Micro final.pptx
- 2. FIVE KINGDOM CLASSIFICATION Five kingdom classification was proposed by RH Whittaker in 1969. * Criteria for classification* 1.Complexity of cell structure- prokaryote, eukaryote. 2.Complexity of organisms- unicellular, multicellular. 3.Mode of nutrition- plants(autotrophs), fungi( heterotroph and saprobic absorption) and animals ( heterotroph and ingestion). 4.Lifestyle- Producers(plants), consumers( animals), decomposers(fungi). 5.Phylogenetic relationships- prokaryote to eukaryote, unicellular to multicellular.
- 4. MONERA • Unicellular and Prokaryotic. • True nucleus and membrane bound organelles are absent. • Some of them have cell wall (bacteria and BGA) and some of them don’t have cell wall (mycoplasma). • Have two Major groups- 1. Eubacteria(true bacteria).It includes bacteria and cyanobacteria 2.Archaebacteria (ancient bacteria) • Examples- E.coli, Bacteria, Anabaena, etc.
- 5. PROTISTA • Unicellular and Eukaryotic. • True nucleus is Present. • Protista are mainly Protozoans. • The structures like cilia, flagella and pseudopodia are presented in these organisms which help in locomotion and food capturing. • Examples — Diatoms, amoeba, paramecium, algae, euglena, etc.
- 6. FUNGI • Heterotrophic and Eukaryotic. • Mainly have Multicellular body with the exception of yeast which is unicellular fungi. • True nucleus is Present. • Their cell wall is made up of chitin. • .They have saprophytic nutrition i.e. live on the dead and decaying matter. • Examples- Yeast, Penicillium, aspergillus, penicillium, etc.
- 7. PLANTAE • They are Eukaryotic, Multicellular and Autotrophs. • They have an additional covering on plasma membrane called Cell membrane. • They have cell wall, made up of cellulose and chlorophyll pigments which help in photosynthesis. • Presence of vascular tissues. • They are non-motile or static. • The plant kingdom is classified into 5 phylum.
- 8. ANIMALIA • They are Eukaryotic and Multicellular. • They are Heterotrophs. • They do not have cell wall and chlorophyll! pigments. • Generally have locomotory organs and are motile. • They have a well developed sensory and neuromuscular system. • This group contains all invertebrates and vertebrates. • The animal kingdom is classified into 10 divisions.
- 10. •PROKARYOTES CELL were the first and for billions of years were the only form of life on earth. •unicellular organism. •simplest type of cell. •have diffused nucleus with no nuclear membrane, nucleolus, ribonucleoprotien. •Genetic material is dispersed throughout cytoplasm. •Don’t have membrane bound organelles •Major group includes bacteria, blue green algae. •0.2-1.5 micrometer diameter 3-5 micrometer length
- 11. •Tough rigid structure 10-25nm thick •has peptidoglycan layer ,teicholic acid (in gram +ve) , lipopolysaccharide (in gram –ve) CELL WALL
- 12. Gram positive cell wall diff
- 13. •Function of cell wall – 1) Gives protection to bacteria against cell lysis , toxic substance 2) Rigidity to bacteria due to presence of peptidoglycan layer 3) Virulence factor eg endotoxin contribute to pathogenicity 4)Immunity : antibody raised against specific cell wall antigen may give immunity against some bacterial infection
- 14. •Cell membrane- - 5-10nm thick lack sterols such as cholestrol except in mycoplasma -some have pentacyclic sterol like molecules called hopanoids’ •Cytoplasmic matrix – have 70S ribosomes (30S and 50S subunits) •Intracytoplasmic inculsions storage sites of nutrient/ energy in some bacteria are of 2 types – 1) organic inculsion bodies eg. glycogen granules 2) Inorganic inculsion bodies eg. polymetaphosphate , volutin
- 15. •Mesosomes – - invagination of plasma membrane in shape of vesicle tubules lamella - Site of bacterial respiration -Involved in cell wall formation and cell division •Plasmid – - extrachromosomal DNA -Non essential for life -capable of independent replication -used as vectors -provide antibiotic resistance to bacteria
- 16. •Capsule/slime layer- - glycocalyx layer outside the cell wall.eg streptococcus salivarius -Function- 1) contribute to bacterial virulence by protecting from phagocytosis, drying out, action of lysozome and bacteriophages, 2) may be toxic to host cell 3) biofilm formation 4) Source of nutrition eg streptococcus mutans 5) Capsule as vaccine eg haemophilus influenza
- 17. •Flagella -thread like appendages -Provide bacterial motility •Fimbrae- -short fine hair like appendages -Helps in bacterial adhesion
- 19. INTRODUCTION Eukaryotic cells have an organized nucleus with a nuclear envelope. Eukaryotic cells have organelles and organized DNA. Extra chromosomal DNA is found in mitochondria. Major groups included in eukaryotes are Algae, Fungi and parasites(protozoa and helminths)
- 20. STRUCTURES EXTERNAL STRUCTURES: • FLAGELLA • CILIA • GLYCOCALYX • CELL WALL • CYTOPLASMIC MEMBRANE INTERNAL STRUCTURES: • NUCLEUS • ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM • GOLGI APPARATUS • LYSOSOMES • VACUOLES • MITOCHONDRIA • CHLOROPLAST • RIBOSOMES • CYTOSKELETON
- 23. FUNCTIONS PLASMA MEMBRANE • A fluid like bilipid membranous layer composed of proteins and carbohydrates. • It separates the cell from its external environment , protects the cell and provides shape, stability and integrity of the cell. • Selectively permeable. NUCLEUS • Brain or control centre of the cell • Surrounded by a nuclear membrane • Contains DNA • Regulates gene expression via chromosomes
- 24. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM • Carry materials throughout the cell and is the “transport system” of the cell. • They are of two types: 1.RER-lined with ribosome 2.SER-absence of ribosome GOLGI BODIES • Moves material inside and outside the cell. • Temporarily stores proteins,modifies and packs macromolecules.
