F&E Transes (1).pdf
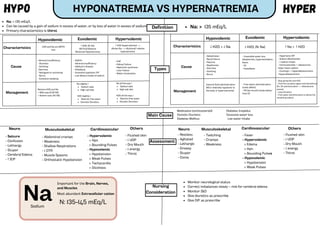
- 1. Definition Types Hypervolemic Characteristics Cause Management ↑ H2O; (N: Na) (N) Fluid Balance Dilutional Hyponatremia ↑ H2O (hypervolemia) --> dilutes Na --> dilutional/ relative hyponatremia - SIADH - Adrenal insufficiency - Addison’s disease - Polydipsia - Excessive hypotonic IVF - Low dietary intake of sodium Sodium tabs High salt diet Restrict free water Osmotic Diuretics Na slightly ↑ H2O slightly ↓ Sodium tabs High salt diet Restrict free water Osmotic Diuretics Na all the way ↑ H2O all the way ↓ Characteristics Management ↓ H2O > ↓ Na - Dehydration - Renal Failure - Polyuria - Diaphoresis - Diarrhea - Vomiting - Burns - Insensible water loss (diaphoresis, hyperventilation, fever) - DI - Hypodipsia - Hypertonic IVF - Sodium Bicarbonate - ↑ sodium intake - Corticosteroids → aldosterone helps retain sodium - Cushing’s → Hyperaldosteronism -Hyperaldosteronism - Free water administration (treat deficit) - PO (by mouth) intake better than IV - Stop giving Na and H2O - Find the causative agent and discontinue (Ex: 3% administration --> Aldosterone excess) - Loop diuretics - Free water administration to dilute the remaining sodium - Fever - Hypervolemic > Edema > Hpn > Bounding Pulses - Hypovolemic > Hypotension > Weak Pulses HYPONATREMIA VS HYPERNATREMIA HYPO HYPER Na: < 135 mEq/L Can be caused by a gain of sodium in excess of water, or by loss of water in excess of sodium Primary characteristics is thirst Na: > 135 mEq/L Hypovolemic Euvolemic H2O and Na are BOTH lost - Adrenal Insufficiency - Diuretics - Vomiting -Diarrhea - Nasogastric suctioning - Burns - Excessive sweating - CHF - Kidney Failure - Nephrotic syndrome - Liver Failure - Water intoxication Restore H2O and Na > Mild case (0.95 NS) > Severe case (3% NS) Hypovolemic Euvolemic Hypervolemic Cause ↑ Na > ↑ H2O Isotonic fluid administration (NS is relatively hypotonic to the body in hypernatremia) ↓ H2O; (N: Na) Main Cause Medication (corticosteroid) Diabetes Insipidus Osmotic Diuretics Excessive water loss Diabetes Mellitus Low water intake Assessment Neuro - Seizure - Confusion - Lethargy - Stupor - Cerebral Edema - ↑ ICP Musculoskeletal - Abdominal cramps - Weakness - Shallow Respirations - ↓ DTR - Muscle Spasms - Orthostatic Hypotension Cardiovascular - Hypervolemic > Hpn > Bounding Pulses - Hypovolemic > Hypotension > Weak Pulses > Tachycardia > Dizziness Others - Flushed skin - ↓ UOP - Dry Mouth - ↓ energy - Thirst Neuro - Restless - Agitated - Lethargic - Drowsy - Stupor - Coma Musculoskeletal - Twitching - Cramps - Weakness Cardiovascular Others - Flushed skin - ↓ UOP - Dry Mouth - ↓ energy - Thirst Nursing Consideration Monitor neurological status Correct imbalances slowly – risk for cerebral edema Monitor I&O Give diuretics as prescribe Give IVF as prescribe Na Important for the Brain, Nerves, and Muscles N: 135-145 mEq/L Most abundant Extracellular cation Sodium
- 2. HYPO HYPER Definition Causes K: < 3.5- 5.5 mEq/L Assessment Muscle weakness → skeletal and cardiac muscles Numbness Shallow respiration Cramping Hyperactive bowel sounds Diarrhea Management Nursing Consideration HYPOKALEMIA VS HYPERKALEMIA K: > 3.5- 5.5 mEq/L Potassium wasting drugs Inadequate Potassium Intake Dilution of Potassium in the blood (too much water) Fluid loss > Laxatives > Diuretics > Corticosteroids → Steroids (Retention of Na and H20; Excretion of K) > Cushing's syndrome > NPO > Poor Diet > Anorexia nervosa (do not eat) > Bulimia nervosa (eat but vomit) > Alcoholism > Polydipsia > Excessive IVF Administration > NGT suctioning, Vomitting, and