Linnean Classification and Phylogenetic Trees
- 1. 1
- 2. Linnean Classification System; 2 main characteristics: *Binomial nomenclature …Each organism has a 2 part name consisting of genus and species *Hierarchical classification scheme
- 3. Groups species into increasingly broad categories… For example, species that appear to be closely related are grouped into the same genus
- 4. However… Linneaus’s classification was not based on evolutionary relationships but simply on resemblances between organisms.; what characteristics they had in common After Darwin, scientists began classifying organisms based on phylogeny Phylogeny=the study of the evolutionary history or relationships among organisms
- 5. Problems can arise because similar traits can evolve independently in two distant species rather than from in a common ancestor. Homology occurs when traits are similar due to shared ancestry. Homoplasy (aka: analogy) occurs when traits are similar for reasons other than common ancestry Convergent evolution… when natural selection favors similar solutions to problems posed by a similar way of life… structures in unrelated organisms evolve to perform similar function
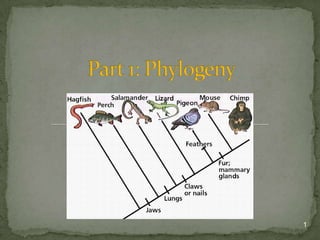
- 6. Phylogenies are usually summarized and depicted in the form of a phylogenetic tree… graphical representation of evolutionary history shows ancestor-descendant relationships among groups of organisms *In this lab today, you will learn how to construct, read, and interpret a phylogenetic tree
- 7. A branch represents a population through time A node (or fork), the point where two branches diverge… represents the point in time when an ancestral group split into two or more descendant groups The root is the first or most basal node on the tree A tip (or terminal node), the endpoint of a branch, represents a group (a species or larger taxon) that is living today or ended in extinction.
- 8. *Left is the most ancient. As move to the right (or up the tree) become more recent 8
- 9. Outgroup… Species or group of species that is closely related to, but not a member of, the group under study (ingroup) Serves as a basis of comparison Assumed to represent a distant ancestor 9
- 10. There are many equivalent ways of drawing the same tree
- 11. The cladistic approach to inferring trees is based on identifying the shared derived characteristics of the group under study… synapomorphies Synapomorphy is a trait that certain groups of organisms have that exists in no others Synapomorphies are characteristics that are shared because their common ancestor had them
- 12. Allow biologists to recognize monophyletic groups— also called clades or lineages. Clade Species that share a common ancestor as indicated by the possession of shared derived characters Evolutionary units; refer to a common ancestor and all descendants Cladogram= type of phylogenetic tree *This is the approach we will be using!!!
- 13. An ancestral trait is a characteristic that existed in an ancestor; prior to the common ancestor of the group A derived trait is one that is a modified form of the ancestral trait, found in a descendant; similarity that is inherited from the most recent common ancestor of an entire group Ancestral and derived traits are relative.
- 14. Characters should exist in recognizable character states Present or Absent Example: Character “hair” in vertebrates has two states…present in mammals and absent in fish, amphibians, and reptiles 14
- 15. “1” = ; the organism has the trait; possession of derived character state “0” = the organism lacks the trait; possession of ancestral character state
- 16. The derived characters between the cladogram branch points are shared by all organisms above the branch points and are not present in any below them. The outgroup (in this case, the lamprey) does not 16 possess any of the derived characters.
- 17. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Salamander Frog Lizard Tiger Gorilla Human Salamander Lizard T iger Frog Gorilla Human Hair loss Amniotic membrane loss Hair Tail loss Amniotic Hair membrane Amniotic Tail loss membrane a. b. Based on the principle of parsimony, the cladogram that requires the fewest number of evolutionary changes is favored Parsimony…principle of logic stating that the most likely explanation is the one that implies the least amount of change.; It favors simple explanations over complicated ones 17
- 18. *What type of data to scientists look at when trying to reconstruct phylogenies? Morphology (e.g. stuctures)* Molecular (e.g. DNA sequences)* Physiology Behavior *When use morphological characteristics vs. molecular characteristics can get very different results… different possible evolutionary relationships
- 19. *Phylogeny Activities… Activity 1: Constructing a simple phylogenetic tree Activity 2: Reading and interpreting a phylogenetic tree… compare a tree based on morphological data and a tree based on molecular data 19
- 20. STEP 1: Choose a group of organisms STEP 2: Choose the traits (or characters) you will compare in your clade STEP 3: Polarize the characters… this means to determine presence or absence; You then have to determine if the characters are ancestral or derived STEP 4: Group the organisms by shared derived characters STEP 5: Using those groupings, create a cladogram Shared derived traits are listed after branch points Organisms go at the tips of the branches 20 *Steps 1 and 2 all already done for you
- 21. Artiodactyls, including hippos, cows, deer, and pigs, are mammals that have hooves, an even number of toes, and an unusual pulley-shaped ankle bone (astragalus). Traditionally, phylogenetic trees based on morphological data place whales as the outgroup DNA sequence data, however, suggest a close relationship between whales and hippos. This tree would require two changes to the astragalus trait.
