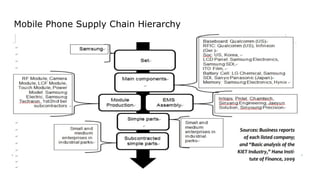
Samsung Electronics has a complex supply chain network in South Korea. It relies on subsidiaries it owns and controls as first-tier suppliers. Second-tier includes large component makers it depends on strategically. Third and fourth tiers are manufacturers and parts suppliers Samsung can replace if needed. The lowest tier includes small vendors competing on price. Samsung monitors workers closely to prevent unionization, though workers struggle for better health and associational rights. It pays high wages but exploits subcontractors, and production is flexible without minimum wages.