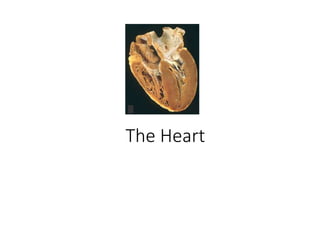
The Heart - A Medical Overview
- 1. The Heart
- 2. Normal Heart • Weight • 250 – 300 g in Females • 300 – 350 g in Males • Thickness • R ventricle – 0.3 -0.5 cm • L ventricle – 1.3 – 1.5 cm • Increase in weight or ventricular thickness HYPERTROPHY • Increase in chamber size DILATATION
- 3. MYOCYTES 1. Cell Membrane 2. Sarcoplasmic Reticulum 3. Contractile Elements 4. Mitochondria 5. Nucleus 5 major components: Normal Heart
- 4. Other Histological Features • Specific atrial granules • Sites of storage of Atrial Natriuretic Peptide • Intercalated discs • Specialized gap junctions • Specialized excitatory and conducting myocytes • SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, left and right bundle branches Normal Heart
- 5. Blood Supply • Epicardial coronary arteries • Left anterior descending • Left circumflex arteries • Right coronary arteries • Intramural arteries • Blockage of these arteries can cause myocardial ischemia Normal Heart
- 6. Valves •2 semilunar valves • Aortic and Pulmonary • Node of Arantius •2 atrioventricular valves • Mitral and Tricuspid • Chordae Tendinae MICROSTRUCTURE: Normal Heart
- 7. Cardiac Dysfunction 5 principal mechanisms 1. Failure of the pump 2. Obstruction to flow 3. Regurgitant flow 4. Disorder of cardiac conduction 5. Disruption of continuity of circulation
- 8. HEART FAILURE • Inability of the heart to pump blood at a rate commensurate with the requirements of metabolizing tissues • Mechanisms by which cardiovascular system maintains pressure and perfusion at the presence of excessive hemodynamic burden • Frank- Starling mechanism • Myocardial structure changes • Activation of neurohumoral systems
- 9. CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY • Pressure overload • Cross sectional area of myocytes in expanded but cell length is not increased • Concentric hypertrophy • Volume overload • Both cell length and width is increased
- 10. CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY • Increase in myocyte size causes • Decreased capillary density • Increased intercapillary distance • Deposition of fibrous tissue FORMING ABNORMAL TISSUE • Hypertrophy is both adaptive and deleterious
- 11. CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE • Features • Increase in weight • Chamber dilatation • Thin walls • Microscopic changes of hypertrophy
- 12. LEFT SIDED HEART FAILURE • Caused by: 1. Ischemic heart diesease 2. Hypertension 3. Aortic and Mitral Valvular Diseases 4. Non-ischemic myocardial disease
- 13. LEFT SIDED HEART FAILURE • Systemic Effects • Lungs – pulmonary edema • Kidney – prerenal azotemia • Brain – hypoxic encephalopathy
- 14. RIGHT SIDED HEART FAILURE • Causes • Left sided heart failure • Pulmonary hypertension (cor pulmonale)
- 15. RIGHT SIDED HEART FAILURE • Effects • Liver and portal system– congestive hepatomegaly, passive congestion, centrilobular necrosis, congestive splenomegaly, ascites • Kidney – peripheral edema, azotemia • Brain – hypoxia • Pleural and pericardial effusion • Subcutaneous tissue – edema (hallmark)
- 16. FIVE MAJOR FORMS OF HEART DISEASE 1. Congenital heart disease 2. Ischemic heart disease 3. Hypertensice heart disease 4. Valvular heart disease 5. Nonischemic (primary) myocardial disease
- 17. Congenital Heart Disease • Abnormalities of the heart present from birth • Insult occurs at 3-8 weeks AOG, where cardiovascular structures would develop • 3 MAJOR CATEGORIES • Malformations causing a Left to Right shunt • Malformations causing a Right to Left shunt • Malformations causing an obstruction
- 18. Left to Right Shunts 1. Atrial Septal Defect 2. Ventricular Septal Defect 3. Patent Ductus Arteriosus 4. Atrioventricular Septal Defect Congenital Heart Disease
- 19. 1. Atrial Septal Defect • Abnormal opening between the left and right atria • Types: • Secundum – deficient or fenestrated oval fossa • Primun – at adjacent AV valves • Venosus – near entrance of SVC Congenital Heart Disease
