Recommended
Recommended
This presentation provides an overview of trap crop research and demonstrations in tomato (mainly) and squash production system. This paper was presented at the International IPM Symposium, Baltimore, MD (March 20, 2018). Trap crop research overview (2011-2017)

Trap crop research overview (2011-2017)Ayanava Majumdar (Dr. A), Alabama Cooperative Extension System
Early blight of potato caused by Alternaria alternata (Fries) Keissler is one of the factors that affect
potato production. Using chemical control to reduce disease severity represent another risk for
agriculture. Biological control, using microorganisms, as well as plant extract and compost are safe
measures that give reliable control. Applying either measure of control reduced disease incidence to less
than 2% during two successive seasons. Microbial spray of diseased potato reduced the disease to various
extents. Trichoderma sp. was the most effective among all tested microorganisms, followed by
Penicillium sp. On the other hand, alcoholic extract of three plants was more effective than their water
extract. However, water extract showed highly significant reduction of disease incidence. Polygonum
gave the highest reduction of disease incidence in both cases. Also water extract of compost greatly
suppressed early blight when applied as spray to potato leaves. Duration of extraction may affect the
ability of compost extract to suppress disease. All results were comparable to that of fungicides.Non-chemical Control of Potato Early Blight Caused by Alternaria alternata

Non-chemical Control of Potato Early Blight Caused by Alternaria alternatathe Egyptian Society for Environmental Sciences
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (7)
MISSPECIFYING OPERATIONAL DELAYS MAY PRODUCE BIASED FORECASTS: A RETROSPECTIV...

MISSPECIFYING OPERATIONAL DELAYS MAY PRODUCE BIASED FORECASTS: A RETROSPECTIV...
Similar to V087
This presentation provides an overview of trap crop research and demonstrations in tomato (mainly) and squash production system. This paper was presented at the International IPM Symposium, Baltimore, MD (March 20, 2018). Trap crop research overview (2011-2017)

Trap crop research overview (2011-2017)Ayanava Majumdar (Dr. A), Alabama Cooperative Extension System
Early blight of potato caused by Alternaria alternata (Fries) Keissler is one of the factors that affect
potato production. Using chemical control to reduce disease severity represent another risk for
agriculture. Biological control, using microorganisms, as well as plant extract and compost are safe
measures that give reliable control. Applying either measure of control reduced disease incidence to less
than 2% during two successive seasons. Microbial spray of diseased potato reduced the disease to various
extents. Trichoderma sp. was the most effective among all tested microorganisms, followed by
Penicillium sp. On the other hand, alcoholic extract of three plants was more effective than their water
extract. However, water extract showed highly significant reduction of disease incidence. Polygonum
gave the highest reduction of disease incidence in both cases. Also water extract of compost greatly
suppressed early blight when applied as spray to potato leaves. Duration of extraction may affect the
ability of compost extract to suppress disease. All results were comparable to that of fungicides.Non-chemical Control of Potato Early Blight Caused by Alternaria alternata

Non-chemical Control of Potato Early Blight Caused by Alternaria alternatathe Egyptian Society for Environmental Sciences
2003. nematocidal effects of mexican – medicinal plant extracts

2003. nematocidal effects of mexican – medicinal plant extractsRicardo Reyes Chilpa. Instituto de Química. UNAM
Similar to V087 (20)
Correlation between populations of xanthomonas axonopodis pv. vignicola build...

Correlation between populations of xanthomonas axonopodis pv. vignicola build...
Prevalence, occurrence and biochemical characterization of Xanthomonas campes...

Prevalence, occurrence and biochemical characterization of Xanthomonas campes...
Management Of Apple Scab (Venturia Inaequalis) In Albania Based On Mills Tabl...

Management Of Apple Scab (Venturia Inaequalis) In Albania Based On Mills Tabl...
The Behavior of Some Peach and Nectarine Cultivars to Powdery Mildew (Sphaero...

The Behavior of Some Peach and Nectarine Cultivars to Powdery Mildew (Sphaero...
Research Journal of Aklan State University - 2015 (Volume 3, No. 1)

Research Journal of Aklan State University - 2015 (Volume 3, No. 1)
Mutation Induction for Improvement of Banana (Musa Spp). "Berangan Cv. Intan-...

Mutation Induction for Improvement of Banana (Musa Spp). "Berangan Cv. Intan-...
Mutation Induction for Improvement of Banana (Musa Spp.) Berangan Cv. Intan-AAA

Mutation Induction for Improvement of Banana (Musa Spp.) Berangan Cv. Intan-AAA
Efficacy of fungicides to control Early Blight genotypes

Efficacy of fungicides to control Early Blight genotypes
Effectiveness of organic substances in the control of powdery mildew (Sphaero...

