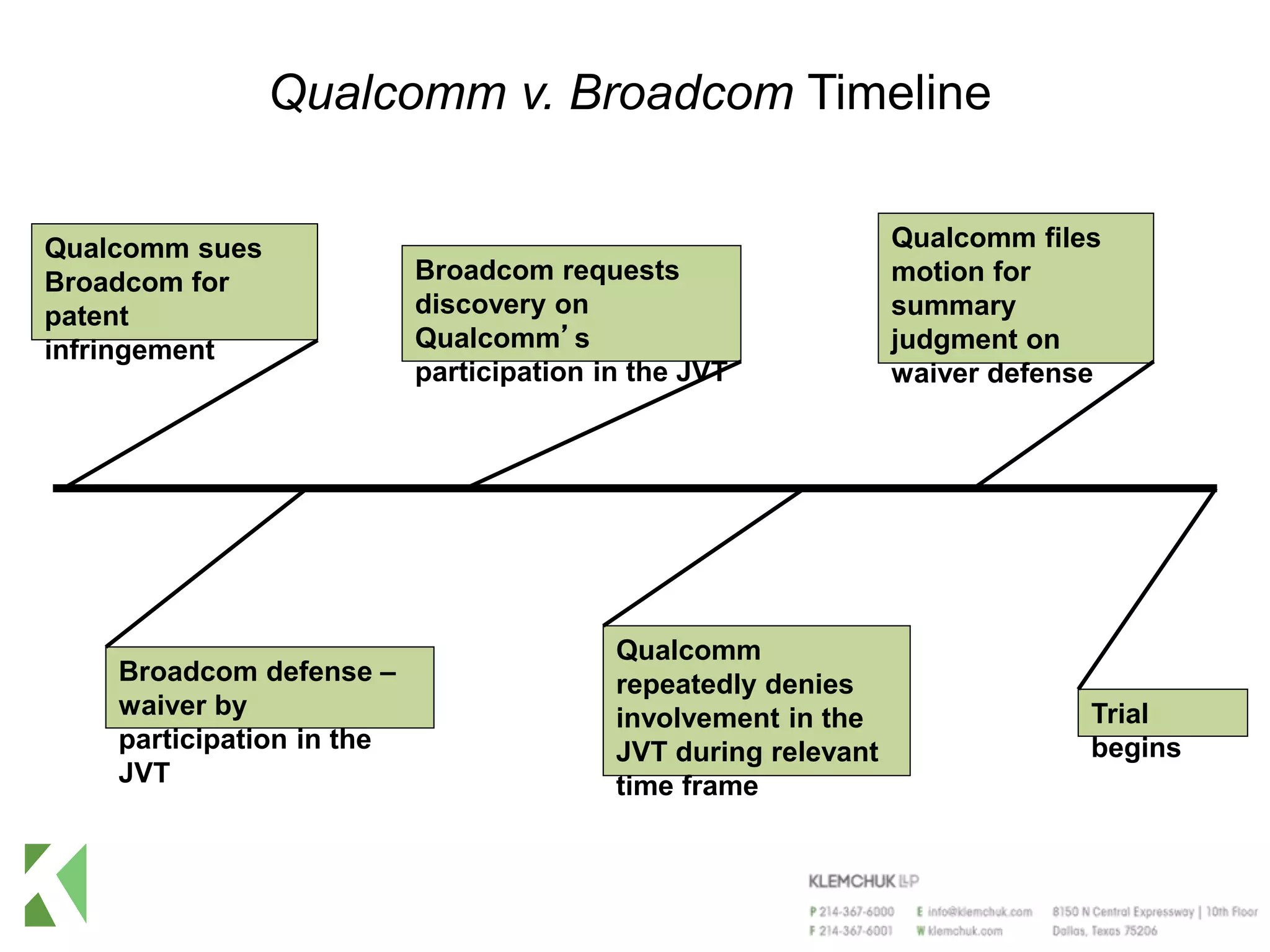
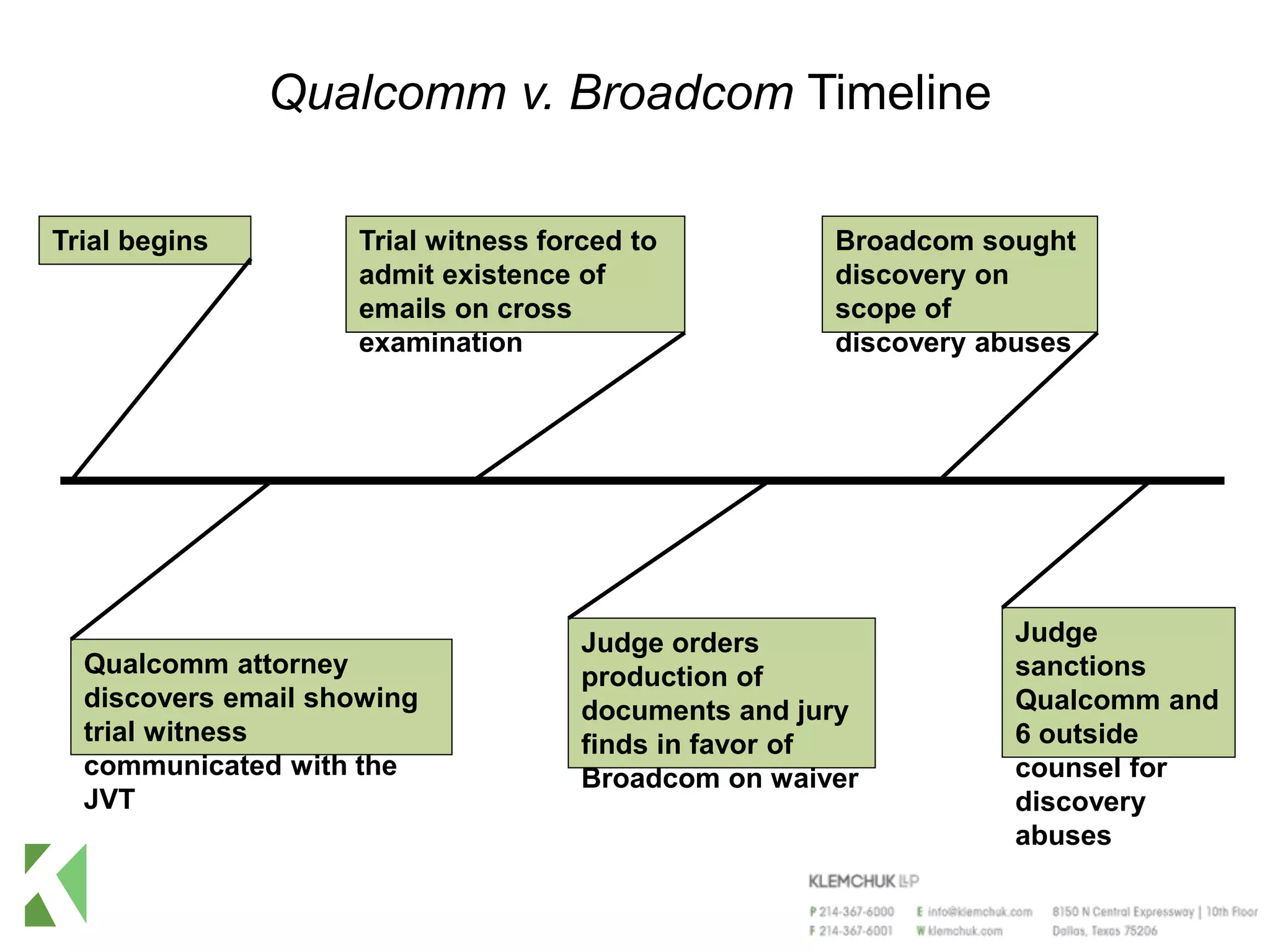
The document outlines the ethical issues surrounding electronic discovery in the case of Qualcomm v. Broadcom, highlighting significant discoveries and sanctions resulting from the trial. Key lessons include the importance of truthfulness in discovery, the necessity for outside counsel to ensure compliance with discovery obligations, and the need for effective document management strategies. Sanctions against Qualcomm included substantial financial penalties and referrals for outside counsel's ethical violations.