- 20. 2. Ventricular Septal Defect • Incomplete closure of ventricular septum • Types: • Membranous – region of membranous septum • Infundibular – below pulmonary valve • Muscular – within muscular septum, “swiss chesse” Congenital Heart Disease
- 21. 3. Patent Ductus Arteriosus • 90% isolates • Harsh – machinery like murmur • Can cause obstructive pulmonary vascular disease upon reversal of flow • With other defects, can be life saving Congenital Heart Disease
- 22. 4. Atrioventricular Septal Defect • Types: • Partial- primum ASD with cleft • Complete – AV septal defect • Hole in the heart Congenital Heart Disease
- 23. Right to Left Shunts 1. Tetralogy of Fallot 2. Transposition of Great Arteries 3. Persistent Truncus Arteriosus 4. Tricuspid Atresia 5. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection Congenital Heart Disease
- 24. 1. Tetralogy of Fallot • Most common cyanotic congenital heart disease • 4 features 1. Ventricular Septal Defect 2. Right ventricular output obstruction 3. Aorta overriding VSD 4. Right ventricular hypertrophy – Boot-shaped heart Congenital Heart Disease
- 25. 2. Transposition of the Great Arteries •Ventriculoarterial discordance • Right ventricle Aorta • Left ventricle Pulmonary artery •Separation of systemic and pulmonic circulation •Incompatible with life unless a shunt exists • VSD – stable shunt • Patent foramen ovale, PDA – unstable shunt Congenital Heart Disease
- 26. 3. Truncus Arteriosus • Developmental failure of separation of the embryonic truncus arteriosus into the aorta and the pulmonary • Single artery receives blood from both ventricles • Increased pulmonary blood blow irreversible pulmonary hypertension Congenital Heart Disease
- 27. 4. Tricuspid Atresia • Occlusion of tricuspid valve orifice • Caused by the unequal division of AV canal • Accompanied by hypoplasia of right ventricle • Circulation is maintained by ASD or patent foramen ovale Congenital Heart Disease
- 28. 5. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection • No pulmonary vein joins the left atrium • Primitive systemic venous channels from lung remain patent • Foramen ovale or ASD allow blood to enter left atrium • Volume and pressure hypertrophy of right atrium and ventricle Congenital Heart Disease
- 29. Obstructive Congenital Anomalies 1. Coarctation of the aorta 2. Pulmonary stenosis and atresia 3. Aortic stenosis and atresia Congenital Heart Disease
- 30. 1. Coarctation of the Aorta • Infantile – tubular hypoplasia • Adult – discrete infolding • Coarctation with PDA – poor prognosis without PDA – asymptomatic except for hypertension in upper extremities Congenital Heart Disease
- 31. 2. Pulmonary stenosis and atresia • Obstruction at the pulmonary valve, can be isolated, or part of a complex anomaly • Usually with right ventricular hypertrophy and post stenotic dilatation • When valve is totally atretic, there is a hypoplastic right ventricle • Mild stenosis may be asymptomatic Congenital Heart Disease
- 32. 3. Aortic stenosis and atresia • 3 major types 1. Valvular- cusps are hypoplastic, dysplastic, or abnormal in number 2. Subaortic stenosis • Thickened ring ( discrete type) • Collar (tunnel type) 3. Supravalvular Congenital Heart Disease
- 33. Ischemic Heart Disease • Insufficiency of oxygen with reduced availability of nutrient substrates and inadequate removal of metabolites • The clinical manifestations of IHD can be divided into 4 syndromes 1. Myocardial infarction 2. Angina pectoris 3. Chronic heart disease and heart failure 4. Sudden cardiac failure
- 34. Pathogenesis • Acute plaque change • Inflammation • Coronary thrombosis • Vasoconstriction Ischemic Heart Disease
- 35. Angina Pectoris • Symptom complex of IHD characterized by paroxysmal and usually recurrent attacks of discomfort • Caused by transient myocardial ischemia that falls short of inducing the cellular necrosis that defines infarction Ischemic Heart Disease
