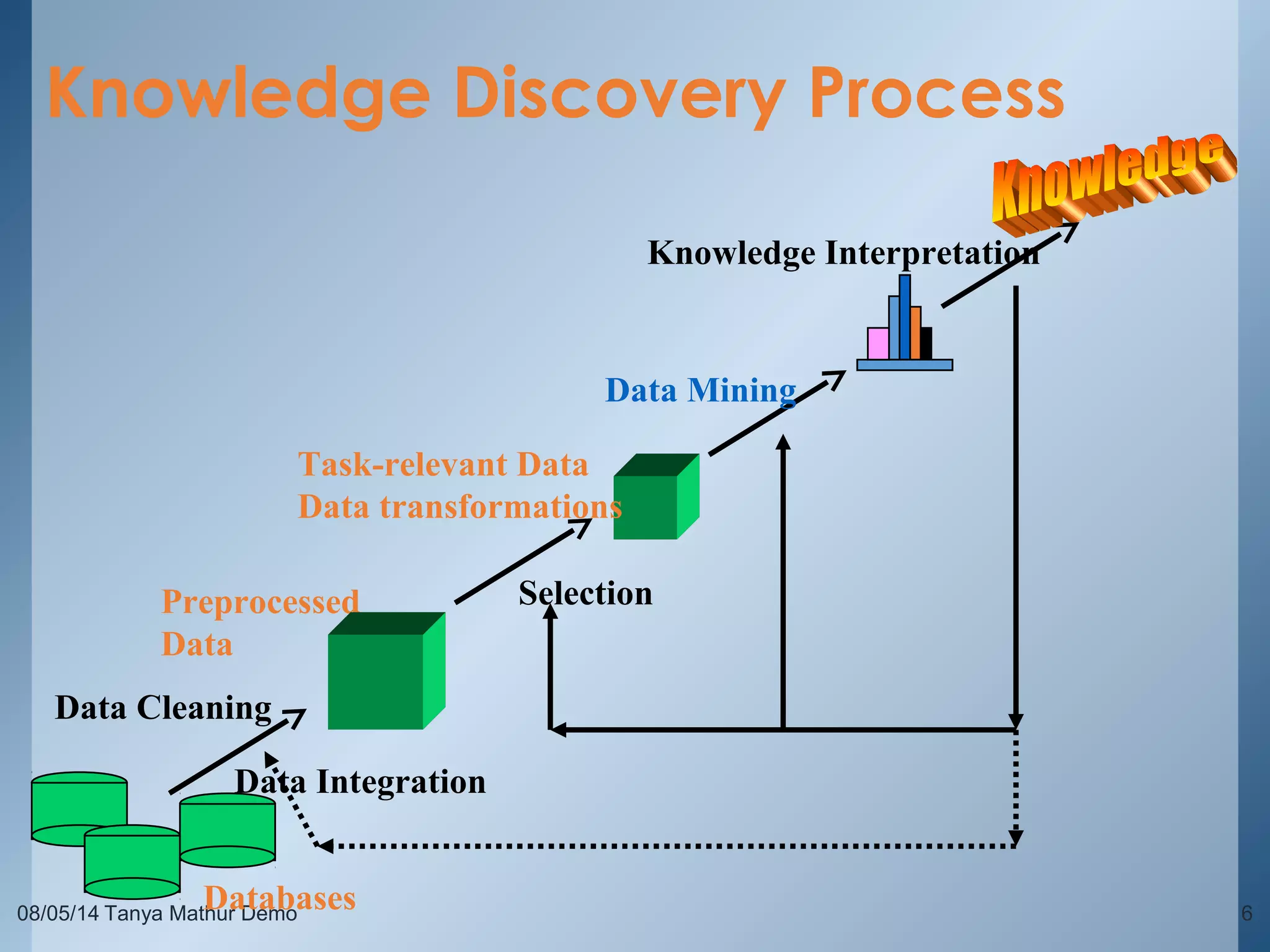
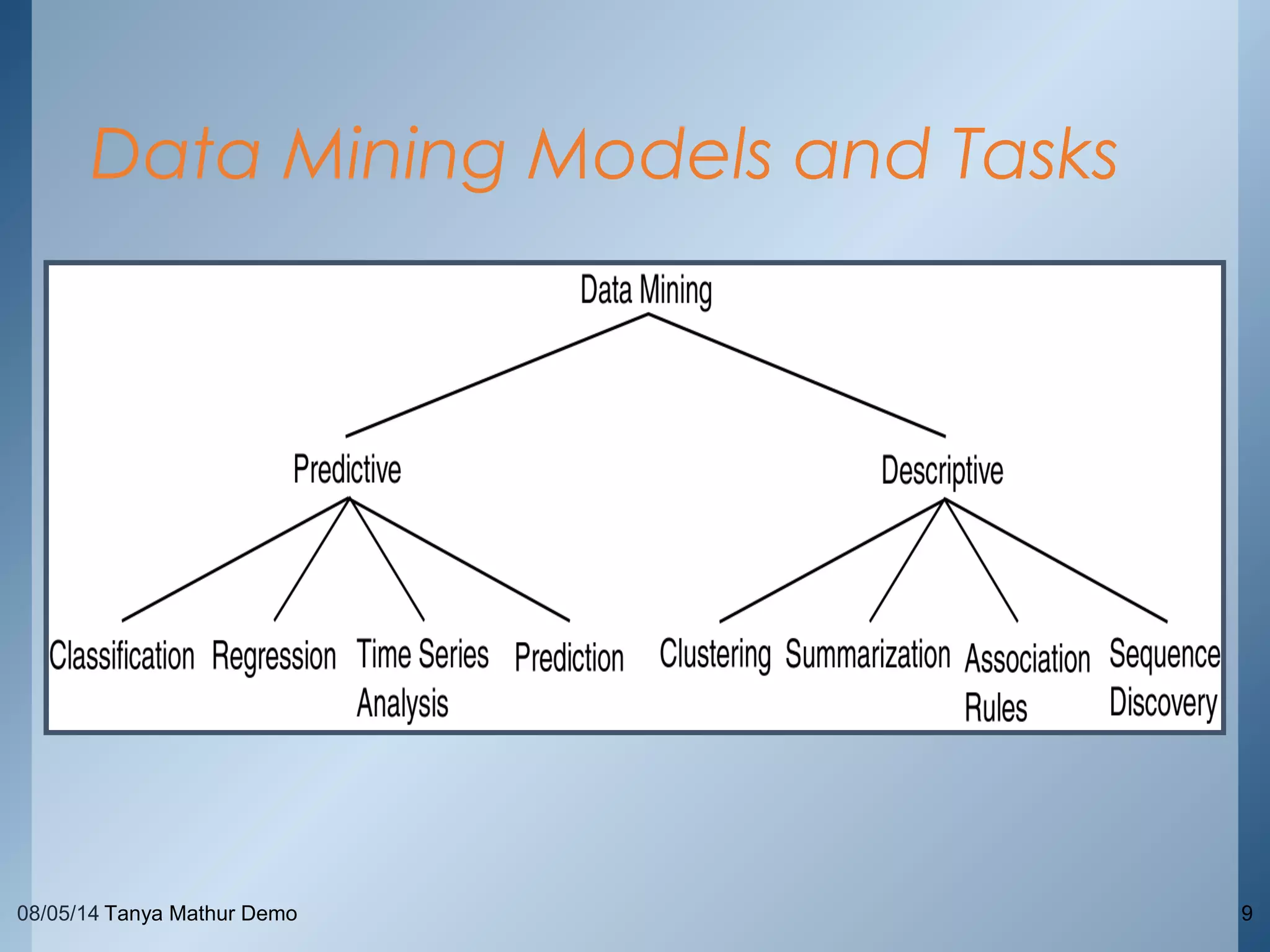
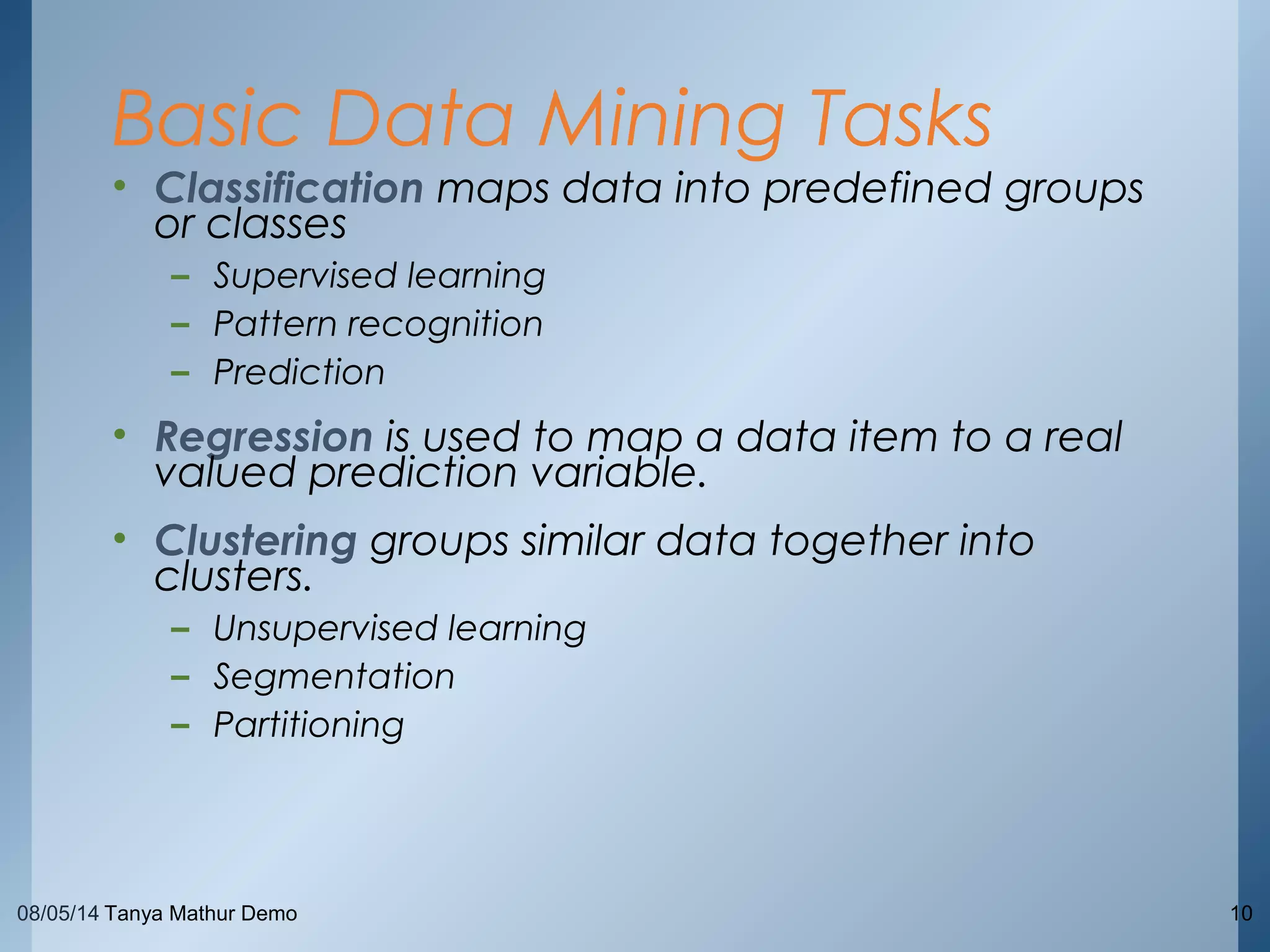
