Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
More Related Content
Similar to abstract.visualizingperformance.flowchart
Similar to abstract.visualizingperformance.flowchart (20)
An Empirical Study Of Requirements Model Understanding

An Empirical Study Of Requirements Model Understanding
An Empirical Study Of Requirements Model Understanding Use Case Vs. Tropos M...

An Empirical Study Of Requirements Model Understanding Use Case Vs. Tropos M...
2005-Model-guided information discovery for intelligence analysis-p269-alonso

2005-Model-guided information discovery for intelligence analysis-p269-alonso
Adaptive guidance model based similarity for software process development pro...

Adaptive guidance model based similarity for software process development pro...
Exploration exploitation trade off in mobile context-aware recommender systems

Exploration exploitation trade off in mobile context-aware recommender systems
IMPLEMENTATION OF DYNAMIC COUPLING MEASUREMENT OF DISTRIBUTED OBJECT ORIENTED...

IMPLEMENTATION OF DYNAMIC COUPLING MEASUREMENT OF DISTRIBUTED OBJECT ORIENTED...
IMPLEMENTATION OF DYNAMIC COUPLING MEASUREMENT OF DISTRIBUTED OBJECT ORIENTED...

IMPLEMENTATION OF DYNAMIC COUPLING MEASUREMENT OF DISTRIBUTED OBJECT ORIENTED...
Methods for analysis and design of an information system.pdf

Methods for analysis and design of an information system.pdf
A SIMILARITY MEASURE FOR CATEGORIZING THE DEVELOPERS PROFILE IN A SOFTWARE PR...

A SIMILARITY MEASURE FOR CATEGORIZING THE DEVELOPERS PROFILE IN A SOFTWARE PR...
A Comparison of Traditional Simulation and MSAL (6-3-2015)

A Comparison of Traditional Simulation and MSAL (6-3-2015)
Model Based Software Timing Analysis Using Sequence Diagram for Commercial Ap...

Model Based Software Timing Analysis Using Sequence Diagram for Commercial Ap...
abstract.visualizingperformance.flowchart
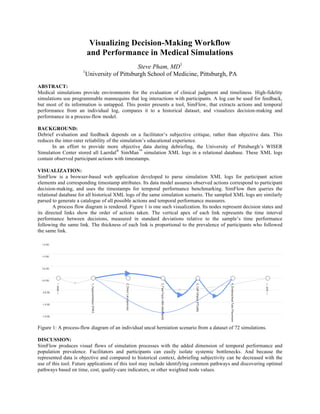
- 1. Visualizing Decision-Making Workflow and Performance in Medical Simulations Steve Pham, MD1 1 University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pittsburgh, PA ABSTRACT: Medical simulations provide environments for the evaluation of clinical judgment and timeliness. High-fidelity simulations use programmable mannequins that log interactions with participants. A log can be used for feedback, but most of its information is untapped. This poster presents a tool, SimFlow, that extracts actions and temporal performance from an individual log, compares it to a historical dataset, and visualizes decision-making and performance in a process-flow model. BACKGROUND: Debrief evaluation and feedback depends on a facilitator’s subjective critique, rather than objective data. This reduces the inter-rater reliability of the simulation’s educational experience. In an effort to provide more objective data during debriefing, the University of Pittsburgh’s WISER Simulation Center stored all Laerdal® SimMan™ simulation XML logs in a relational database. These XML logs contain observed participant actions with timestamps. VISUALIZATION: SimFlow is a browser-based web application developed to parse simulation XML logs for participant action elements and corresponding timestamp attributes. Its data model assumes observed actions correspond to participant decision-making, and uses the timestamps for temporal performance benchmarking. SimFlow then queries the relational database for all historical XML logs of the same simulation scenario. The sampled XML logs are similarly parsed to generate a catalogue of all possible actions and temporal performance measures. A process flow diagram is rendered. Figure 1 is one such visualization. Its nodes represent decision states and its directed links show the order of actions taken. The vertical apex of each link represents the time interval performance between decisions, measured in standard deviations relative to the sample’s time performance following the same link. The thickness of each link is proportional to the prevalence of participants who followed the same link. Figure 1: A process-flow diagram of an individual uncal herniation scenario from a dataset of 72 simulations. DISCUSSION: SimFlow produces visual flows of simulation processes with the added dimension of temporal performance and population prevalence. Facilitators and participants can easily isolate systemic bottlenecks. And because the represented data is objective and compared to historical context, debriefing subjectivity can be decreased with the use of this tool. Future applications of this tool may include identifying common pathways and discovering optimal pathways based on time, cost, quality-care indicators, or other weighted node values.