- 36. Myocardial Infarction • Death of cardiac muscle resulting from ischemia • Types • Transmural – full thickness • Subendocardial – 1/3 to ½ of ventricular wall Ischemic Heart Disease
- 37. Pathogenesis Coronary arterial occlusion 1. Sudden change in the morphology of an atheromatous plaque 2. Platelets undergo adhesion, aggregation, activation, and release of potent aggregators 3. Vasospasm 4. Activation of extrinsic pathway of coaglation 5. Thromus evolution to completely occlude the lumen of the coronary vessel Ischemic Heart Disease
- 38. Myocardial Infarction Ischemic Heart Disease
- 39. Reperfusion• Salvaging of myocardium Ischemic Heart Disease
- 40. Myocardial Infarction Ischemic Heart Disease
- 41. Clinical Consequences of Myocardial Infarction 1. Contractile dysfunction 2. Arrythmias 3. Myocardial rupture 4. Pericarditis 5. Right ventricular infarction 6. Infarct extension 7. Infarct expansion 8. Mural thrombus 9. Ventricular aneurysm 10. Papillary muscle dysfunction 11. Progressive late heart failure Ischemic Heart Disease
- 42. Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease •Cardiac findings in patients, who develop progressive heart failure as a consequence of ischemic myocardial damage •Gross • Cardiomegaly • Severe stenosisng atherosclerosis • Discrete gray-white scars •Microscopically • Myocardial hypertrophy • Diffuse subendocardial vacuolization • Scars of previously healed infarcts Ischemic Heart Disease
- 43. Sudden Cardiac Death • Unexpected death from cardiac causes early after symptom onset or without onset of symptoms • Gross • Marched coronary atherosclerosis and critical stenosis • Acute plaque disruption • Healed myocardial infarct • Subendocardial myocyte vacuolization Ischemic Heart Disease
- 44. Hypertensive Heart Disease • Response of the heart to increased demands induced by systemic hypertension (left-sided) or pulmonary hypertension (right-sided)
- 45. Systemic Hypertensive Heart Disease • Minimal criteria 1. Left ventricular hypertrophy 2. History or pathologic evidence of hypertension • Gross - LV wall thickness exceeds 2.0 cm - Heart weight exceeds 500 gms • Microscopic - Increase in transverse diameter of myocytes - Variation in cell size - Interstitial fibrosis Hypertensive Heart Disease
- 46. Pulmonary Hypertensive Heart Disease • Cor pulmonale • Acute • Dilatation without hypertrophy • Caused by: massive pulmonary embolus • Chronic • (+) hypertrophy • Caused by: emphysema, primary pulmonary hypertension Hypertensive Heart Disease
- 47. Valvular Heart Disease • Stenosis – failure to open completely • Insufficiency – failure to close completely • Pure- only stenosis or insufficiency • Mixed – both are present • Isolated – 1 valve • Combined – more than 1 valve • Functional regurgitation- incompetency of valve due to dilatation of ventricle or artery
- 48. Calcific Aortic Stenosis • Most common of all valvular abnormalities • Acquired aortic stenosis is the consequence of calcification due to ‘wear and tear’ • Incidence increases with the rising average age of the population • Hallmark – heaped up calcified masses within the aortic cusps that ultimately protrude through the outflow surfaces into the sinuses of Valsalva, preventing the opening of the cusps Valvular Heart Disease
- 49. Calcific Stenosis of Congenitally Bicuspid Aortic Valve • Bicuspid aortic valves are neither stenotic nor symptomatic at birth or throughout early life • However, they are predisposed to progressive degenerative calcification, similar to that of calcific aortic stenosis. Valvular Heart Disease
- 50. Mitral Annular Calcification • Calcific deposits can develop in the fibrous ring of the mitral valve • Seen as irregular, stony hard and occasionally ulcerated nodules that lie behind the leaflets Valvular Heart Disease
- 51. Myxomatous Degeneration of the Mitral Valve (MVP) • One or more mitral leaflets are “floppy” and prolapse/balloon back to left atrium during systole Valvular Heart Disease