- 25. MITOCHONDRIA • Double membranous structure. • Powerhouse of the cell- helps in the formation of ATP through respiration CHLOROPLAST • Present in plants only , contains the green pigment chlorophyll • Responsible for performing photosynthesis in plants. LYSOSOMES • Contains digestive enzymes that degrades worn out cell parts. • Also known as “suicidal bags” Peroxisomes • Contains reducing enzymes CATALASE and OXIDASE that oxidise certain organic substances. CENTRIOLES • Made up of microtubules ,a pair of cylindrical organelles near the nucleus. VACUOLES • Stores materials such as food ,water ,sugars , minerals and waste products CYTOSKELETON • Made up of microtubules , actin and intermediate filaments • Gives the cell its shape and helps organize the cell parts and also help the cell to move.
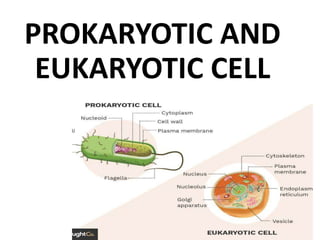
- 26. DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PROKARYOTIC CELL AND EUKARYOTIC CELL
- 27. PROKARYOTIC CELL EUKARYOTIC CELL UNICELLULAR MULTICELLULAR OR UNICELLULAR HAVE DIFFUSED NUCLEUS i.e. WITHOUT NUCLEAR MEMBRANE NUCLEUS WITH NUCLEAR MEMBRANE CIRCULAR DNA LINEAR DNA ABSENCE OF MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES PRESENCE OF MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES RIBOSOMES : 70 S RIBOSOMES : 80 S EXTRACHROMOSOMAL DNA FOUND IN PLASMID EXTRACHROMOSOMAL DNA FOUND IN MITOCHONDRIA
- 28. PROKARYOTIC CELL EUKARYOTIC CELL CELL MEMBRANE DOES NOT CONTAIN STEROLS EXCEPT IN MYCOPLASMA CELL MEMBRANE CONTAIN STEROLS SITE OF RESPIRATION IS MESOSOME SITE OF RESPIRATION IS MITOCHONDRIA PINOCYTOSIS IS ABSENT PINOCYTOSIS IS PRESENT CELL DIVISION BY BINARY FISSION CELL DIVISION BY MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS MAJOR GROUPS : BACTERIA, BLUE GREEN ALGAE MAJOR GROUP: FUNGI, PARASITE, OTHER ALGAE, PLANTS AND ANIMALS
- 29. CLINICAL CASES
- 30. GRAM POSITIVE COCCI INFECTION- (1) STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS – • SKIN AND SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONS LIKE FOLLICULITIS, FURUNCLE, AND CELLULITIS, ETC. • MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS LIKE OSTEOMYELITIS, SEPTIC ARTHRITIS AND ABSCESS. • TOXIN MEDIATED INFECTIONS SUCH AS SCALDED SKIN SYNDROME, FOOD POISONING, AND TOXIC SHOCK SYNDROME. BACTERIAL INFECTIONS -
- 31. (2) STREPTOCOCCUS PYOGENES – SUPPURATIVE MANIFESTATIONS INCLUDE - • SORE THROAT • SCARLET FEVER • SKIN AND SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONS NON SUPPURATIVE MANIFESTATIONS INCLUDE - • ACUTE RHEUMATIC FEVER • POST STREPTOCOCCAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
- 32. GRAM NEGATIVE COCCI INFECTIONS – (1) NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS – • PYOGENIC MENINGITIS AND SEPTICEMIA (2) NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE – • GONORRHEA • CONJUNCTIVITIS IN NEW BORN
- 33. GRAM POSITIVE BACILLI INFECTIONS – (1) CORYNEBACTERIUM DIPHTHERIAE – • DIPHTHERIA • MYOCARDITIS • POLYNEUROPATHY (2) BACILLUS ANTHRACIS – • CAUSATIVE AGENT OF ANTHRAX (3) MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS – • PULMONARY AND EXTRAPULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
- 34. GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI INFECTIONS – (1) ESCHERICHIA COLI – • HARMLESS IN HUMAN INTESTINE • URINARY TRACT INFECTION AND DIARRHOEA (2) KLEBSIELLA PNEUMONIAE – • UTI • LOBAR PNEUMONIA, MENINGITIS AND SEPTICEMIA (3) SHIGELLA – • BACILLARY DYSENTERY (4) SALMONELLA TYPHI – • TYPHOID
- 35. THANK YOU By 31 Dhruv bharti 32 Divya 33 Divyansh Sharma 34 Divyansha Goel 35 Divyanshu Seervi