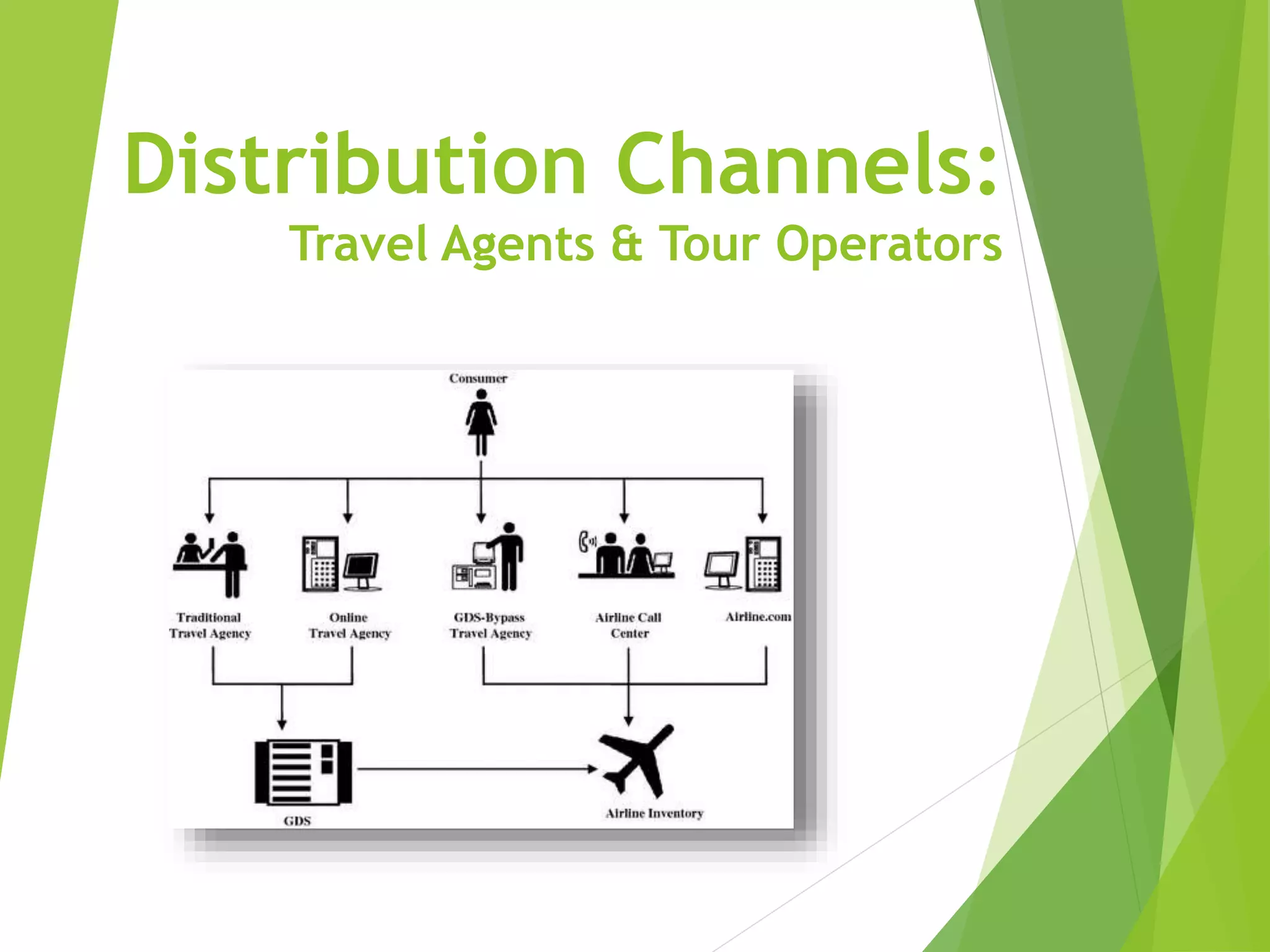
This document discusses distribution channels and channel conflict in marketing. It describes different types of channel conflict including vertical, horizontal, and multichannel conflict. It also outlines strategies for managing channel conflict and discusses channel design decisions including analyzing customer needs, setting objectives, identifying alternatives, and evaluation. Finally, it covers distribution systems in travel and tourism, the role of travel intermediaries, and the impact of technology on travel distribution.