- 52. Myxomatous Degeneration of the Mitral Valve (MVP) • Morphology • Gross – the affected leaflets are often enlarged, redundant, thick and rubbery. Tendinous cords are elongated, thinned, and occasionally ruptured • Histological- there is attenuation of the fibrosa layer of the valve, thickening of the spongiosa layer with deposition of mucoid/ myxomatous material • 4 serious complications 1. Infective Endocarditis 2. Mitral Insufficiency 3. Stroke or other systemic infarct 4. Arrythmias Valvular Heart Disease
- 53. Rheumatic Fever and RHD • Acute Rheumatic Fever • Aschoff bodies • Anitschow – pathognomic for RF, ‘caterpillar cells’ • Pancarditis • Mac Callun plaques Valvular Heart Disease
- 54. Rheumatic Fever and RHD • Chronic RHD Organization of acute inflammation to subsequent fibrosis • Cardinal Anatomic Changes 1. leaflet thickening 2. commisural fusion and shortening 3. thickening and fusion of the tendinous cords Aschoff bodies are replaced by a fibrous scar Valvular Heart Disease
- 55. Infective Endocarditis •Colonization or invasion of the heart valves or mural endocardium by a microbe, leading to the formation of bulky, friable vegetations •Acute endocarditis – decribes a destructive infection, frequently of a previously normal heart valve with a highly virulent organism which leads to death within days or weeks •Subacute endocarditis – with organisms or low virulence in a previously abnormal heart. The disease may aappear insidiously or pursue a protracted course of weeks to months Valvular Heart Disease
- 56. Non-infected Vegetation NBTE –Nonbacterial Thrombotic Endocarditis- characterized by the deposition of fibrin, platelets, and other blood components on the leaflets of cardiac valves. Does not contain microorganisms Libman-Sacks Disease – mitral and tricuspid valvulitis with small sterile vegetations seen in SLE Valvular Heart Disease
- 57. Carcinoid Heart Disease • The cardiac manifestation if the systemic syndrome caused by carcinoid tumors • Involves the endocardium and valves of the right heart • Morphology – fibrous intimal thickenings in the inside surfaces of the cardiac chambers and valvular leaflets
- 58. Cardiomyopaties • Heart disease resulting from a primary abnormality in the myocardium • Types 1. Dilated Cardiomyopathy 2. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy 3. Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
- 59. 1. Dilated Cardiomyopathy •Characterized by progressive cardiac dilatation and contractile (systolic) dysunction, usually with concomitant hypertrophy •The heart is usually heavy, often weighing two to three times normal, large and flabby, with dilatation of all chambers •Mural thrombi are common •Histologically, muscle cells are hypertrophied with enlarged nuclei, but many are attenuated, stretched, and irregular. Endocardial fibrosis of variable degree is present Cardiomyopathies
- 60. 2. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy • Characterized by myocardial hypertrophy, abnormal diastolic filling and in 1/3 of cases, intermittent ventricular outflow obstruction. • Massive myocardial hypertrophy without ventricular dilatation. • On cross section, the ventricular cavity loses it’s round-to-ovoid shape, and is compressed into a ‘banana-like’ configuration Cardiomyopathies
- 61. 3. Restrictive Cardiomyopathy • Characterized by a primary decrease in ventricular compliance, resulting in impaired ventricular filling during diastole • Ventricles are approximately normal size or slightly enlarged, the cavities are not dilated, and the myocardium is firm. Cardiomyopathies
- 62. Myocarditis • Inflammatory process of the myocardium which result in injury to the cardiac myocytes • Types of myocarditis 1. Lymphocytic myocarditis 2. Hypersensitivity myocarditis 3. Giant cell myocarditis 4. Myocarditis of Chagas disease
- 63. Pericardial Disease •Pleural effusion and hemopericardium Normal 30-50 ml, thin, clear, straw-like fluid •Hemopericardium – blood •Pericardial effusion – fluid of variable composition •Purulent pericarditis – pus •Slow accumulation – enlargement of cardiac shadow •Rapid accumulation – cardiac tamponade
