Energy Transformation PPT.pptx
- 2. What is Energy? • Definition: the capacity to do work • Work Moving matter against an opposing force
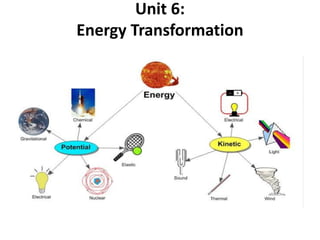
- 3. Potential Energy Energy that results from the location or position of an object.
- 4. Kinetic Energy Energy of moving objects.
- 5. Organisms and machines need energy to grow.
- 6. Chemical potential energy is stored in chemical bonds.
- 7. The activities of living organisms are fueled by breaking chemical bonds in food and harnessing the released energy.
- 8. Which answer is an example of potential energy? a) Heat from a fire b) Sledding down a hill c) A candy bar d) Walking to your car
- 9. Thermodynamics The study of the transformation of energy from one type to another.
- 10. First Law of Thermodynamics Energy can not be created or destroyed. It can only change from one form to another.
- 11. Second Law of Thermodynamics Every conversion of energy includes the transformation of some energy into heat. Heat is almost completely useless to living organisms.
- 12. Energy Flow and Trophic Levels
- 16. Photosynthesis Why is it so important?
- 17. • Makes organic molecules (glucose) out of inorganic materials (carbon dioxide and water.) • It begins all food chains/ food webs. Thus, all life is supported by this process. • It also makes oxygen gas!!! – (which animals breathe!)
- 18. The word photosynthesis comes from the Greek language: ‘photo’ means ‘light’ ‘synthesis’ means ‘putting together’
- 19. Using light energy, the carbon and oxygen from atmospheric carbon dioxide, and the hydrogen from water absorbed from the environment, is combined to make sugar. Oxygen gas is released as a by-product.
- 20. • Food is used by ALL organism. • During cellular respiration (a series of reactions) the energy in the sugar is released in a form that organisms can use.
- 21. Producers • What kind of organisms can produce their own food? • organisms that photosynthesize, make their own food. — They are called PHOTOAUTOTROPHS Photo – light Auto – self Troph – feed
- 22. Consumers • Organisms that cannot make their own food. Called heterotrophs must eat to get their energy. • Hetero – other • Troph – feed • Other than plants, most organisms including all animals and fungi, are heterotrophs.
- 23. • What is the original source of food for almost all heterotrophs?
- 24. Where does the mass of an autotroph come from? • Where does a plant’s mass come from? • • In 1634, agents of the Spanish Inquisition arrested Jan Baptist van Helmont for the crime of studying plants and other phenomena. While under house arrest, he started to consider how plants grew. The prevailing theory at the time was that plants grew by eating soil, and van Helmont devised a clever investigation to test this idea. • • This is an excerpt from van Helmont’s diary: • • “I took an earthenware pot in which I put 200 pounds of earth that had dried in a furnace. I moistened it with rainwater and implanted in it a trunk of a willow tree weighing 5 pounds. I planted it in the garden and covered the earth with an iron lid punched with many holes to allow rainwater in. • • At length, after 5 years, the tree did weigh 169 pounds and 3 ounces. I again dried the earth in the vessel and found it weighed almost 200 pounds (less about 2 ounces). Therefore 164 pounds of wood, bark and roots arose out of water only.” • • What was the change in mass of the tree? ________________ • What was the change in mass of the soil? ________________ • What did van Helmont conclude from his experiment? _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ __________ • Do you agree with his conclusion? ________________ • What other explanations could there be for the results he found? • I agree with van Helmont. Only the water could have made this much difference. • _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ __________ • But I think that plants make their food from sunlight • 1. • • 2. • • Some of the tree may have grown from minerals in the soil. • van Helmont may not have known about the gases in the air. • 4. • 3. • Which student do you agree with? __________________________________________________
- 25. We know that the food that plants make from photosynthesis are called CARBOHYDRATES. • If we look at the word.......CARBOHYDRATE... We can tell quite a lot about it.. • Carbohydrates contain the atoms CARBON, HYDROGEN, and OXYGEN • So, which part of the word means that it contains carbon? • And which part of the word means that it contains hydrogen? • Now, can you suggest what the letters ATE mean when placed on the end of a chemical name?