- 22. Recent data on gene sequences called short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) show that whales and hippos share several SINE genes that are absent in other artiodactyl groups. These SINEs are shared derived traits (synapomorphies) and support the hypothesis that whales and hippos are indeed closely related.
- 23. 23
- 24. Development proceeds in ordered phases Gametogenesis... Formation of sperm and egg Fertilization… sperm and egg unite to form a zygote (fertilized egg) Cleavage… zygote undergoes cell division Gastrulation Organogenesis *Sexual Reproduction
- 25. Cleavage is the set of rapid cell divisions that take place in a zygote immediately after fertilization… mitosis! Cleavage is the first step in the process that makes a single-celled zygote into a multicellular embryo The cells created by cleavage divisions are called blastomeres… have specific fates Eventually you get a ball of cells called a morula
- 26. When cleavage is complete the embryo consists of a hollow ball of cells called a blastula Blastocoel – fluid-filled cavity
- 27. Cleavage partitions the egg cytoplasm without any additional growth taking place… No increase in the overall size of the embryo Rapid division of the zygote into a larger and larger number of smaller and smaller cells (blastomeres) Animal pole Forms external tissues Vegetal pole Forms internal tissues 27
- 28. Cleavage patterns are quite diverse Relative amount and distribution of nutritive yolk in the egg is the characteristic that most affects the cleavage pattern of an animal embryo Sea Urchin Frog Chicken Animal pole Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Shell Nucleus Plasma Nucleus Air membrane bubble Albumen Yolk Yolk Vegetal pole Yolk 28 a. b. c.
- 29. Eggs with little or no yolk (or moderate yolk) Holoblastic (complete) * cleavage Invertebrates, amphibians, * mammals Eggs with large amounts of yolk Meroblastic (incomplete) cleavage Fish, reptiles, birds Embryo forms thin cap on yolk 29
- 30. Gastrulation begins with the formation of the blastopore…blastula indents to form a gastrula with a blastopore = opening to outside Cells from the periphery move inward through the blastopore, forming a tube-like structure that will become the gut… archenteron = Primitive gut
- 31. During gastrulation, extensive and highly organized cell movements radically rearrange the embryonic cells into a structure called the gastrula Gastrulation results in the formation of embryonic tissue layers. Most early embryos have 3 primary tissue layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm These embryonic tissues are called germ layers because they give rise to adult tissues and organs.
- 32. Ectoderm forms the outer covering of the adult body and the nervous system. Mesoderm gives rise to muscle, most internal organs, and connective tissues such as bone and cartilage. Endoderm produces the lining of the digestive tract or gut, along with some of the associated organs.
- 33. At the end of gastrulation, the three embryonic tissues are arranged in layers, the gut has formed, and the major body axes have become visible.
- 34. Organogenesis is the process of tissue and organ formation that begins once gastrulation is complete and the embryonic germ layers are in place. During organogenesis, cells proliferate and become differentiated, meaning that they become a specialized cell type.
- 35. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lXN_sDnd1ng http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2V2_aTiOwj4&feature =topics http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Lgb4wMsZwZA&featu re=topics http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qisrNX3QjUg&feature =related
- 36. Based on certain aspects of early development, most animals are categorized as having one of two developmental patterns Protostome development… “first mouth” *Arthopods, Mollusks, Annelids Deuterostome development… “second mouth” *Echinoderms and Chordates
- 37. Protostomes and Deuterostome differ from each other in 4 fundamental embryological features: 1. Cleavage pattern of embryonic cells 2. Developmental fate of cells 3. Fate of the blastopore 4. Origin of the coelom* *will discuss this at later date 37
- 38. Protostomes… spiral cleavage *the first two divisions are equal, but the rest are unequal. *planes of cell division are diagonal to the vertical axis of the embryo; upper cells lay in the grooves between the underlying cells Deuterostomes… radial cleavage *each cell division is equal and results in cells of all the same size *planes of division are either parallel or perpendicular to the vertical axis of the embryo; tiers of cells are aligned, one directly above the other
- 39. *Difference between spiral & radial can be seen at 8-cell stage http://worms.zoology.wisc.edu/urchins/rad_spir.html
- 40. Protostomes… determinate (mosaic) development *developmental fate of each embryonic cell is determined very early Deuterostomes… indeterminate (regulative) development *each cell produced by early cleavage divisions retains the capacity to develop into a complete embryo
- 41. Protostomes… develop the mouth first from or near the blastopore Deuterostomes… develop the anus first from the blastopore 41
- 42. *You are going to compare spiral cleavage in a ribbon worm (a protostome) with radial cleavage in a sea star (a deuterostome) 42
- 43. *Spiral Cleavage: The Ribbon Worm, Cerebratulus unfert egg fert egg (zygote) 2 cell 4 cell 8 cell morula blastula gastrula later gastrula later in dev
- 44. *Radial Cleavage: The Sea Star, Asterias unfert egg fert egg early cleavage late cleavage blastula gastrula http://www1.broward.edu/~fsearcy/Zoology/index.htm