Effectiveness of organic substances in the control of powdery mildew (Sphaero...
Non-chemical Control of Potato Early Blight Caused by Alternaria alternata

Non-chemical Control of Potato Early Blight Caused by Alternaria alternata
Turcicum Leaf Blight Resistance Screening and Combining ability studies in Maize

Turcicum Leaf Blight Resistance Screening and Combining ability studies in Maize
Epidemiology, etiology and management of fusarium wilt of muskmelon

Epidemiology, etiology and management of fusarium wilt of muskmelon
2003. nematocidal effects of mexican – medicinal plant extracts

2003. nematocidal effects of mexican – medicinal plant extracts
Resistance of corn inbred lines to foliar diseases in two planting dates

Resistance of corn inbred lines to foliar diseases in two planting dates
Effect of glyphosate herbicide on the behavior of soil arthropods in non-orga...

Effect of glyphosate herbicide on the behavior of soil arthropods in non-orga...
V087
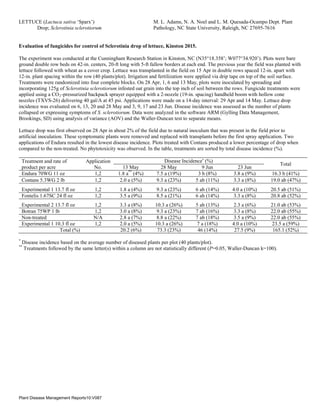
- 1. LETTUCE (Lactuca sativa ‘Sparx’) Drop; Sclerotinia sclerotiorum M. L. Adams, N. A. Noel and L. M. Quesada-Ocampo Dept. Plant Pathology, NC State University, Raleigh, NC 27695-7616 Evaluation of fungicides for control of Sclerotinia drop of lettuce, Kinston 2015. The experiment was conducted at the Cunningham Research Station in Kinston, NC (N35°18.358’; W077°34.920’). Plots were bare ground double row beds on 42-in. centers, 20-ft long with 5-ft fallow borders at each end. The previous year the field was planted with lettuce followed with wheat as a cover crop. Lettuce was transplanted in the field on 15 Apr in double rows spaced 12-in. apart with 12-in. plant spacing within the row (40 plants/plot). Irrigation and fertilization were applied via drip tape on top of the soil surface. Treatments were randomized into four complete blocks. On 28 Apr, 1, 6 and 13 May, plots were inoculated by spreading and incorporating 125g of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum infested oat grain into the top inch of soil between the rows. Fungicide treatments were applied using a CO2-pressurized backpack sprayer equipped with a 2-nozzle (19-in. spacing) handheld boom with hollow cone nozzles (TXVS-26) delivering 40 gal/A at 45 psi. Applications were made on a 14-day interval: 29 Apr and 14 May. Lettuce drop incidence was evaluated on 6, 13, 20 and 28 May and 3, 9, 17 and 23 Jun. Disease incidence was assessed as the number of plants collapsed or expressing symptoms of S. sclerotiorum. Data were analyzed in the software ARM (Gylling Data Management, Brookings, SD) using analysis of variance (AOV) and the Waller-Duncan test to separate means. Lettuce drop was first observed on 28 Apr in about 2% of the field due to natural inoculum that was present in the field prior to artificial inoculation. These symptomatic plants were removed and replaced with transplants before the first spray application. Two applications of Endura resulted in the lowest disease incidence. Plots treated with Contans produced a lower percentage of drop when compared to the non-treated. No phytotoxicity was observed. In the table, treatments are sorted by total disease incidence (%). * Disease incidence based on the average number of diseased plants per plot (40 plants/plot). ** Treatments followed by the same letter(s) within a column are not statistically different (P=0.05, Waller-Duncan k=100). Treatment and rate of product per acre Application No. Disease Incidence* (%) Total 13 May 28 May 9 Jun 23 Jun Endura 70WG 11 oz 1,2 1.8 a** (4%) 7.5 a (19%) 3 b (8%) 3.8 a (9%) 16.3 b (41%) Contans 5.3WG 2 lb 1,2 2.0 a (5%) 9.3 a (23%) 5 ab (11%) 3.3 a (8%) 19.0 ab (47%) Experimental 1 13.7 fl oz 1,2 1.8 a (4%) 9.3 a (23%) 6 ab (14%) 4.0 a (10%) 20.5 ab (51%) Fontelis 1.67SC 24 fl oz 1,2 3.5 a (9%) 8.5 a (21%) 6 ab (14%) 3.3 a (8%) 20.8 ab (52%) Experimental 2 13.7 fl oz 1,2 3.3 a (8%) 10.3 a (26%) 5 ab (13%) 2.3 a (6%) 21.0 ab (53%) Botran 75WP 1 lb 1,2 3.0 a (8%) 9.3 a (23%) 7 ab (16%) 3.3 a (8%) 22.0 ab (55%) Non-treated N/A 2.8 a (7%) 8.8 a (22%) 7 ab (18%) 3.5 a (9%) 22.0 ab (55%) Experimental 1 10.3 fl oz 1,2 2.0 a (5%) 10.3 a (26%) 7 a (18%) 4.0 a (10%) 23.5 a (59%) Total (%) 20.2 (6%) 73.3 (23%) 46 (14%) 27.5 (9%) 165.1 (52%) Plant Disease Management Reports10:V087