- 64. Pericarditis • Acute 1. Serous – caused by non infectious inflammation - surface with scan number of PMN’s, lymphocutes and monocytes 2. Fibrinous and serofibrinous – most frequent - serous fluid and fibrinous exudates fibrinous – surface is dry, with fine granular roughening serofibrinous – more and thicker fluid which is yellow and cloudy * pericardial friction rub
- 65. Pericarditis c. Purulent or suppurative pericarditis - direct extension - seeding - lymphatic - direct introduction Morphology exudate – thin to creamy pus surface – redenned, granular and coated with the exudate Organization produces CONSTRICTIVE PERICARDITIS
- 66. Pericarditis d. Hemorrhagic Most common cause – malignant neoplasm e. Caseous pericarditis Causes – Tuberculosis, Fungal Infection
- 67. Chronic / Healed Pericarditis A. Adhesive mediastinopericarditis Pericardial sac is obliterated and adherence to external aspect of parietal layer to surrounding structure B. Constrictive pericarditis Pericardial space is obliterated Plaster mold
- 68. Tumors of the Heart Most of the primary tumors are rate, metastasis are more common Primary cardiac tumors: 1. Myxoma 2. Lipoma 3. Papillary fibroelastoma 4. Rhabdomyoma
- 69. Myxoma • Most common primary tumor • Gross • Commonly single • Mostly on fossa ovalis of atria • Size – 4 cm to 10 cm • May be sessile or pedunculated • Microscopic • Stellate/globular myxoma • Etc. Tumors
- 70. Lipoma • Excessive fat accumulations • May occur in the subendocardium, subepicardium or within the myocardium Tumors
- 71. Papillary fibroelastoma • Located on valves • Distinctive cluster of hair like projections up to 1 cm in diameter • Histological features: • Covered by endothelium • Myxoid connective tissue with MPS matrix • Elastic fibers Tumors
- 72. Rhabdomyoma • Most frequent primary tumor of infants and children • Gross • Small , gray- white • Microscopic • Mixed population of cells • Large, rounded or polygonal cells containing numerous glycogen laden vacuoles • SPIDER CELL Tumors
- 73. Mind Bender Challenge for Students I have a challenge for you! Try to solve a Mind Bender. Will you accept the Mind Bender Challenge? Get it here: Mind Bender Mind Bender – Payhip Good Luck!
- 74. THANK YOU!!!
Editor's Notes
- left-to-right shunts increase pulmonary blood flow and are not associated (at least initially) with cyanosis. However, they expose the low-pressure, low resistance pulmonary circulation to increased pressures and volumes; these conditions lead to adaptive changes that increase lung vascular resistance to protect the pulmonary bed, resulting in right ventricular hypertrophy and—eventually—failure. With time, increased pulmonary resistance also can cause shunt reversal (right to left) and late-onset cyanosis.
- With right-to-left shunt, a dusky blueness of the skin (cyanosis) results because the pulmonary circulation is bypassed and poorly oxygenated blood enters the systemic circulation
- (1) VSD; (2) right ventricular outflow tract obstruction (subpulmonic stenosis); (3) overriding of the VSD by the aorta; and (4) right ventricular hypertrophy
- Microscopic features of myocardial infarction and its repair. A, One-day-old infarct showing coagulative necrosis and wavy fibers, compared with adjacent normal fibers (at right). Necrotic cells are separated by edema fluid. B, Dense neutrophilic infiltrate in the area of a 2- to 3-day-old infarct. C, Nearly complete removal of necrotic myocytes by phagocytic macrophages (7 to 10 days). D, Granulation tissue characterized by loose connective tissue and abundant capillaries. E, Healed myocardial infarct consisting of a dense collagenous scar. A few residual cardiac muscle cells are present. D and E are Masson’s trichrome stain, which stains collagen blue.
- Can you solve a Mind Bender? Only a high IQ individual can solve this.