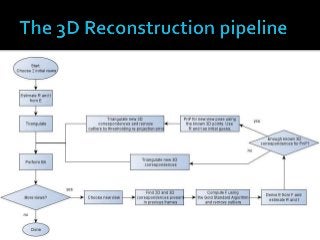
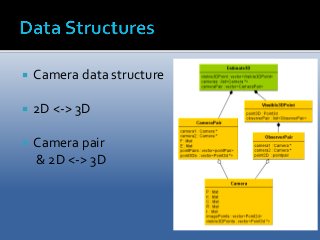
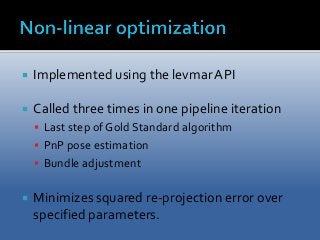
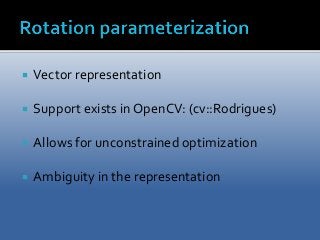
A project performed as a part of the Computer Vision (TSBB15) course at Linköping University. The purpose of the project is to implement a computer program capable of, given a set of images and known intrinsic camera parameters, estimate the location of image points in 3D as well as the camera pose. 3D reconstruction is, in computer vision, defined as the process of capturing shapes, locations and/or appearances of real objects. The project goal was to create a 3D-reconstruction application capable of performing the aforementioned tasks as well as estimating the camera trajectory. The application was implemented in C++ mainly using the OpenCV library.
https://github.com/Epipolarna/3DReconstruction