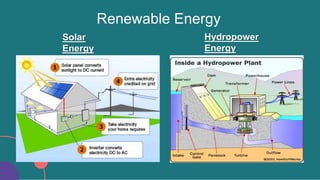
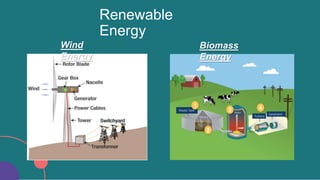
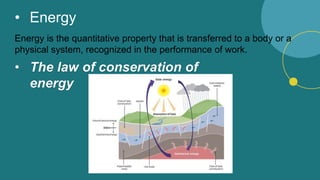
The document discusses energy and climate change. It defines energy and different types of energy sources, distinguishing between non-renewable sources like fossil fuels and renewable sources like solar, hydropower, and wind. It then defines climate and climate change, listing some of the main causes of climate change like greenhouse gases. The document outlines several indicators of climate change and impacts, such as rising sea levels, increasing temperatures, extreme weather events, and effects on ecosystems and human society.


![Non-renewable energy [Fossil Fuels]
Buried Plant & Organism and making Fossil
fuels
Mining Fossil Fuels and
Coal, Oil, Natural Gas, Nuclear
energy, etc.
&](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/energyclimate-220505201831-eceb87f2/85/Energy-Climate-4-320.jpg)