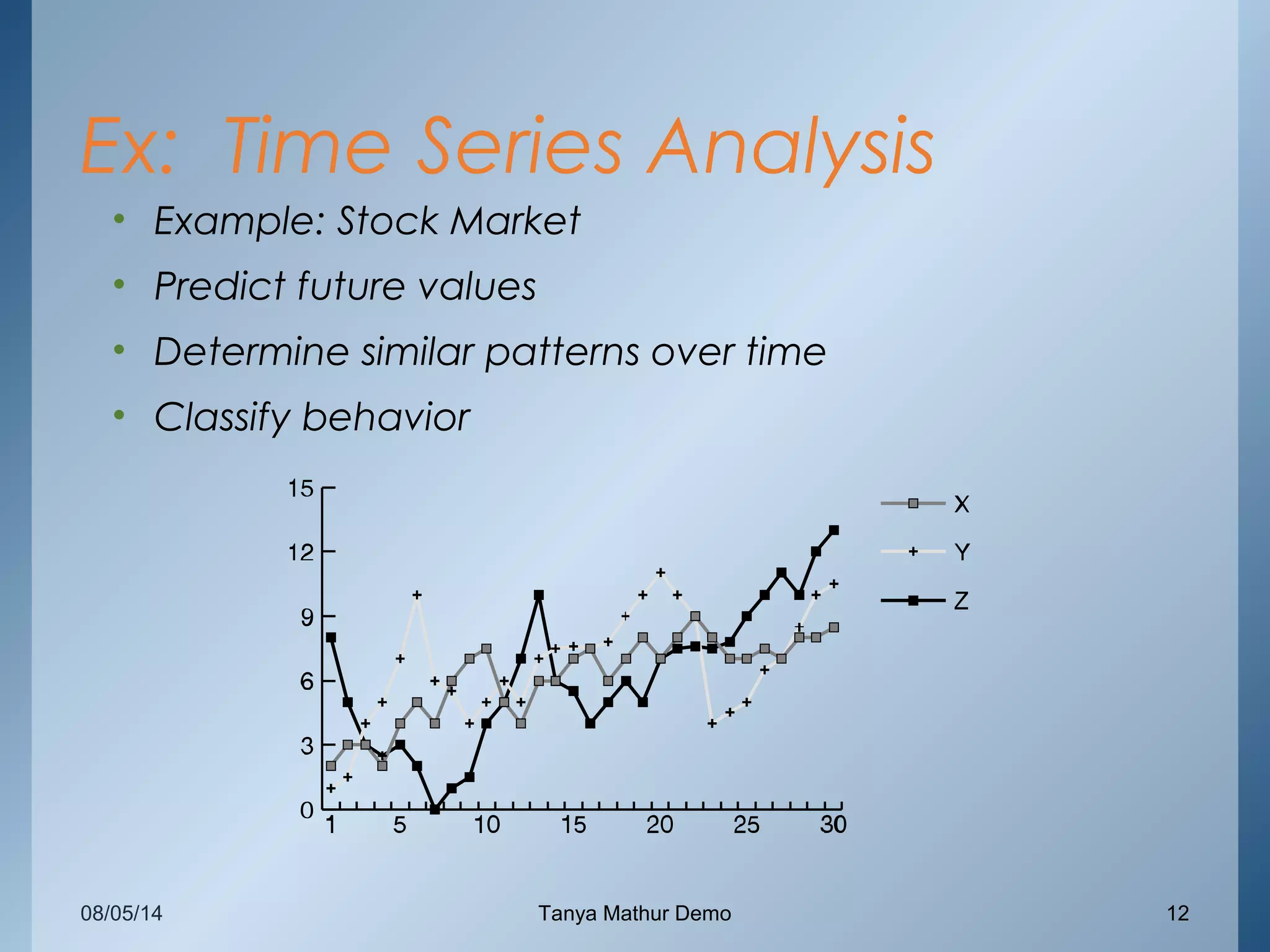
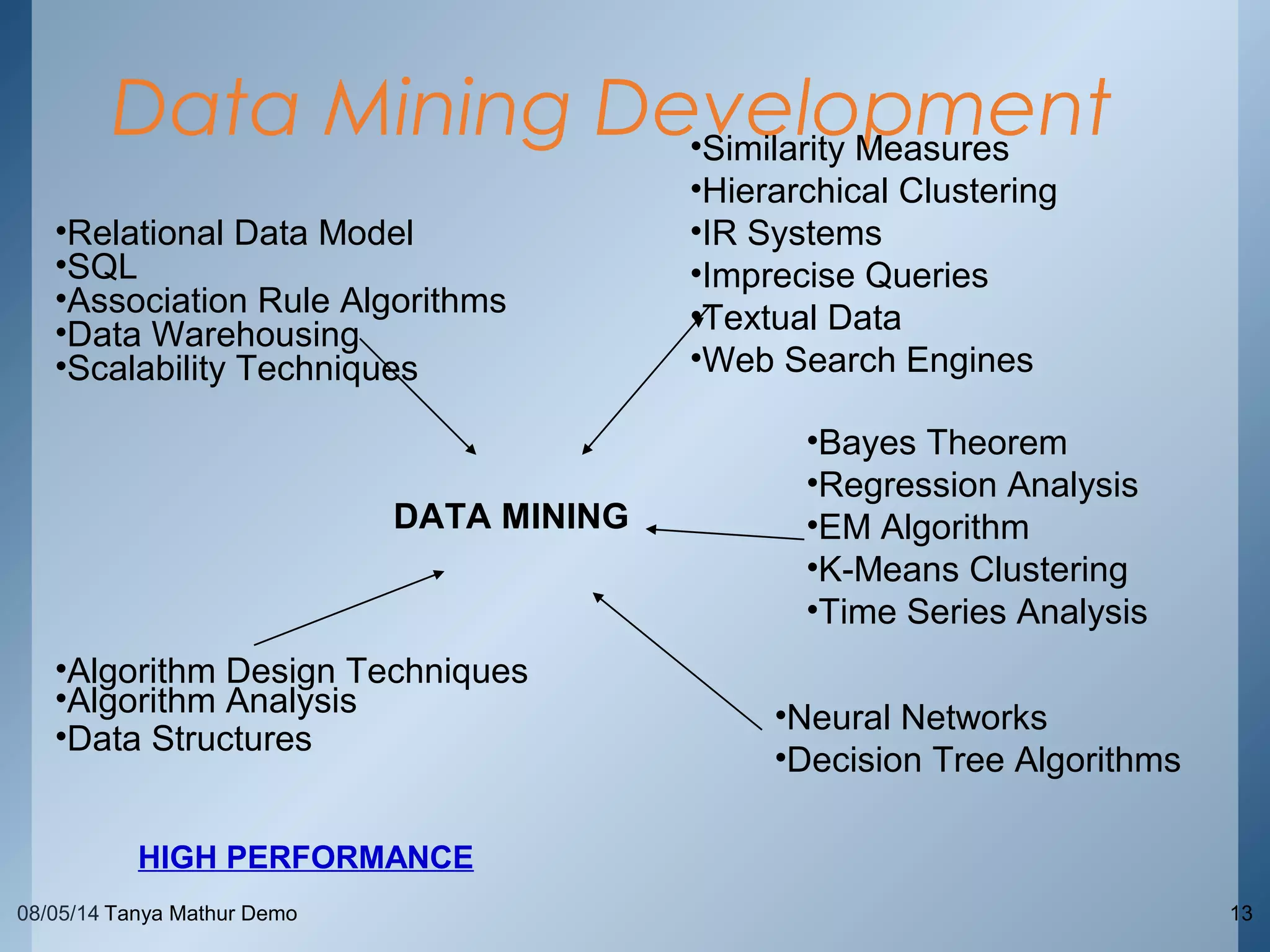
The document provides an overview of data mining through a series of slides presented by Tanya Mathur. It defines key concepts like data mining, knowledge discovery in databases, and basic data mining tasks. It also outlines common issues in data mining like handling large and noisy data sets. The goal is to introduce the topic of data mining and provide a high-level understanding of the process and techniques involved.