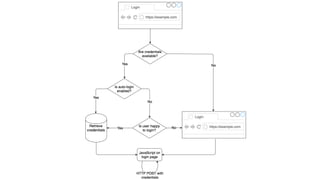
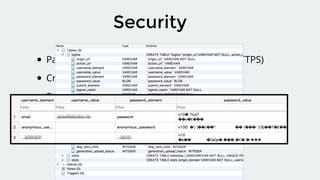
The document discusses the evolution of username/password forms for credential management, highlighting the Credential Management API that facilitates user authentication and password storage. It outlines the process of signing in, validating responses, and storing credentials securely, ensuring security through HTTPS and encryption. The document emphasizes browser support and provides code examples for implementing these features.





![Spec work started early 2015 [1]
Championed by Mike West at Google [2]
Provides 2 key mechanisms
Help the user authenticate by providing access to
credentials
Help the browser store credentials provided by the
user
The Credential Management API
[1]: https://www.w3.org/TR/credential-management-1/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allardis-170417071741/85/James-Allardice-Building-a-better-login-with-the-credential-management-API-8-320.jpg)
![Browser support
[1]: http://caniuse.com/#feat=credential-management](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allardis-170417071741/85/James-Allardice-Building-a-better-login-with-the-credential-management-API-10-320.jpg)