damop poster 2
•
0 likes•189 views
This document studies how Coulomb repulsion and exchange interaction affect the time evolution and pulse duration of two-electron systems. The researchers construct an initial wavefunction for the two-electron system and time-evolve it using the Hamiltonian, which includes terms for both Coulomb repulsion and exchange interaction. Their results show that both effects contribute to increasing the separation between electrons over time, but are within an order of magnitude of each other, suggesting both play a role in limiting ultrafast electron pulse durations.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Prabhakar Singh- II_SEM-Paper V_TRACER TECHNIQUEPrabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-tracer technique

Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-tracer techniqueDepartment of Biochemistry, Veer Bahadur Singh Purvanchal Univarsity, Jaunpur
Recommended
Prabhakar Singh- II_SEM-Paper V_TRACER TECHNIQUEPrabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-tracer technique

Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-tracer techniqueDepartment of Biochemistry, Veer Bahadur Singh Purvanchal Univarsity, Jaunpur
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (18)
Electron Diffusion and Phonon Drag Thermopower in Silicon Nanowires

Electron Diffusion and Phonon Drag Thermopower in Silicon Nanowires
Interaction of small molecules with grapheen supported on metal substrates: A...

Interaction of small molecules with grapheen supported on metal substrates: A...
Similar to damop poster 2
Apartes de la Conferencia de la SJG del 14 y 21 de Enero de 2012Nonlinear ele...

Apartes de la Conferencia de la SJG del 14 y 21 de Enero de 2012Nonlinear ele...SOCIEDAD JULIO GARAVITO
Similar to damop poster 2 (20)
Impact of electronic correlation on the electron-phonon coupling

Impact of electronic correlation on the electron-phonon coupling
Interaction of radiation with Matter - Dr. Vandana

Interaction of radiation with Matter - Dr. Vandana
Energy of Corpuscular-Wave Mechanism_Crimson Publishers

Energy of Corpuscular-Wave Mechanism_Crimson Publishers
Apartes de la Conferencia de la SJG del 14 y 21 de Enero de 2012Nonlinear ele...

Apartes de la Conferencia de la SJG del 14 y 21 de Enero de 2012Nonlinear ele...
More from Maxwell Gregoire
More from Maxwell Gregoire (7)
damop poster 2
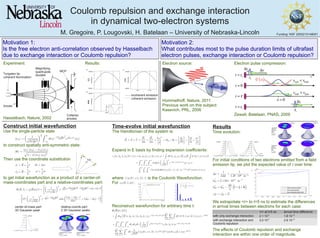
- 1. Coulomb repulsion and exchange interaction in dynamical two-electron systems M. Gregoire, P. Lougovski, H. Batelaan – University of Nebraska-Lincoln |cψ (E)|^2 for l=1, m=-1,0,1is Funding: NSF 2505210148001 Motivation 2: What contributes most to the pulse duration limits of ultrafast electron pulses, exchange interaction or Coulomb repulsion? Motivation 1: Is the free electron anti-correlation observed by Hasselbach due to exchange interaction or Coulomb repulsion? Tungsten tip coherent illumination Anode Magnifying quadrupole doublet Collector anodes MCP - - - incoherent emission coherent emission Experiment: Results: Hasselbach, Nature, 2002 Electron source: Hommelhoff, Nature, 2011 Previous work on this subject: Kasevich, PRL, 2006 Electron pulse compression: Zewail, Batelaan, PNAS, 2009 Construct initial wavefunction Use the single-particle state to construct spatially anti-symmetric state: Then use the coordinate substitution to get initial wavefunction as a product of a center-of- mass-coordinates part and a relative-coordinates part: 1 2 CoM x,y, or z |Χ(R)|^2 center-of-mass part: 3D Gaussian peak Cylindrical plot of r and θ for φ=0: 0<r<rmax , 0<θ<π Cylindrical plot of r and φ for θ=0: 0<r<rmax , 0<φ<2π |ψ(R)|^2 |ψ(R)|^2 relative-coords part: 2 3D Gaussian peaks Time-evolve initial wavefunction The Hamiltonian of the system is: Expand in E basis by finding expansion coefficients: where is the Coulomb Wavefunction. For : Reconstruct wavefunction for arbitrary time t: Results Time evolution: For initial conditions of two electrons emitted from a field emission tip, we plot the expected value of r over time: We extrapolate <r> to t=5 ns to estimate the differences in arrival times between electrons for each case: The effects of Coulomb repulsion and exchange interaction are within one order of magnitude. <r> at t=5 ns arrival time difference with only exchange interaction 2.1∙10-5 1.8∙10-12 with exchange interaction and Coulomb repulsion 3.0∙10-5 2.6∙10-12 |Χ(R)|^2 x |Χ(R)|^2 y or z |ψ(R)|^2 |ψ(R)|^2 |ψ(R)|^2 |ψ(R)|^2 Cylindrical plots of r and θ for φ=0: 0<r<rmax , 0<θ<π Cylindrical plots of r and φ for θ=0: 0<r<rmax , 0<φ<2π