality Again, this can be illustrated by comparing social cost and social benefit. In this case,however, the individual demand curve (D) lies below the social benefit curve (SB) because the external benefit (the beauty of the flowers to others) is not included in the neighbor’s demand curve. The social cost (SC) on the other hand is equal to the individual supply (S) because there are no externalities on the production side. Like in the first illustration, the market equilibrium (E*) is different from the optimal market situation (O*). As a result, there is an undersupply of flowers. Unlike in the previous example, this time, the optimal price (p2) is higher than the equilibrium price (p1). Generally speaking, the overall benefit of positive externalities to society is higher than the one that is taken into account by the actors in their decision-making. This results in an undersupply of beneficial goods or services for society. To correct these market failures, it is important to know whether the externality arises from the production or the consumption side since this affects the desired optimal market equilibrium. Negative externalities Negative externalities are defined as economic activities that have negative effects on unrelated third parties. They can be divided further into negative production and negative consumption externalities.
- 3. Negative production externalities Negative production externalities are adverse effects that originate during the production process of a good or service.The most common example of this kind of externality is the pollution caused by firms during the production of their goods. Pollution affects the entire population; however as long ascompanies are not held accountable for it, they have no incentive to reduce their economic impact (because that would be more expensive). Negative production externality To illustrate this, we shall compare the social cost and social benefit again. Similar to the positive externality example, individual demand (D) represents social benefit (SB). The social cost curve (SC) in this case,however, is higher than the individual supply curve (S) because of the external cost (EC) that is not included in the firm’s supply decision. As a result, the market equilibrium (E*) is different from the optimal market situation (O*) and there is an oversupply of harmful behavior. In this example, the optimal price of the good (p2) is higher than its actualmarket price (p1). Negative consumption externalities Negative consumption externalities are negative effects that arise during the consumption of a good or service. To give an example, we can revisit your neighbor. If she likes to play loud music in the middle of the night, a negative externality on your part could be sleep deprivation. Once again, she may not take this into account as the consequences do not directly affect her.
- 4. Negative consumption externality In this case,the individual demand curve (D) lies above the social benefit curve (SB) because of the external cost (your sleep deprivation) that is not included in the neighbor’s demand curve. The social cost curve (SC) on the other hand is equal to individual supply (S) because there are no externalities on the production side. Again, the market equilibrium (E*) is different from the optimal market situation (O*), and as a result, there is an oversupply of loud music. In this example, the optimal price of the good (p2) is lower than its actual market price (p1). Without any regulatory influence, neither the firm nor your neighbor will take the negative effects of their activities into account. They are not directly affected by the consequences and will thus produce more than the socially efficient amount. This results in an excess supply of harmful behavior. In a Nutshell Externalities are the positive or negative consequencesof economic activities on unrelated third parties. They can arise on the production or the consumption side. In most cases,externalities result in a market failure that can only be avoided by imposing some sort of regulation to internalize them.