Wound Drainage Weakness and Fatigue > Weak muscles > Cramps > Decreased DTR > Flaccidity > Shallow respiration > Increase Urine Output > Decrease Bowel Sounds * Constipation * Abdominal Distention Weak Heart > Orthostatic hypotension > Weak, Thready pulse > Cardiac Dysrhytmias EKG Changes > Prominent u-wave Prevent Arrythmias Cardiac telemetry (ECG, RR and O2 stat direted on central monitor HOLD DIGOXIN (↑risk of toxicity) Prevent Further Potassium Losses Hold Furosemide or other potassium wasting drugs (kayexalate and corticosteriod) More Potassium IV NEVER IV Push Give Slowly Monitor IV site Can cause Phlebitis Extravasation --> Cells Damage Attach on central line Oral Foods to prevent GI upset (n/v) Foods rich in Potassium Too much K moves from intracellular to extracellular Burns Tissue damage Diabetic Ketoacidosis (hyperglycemia → ↑ membrane permeability → ↑ k excretion) Too much total Potassium Renal failure Excessive potassium intake Medications ACE inhibitors K sparing diuretics Impaired contractility → ↓ CO Weak pulses Bradycardia Hypotension EKG changes (Tall peaked T waves) Drive Potassium into the cells D5W + Insulin Albuterol (salbutamol) stimulates Na+/K+-ATPase, which results in intracellular shift of potassium) ↑ SNS → Improve weak pulse and hypotension Bicarbonate (temporarily shifts potassium into body cells) Reduce total body Potassium Kayexelate (K in feeces) Diuretics Hydrochlorothiazide Furosemide Dialysis Last resort Monitor Cardiac Rhythm Discontinue any potassium supplements IV potassium Oral potassium supplements Potassium restricted diet IV calcium gluconate or chloride (Ca protects the heart) Given if EKG changes are present to protect the myocardium. Preventing further EKG Foods High in K Avocado Banana Orange Dried Beans Potatoes K Responsible for nerve impulse conduction (send electrical signal out to the skeletal and heart muscle) N: 2.5-5.5 mEq/L Most abundant intracellular cation Potassium
- 3. HYPO HYPER Definition Causes Ca: < 4.5- 5.5 mEq/L Assessment Management Nursing Consideration HYPOCALCEMIA VS HYPERCALCEMIA K: > 4.5- 5.5 mEq/L Renal Failure (phosphorus level is high) Acute pancreatitis (r/t alcoholism) Malnutrition Malabsorption Celiac Disease Chron’s disease Alcoholism → ↓ absorption in small intestine Vit. D deficiency Hypoparathyroidism HYPEREXCITABLE Irritability Hallucination Paresthesia Tetany Seizures Neuromuscular Hyperactive Bowel Sound Cramping Diarrhea Gastrointestinal Oral calcium supplement Give Vit. D → tuna, sardines, and egg yolk ↑ absorption IV calcium supplement Calcium-rich diet Seizure precaution ↓ environmental stimuli (quiet environment) Move carefully Monitor signs of pathological fracture (may occur with minimal trauma) 10% calcium gluconate (tx for acute calcium deficiency) Excessive intake of calcium Hyperparathyroidism (too much calcium released from the bones and moved into the serum) Excessive intake of vitamin D Breakdown of bones causes calcium to move to the serum Cancer of the bones Immobility Glucocoticoids → prolonged used can reduce how much calcium is stored in the bones Reduced dietary calcium intake Cardiac monitoring IV fluids Loop diuretics → Calcium loss in the urine (hydrate first) Encourage oral hydration Dialysis Calcium binders Discontinue medications containing Calcium or Vit. D Move the client carefully and monitor for signs of a pathological fracture Kidney stones Monitor for flank pain or abdominal pain and strain the urine to check for the presence of urinary stone Avoid food high in calcium Foods High in Ca Leafy greens Cheese Milk Soy milk