- 26. • The diagram below is a chemical picture of one carbohydrate. Count how many carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms this chemical has... • Carbon _____ • Hydrogen ____ • Oxygen ______
- 27. • Glucose is a carbohydrate – it is a simple sugar and you are probably very familiar with its taste if you have eaten or drunk any of the products here.
- 28. How do plants make carbohydrates? • Now.. if you were a plant and you had to make this carbohydrate what atoms are you going to need and where could you get them from? • If we had some carbon dioxide, could we make carbohydrates from it?
- 29. How do plants make carbohydrates? • What element would still be missing? • If we had some water as well as the carbon dioxide, what extra atom could this supply?
- 30. • OK – suppose we have the carbon dioxide and some water – we would need to split the water up to release the hydrogen from it. • The process of splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen is very difficult. • However - with the help of sunlight energy plants can split the water and use the hydrogen to put with the carbon and oxygen from our carbon dioxide.
- 31. • When light energy is used to split water, there is a product left over that is not needed. What is this product? • You may have come across this idea before – it seems that photosynthesis results in the production of carbohydrates and also releases oxygen into the air – which is a good thing for us as we will see later.
- 32. • We know that plants use sunlight energy to split water (H2O) into hydrogen and oxygen. • The hydrogen is added to the carbon dioxide (CO2) to make CARBOHYDRATES such as glucose. • The oxygen produced from this splitting of water is released into our atmosphere. • We summarize this using a chemical equation: CO2 + H2O + light C6H12O6 + O2 energy
- 33. What does synthesis mean? A. Light B. Sugar C. Make D. Feed
- 34. In plants, light is used to: A. Make energy B. Make sugar C. Make carbon dioxide D. Make water
- 35. The carbon used by the plants to make the sugar is from: A.Food B.The air C.Water D.Animals
- 36. The chemical formula for glucose is C6H12O6. Plants are made primarily of glucose in the form of starch and cellulose. Therefore, one could say that most of the plant’s mass comes from: A. The air B. Water C. The ground D.The sun
- 37. A. Animals B. Plants In which of the following groups are there no photoautotrophs?
- 38. Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts
- 39. • The green color of chloroplasts comes from the green pigment they contain, called chlorophyll
- 40. • When chlorophyll is hit by photons of certain wavelengths, the light energy bumps an electron in the chlorophyll molecule to a higher energy level, an excited state.
- 41. • Upon absorbing the photon, the electron briefly gains energy, and the potential energy in the chlorophyll molecule increases.
- 42. Let’s Review 1. What type of organisms can photosynthesize? 2. In which organelle of the cell does photosynthesis take place? 3. What do the cells need in order to carryout photosynthesis? 4. Where do they get each of these materials from?
- 43. Suppose a large meteor hit the earth. How could smoke and soot in the atmosphere wipe out life far beyond the area of direct impact?
- 44. • Scientists believe that if a large meteor hit the earth smoke, soot, and dust in the atmosphere could block sunlight to such an extent that plants in the region, or even possibly all of the plants on earth, could not conduct photosynthesis at high enough levels to survive.
- 45. • As dire as it sounds, all life on earth is completely dependent on the continued excitation of electrons by sunlight.
- 46. How do cells directly fuel their chemical reactions? • None of the light energy from the sun can be used directly to fuel cellular work. • First it must be captured in the bonds of a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
- 48. Adenosine Triphosphate Pop off the third phosphate group * ATP ADP + Phosphate group + energy release Release a little burst of energy! Use this energy to drive chemical reactions necessary for cellular functioning. Building muscle tissue Repairing a wound Growing roots
- 49. Take-home message Cells temporarily store energy in the bonds of ATP molecules. This potential energy can be converted to kinetic energy and used to fuel life-sustaining chemical reactions. At other times, inputs of kinetic energy can be converted to the potential energy of the energy- rich but unstable bonds in the ATP molecule.
