Difference between genomic and cdna library
•
0 likes•2,177 views
Difference between genomic and cdna library https://microbiologynote.com/difference-between-genomic-and-cdna-library/
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Cloning in gram positive bacteria by neelima sharma,neelima.sharma60@gmail.co...

Cloning in gram positive bacteria by neelima sharma,neelima.sharma60@gmail.co...
Dna sequencing (bacteriophage m13 and primer walking)

Dna sequencing (bacteriophage m13 and primer walking)
More from Microbiology Note
More from Microbiology Note (9)
Electron Microscope: Definition, Types, Parts, Application, Advantages, Disad...

Electron Microscope: Definition, Types, Parts, Application, Advantages, Disad...
Parts of a Microscope and Their Functions - Microbiologynote.com

Parts of a Microscope and Their Functions - Microbiologynote.com
Difference between Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Chemical Oxygen Demand...

Difference between Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Chemical Oxygen Demand...
Difference between genomic and cdna library
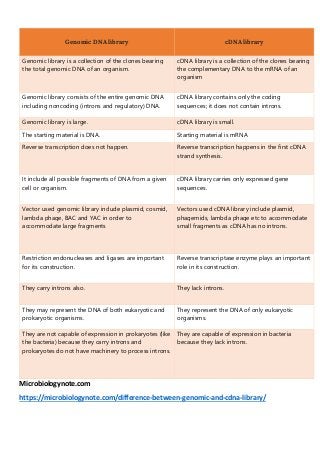
- 1. Microbiologynote.com https://microbiologynote.com/difference-between-genomic-and-cdna-library/ Genomic DNA library cDNA library Genomic library is a collection of the clones bearing the total genomic DNA of an organism. cDNA library is a collection of the clones bearing the complementary DNA to the mRNA of an organism Genomic library consists of the entire genomic DNA including noncoding (introns and regulatory) DNA. cDNA library contains only the coding sequences; it does not contain introns. Genomic library is large. cDNA library is small. The starting material is DNA. Starting material is mRNA Reverse transcription does not happen. Reverse transcription happens in the first cDNA strand synthesis. It include all possible fragments of DNA from a given cell or organism. cDNA library carries only expressed gene sequences. Vector used genomic library include plasmid, cosmid, lambda phage, BAC and YAC in order to accommodate large fragments Vectors used cDNA library include plasmid, phagemids, lambda phage etc to accommodate small fragments as cDNA has no introns. Restriction endonucleases and ligases are important for its construction. Reverse transcriptase enzyme plays an important role in its construction. They carry introns also. They lack introns. They may represent the DNA of both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms. They represent the DNA of only eukaryotic organisms. They are not capable of expression in prokaryotes (like the bacteria) because they carry introns and prokaryotes do not have machinery to process introns. They are capable of expression in bacteria because they lack introns.