Tofu Sardines Ca Stored in the bones, Absorbed in GI, excreted in Kidney Bones, teeth, nerves, and muscles important for coagulation Controlled by PTH (↑ PTH -> ↑ Ca) and Vit. D (activates Ca) Inverse relationship with Phosphorus N: 4.5-5.5 mEq/L Calcium Weak bones (↑ risk of fracture) Brittle Nails Arrhythmias (ventricular tachycardia) Others Muscle Spasm Chvostek Sign (facial nerve) Trousseau’s Sign (bp cuff → hands involuntary movement) SEDATIVE Weakness Flaccidity ↓ DTR Neuromuscular Bradycardia Cyanosis DVT Cardiovascular ↓ peristalsis Hypoactive bowel sounds Abdominal Pain Nausea Vomiting Constipation Kidney stones Gastrointestinal Neuro Fatigue ↓ LOC
- 4. HYPO HYPER Definition Causes PO4: < 1.2-3 mEq/L Assessment Management HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA VS HYPERPHOSPHATEMIA PO4: > 1.2-3 mEq/L Malnutrition Alcoholism TPN (total parenteral Nutrition)- P is hard to deliver via TPN Hyperthyroidism ( ↑ Ca → ↓ P) Treat the cause Phosphorus replacement Per Orem with Vit. D IV (slowly because of the risk of Hyperphosphatemia) Move the patient carefully (pathologic fractures) Diet low in calcium but high in Phosphorus Excessive dietary intake of phosphorus Tumor lysis syndrome → when a tumor burst and release intracellular component Renal Failure Hypoparathyroidism ( ↓ Ca → ↑ P) PO4 Major role in cellular metabolism and energy production of ATP Makes up phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes Large component of bones and teeth Inverse relationship with Ca N: 1.2- 3 mEq/L Phosphate HYPEREXCITABLE Irritability Hallucination Paresthesia Tetany Seizures Neuromuscular Hyperactive Bowel Sound Cramping Diarrhea Gastrointestinal Weak bones (↑ risk of fracture) Brittle Nails Arrhythmias (ventricular tachycardia) Others Muscle Spasm Chvostek Sign (facial nerve) Trousseau’s Sign (bp cuff → hands involuntary movement) SEDATIVE Weakness Flaccidity ↓ DTR Neuromuscular Bradycardia Cyanosis DVT Cardiovascular ↓ peristalsis Hypoactive bowel sounds Abdominal Pain Nausea Vomiting Constipation Kidney stones Gastrointestinal Neuro Fatigue ↓ LOC Same with Hypercalcemia Same with Hypocalcemia Administer Phosphate binder (sevelamer) Binds to phosphorus in food and increases fecal excretion of phosphorus Take it with meals or immediately after meals ↓ intake of food rich in phosphorus Dairy Products (prevent; ↑ Ca) Fish Nuts and Seeds Pumpkin and Squash Organ Meat Pork, beef, chicken Whole grains, bread, and cereals
- 5. HYPO HYPER Definition Causes Mg: < 1.5-2.5 mEq/L Assessment Management HYPOMAGNESEMIA VS HYPERMAGNESEMIA Mg: > 1.5-2.5 mEq/L Alcoholism Malnutrition Malabsorption Hypoparathyroidism Hypocalcemia Persistent and severe diarrhea (Mg is located in the lower gut) Treat the cause Monitor cardiac rhythm Administer Magnesium PO- Magnesium hydroxide IV- given very slowly Excessive dietary intake Too many magnesium-containing medications - Antacids Overcorrection of hypomagnesemia Renal failure Mg Stored in bones and Cartilage Major role in muscle contraction Important in ATP formation Activates vitamins Necessary for cellular growth Directly related to calcium N: 1.2- 3 mEq/L Magnesium Numbness Tingling Cramping Tetany Seizures ↑ DTR Neuromuscular Torsade de pointes Cardiovascular Nausea and Vomitting Gastrointestinal Psychosis Confusion Neuro Treat the cause Hold any fluids or medication containing Mg Loop diuretics Calcium gluconate→ protects the heart Dialysis Weakness Shallow breathing Slowed reflexes ↓ DTR Neuromuscular Bradycardia Hypotension Vasodilation Feels warm Flushed Cardiovascular Drowsy Lethargy Coma Neuro