- 50. Two Stages of Photosynthesis 1. Light-dependent reactions (“PHOTO” reactions) capture the energy of light and use it to make high-energy molecules 2. Light-independent reactions (Calvin- Benson Cycle, and formerly known as the Dark Reactions, “SYNTHESIS” reactions) use the high- energy molecules to capture carbon dioxide (CO2) and make glucose.
- 52. Light Reactions 1. Light energy is captured by pigments like chlorophyll. 2. The energy is transferred to electrons and hydrogen ions produced by the splitting of water. 3. The energy of these electrons and ions is transferred into chemicals – NADPH and ATP. 4. Oxygen is a waste product.
- 53. Which of the following is a by-product of photosynthesis? A.Sugar B.Oxygen C.Carbon dioxide D.Water
- 54. Light is necessary in photosynthesis to? A.Split water and release electrons B.Produce water C.Make food D.Get rid of carbon dioxide
- 55. What are the three necessary materials for photosynthesis? A. Sugar, oxygen and light. B. Carbon dioxide, water and light. C. Plants, carbon dioxide and light. D. Carbon dioxide, oxygen and sugar.
- 56. • Products from the “Photo” Portion ATP and NADPH • Time for the “synthesis” part!
- 57. Calvin-Benson Cycle 1. The high energy chemicals (NADPH and ATP) made in the light reaction are used to synthesize more complex chemicals. 2. Carbon dioxide is gathered from the air and used to build molecules of glucose. 3. This glucose can then be used as food by the photosynthesizer.
- 59. The materials required for the Calvin Benson cycle to function are A. Water and electrons B. Sugar C. Carbon dioxide, and chemicals from the light reaction. D. Oxygen from the light reaction and carbon dioxide
- 60. The end product of the Calvin Benson cycle is: A.Carbon dioxide B.Electrons C.Oxygen D.Sugar
- 61. CELLULAR RESPIRATION • Animals obtain their energy from the food they eat, but plants can make their own food by photosynthesis. • In both cases, however, energy must first be converted into a form that can easily be used by cells. • This process is called cellular respiration.
- 62. Cellular Respiration • Requires (1) fuel and (2) oxygen. Potential energy stored in chemical bonds of sugar, protein, and fat molecules. • Breaks bonds to release the high-energy electrons captured in ATP.
- 63. A Human Example Eat food Digest it Absorb nutrient molecules into bloodstream Deliver nutrient molecules to the cells At this point, our cells can begin to extract some of the energy stored in the bonds of the molecules from the food we eat.
- 64. Where does cellular respiration occur? • Recall that the mitochondria is considered to be the “powerhouse” of the cell because it produces the majority of a cell’s ATP.
- 65. WHAT IS CELLULAR RESPIRATION? • Cellular respiration is the process of releasing energy through the oxidation of glucose molecules. Chemical equation for cellular respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O
- 66. HOW IS ENERGY USED? • The chemical energy produced by respiration, ATP, is used by cells to undertake work. Where might ATP be used? movement – enabling muscles to contract thermoregulation in mammals and birds biosynthesis – building new molecules, cells and tissues active transport – moving molecules against a concentration gradient.
- 67. Energy Is Created During Internal Respiration True False
- 68. • Overall, cellular respiration is a process that is aerobic. Aerobic means that it requires the presence of oxygen. • Some steps within the process of cellular respiration do not require the presence of oxygen and are therefore anaerobic.
- 70. Lactic acid • The body builds up an oxygen debt – this is repaid by continuing to breathe heavily for a period after exercise ceases. • As more oxygen becomes available, it reacts with the lactic acid to form harmless substances. • The rate at which lactic acid is removed can be increased by performing a cool-down at the end of a session.
- 71. Cells can run on protein and fat as well as on glucose.
- 72. In what organelle does cellular respiration take place? A. Nucleus B. Lysosome C. Ribosome D. Mitochondrion