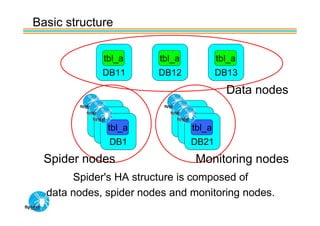
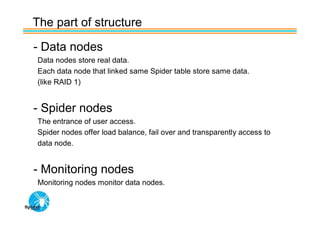
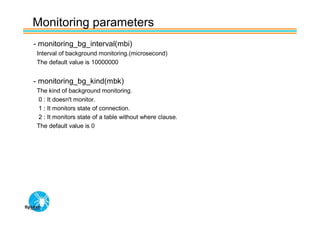
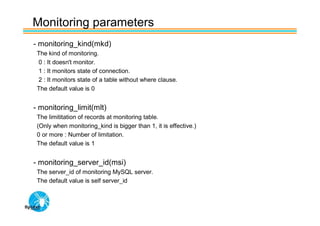
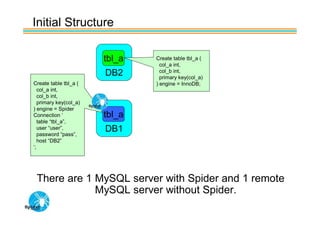
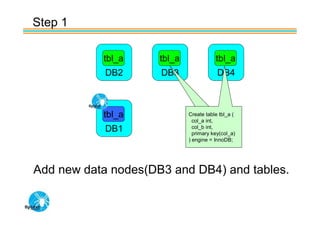
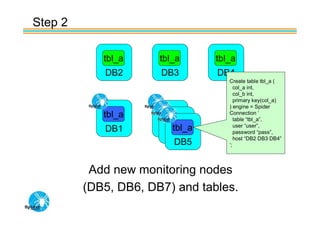
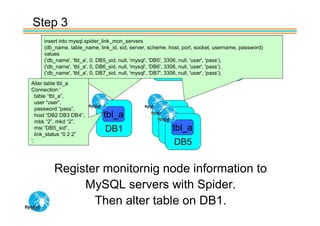
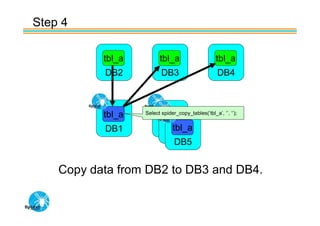
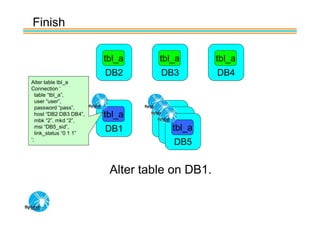
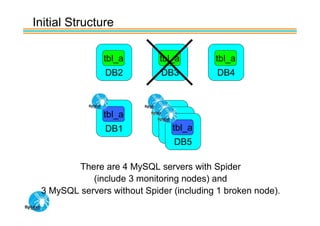
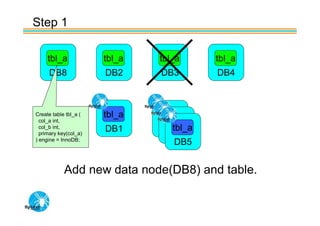
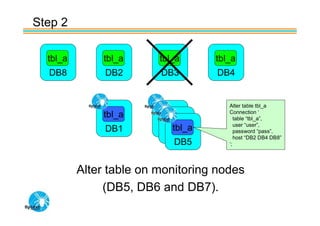
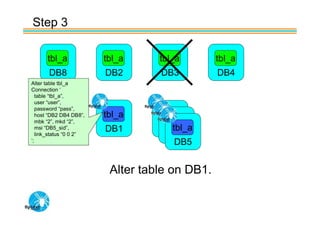
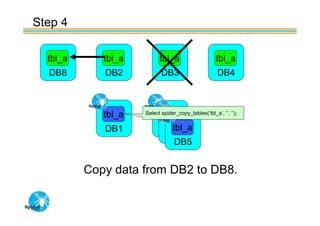
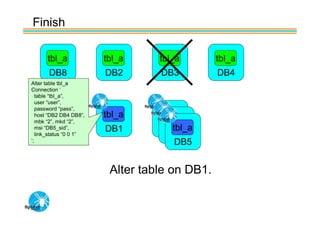
Spider's HA structure includes data nodes, spider nodes, and monitoring nodes. Data nodes store data, spider nodes provide load balancing and failover, and monitoring nodes monitor data nodes. To add a new data node without stopping service: 1) Create a new table on the node, 2) Alter tables on monitoring nodes to include new node, 3) Alter clustered table connection to include new node, 4) Copy data to new node. This maintains redundancy when a node fails without service interruption.