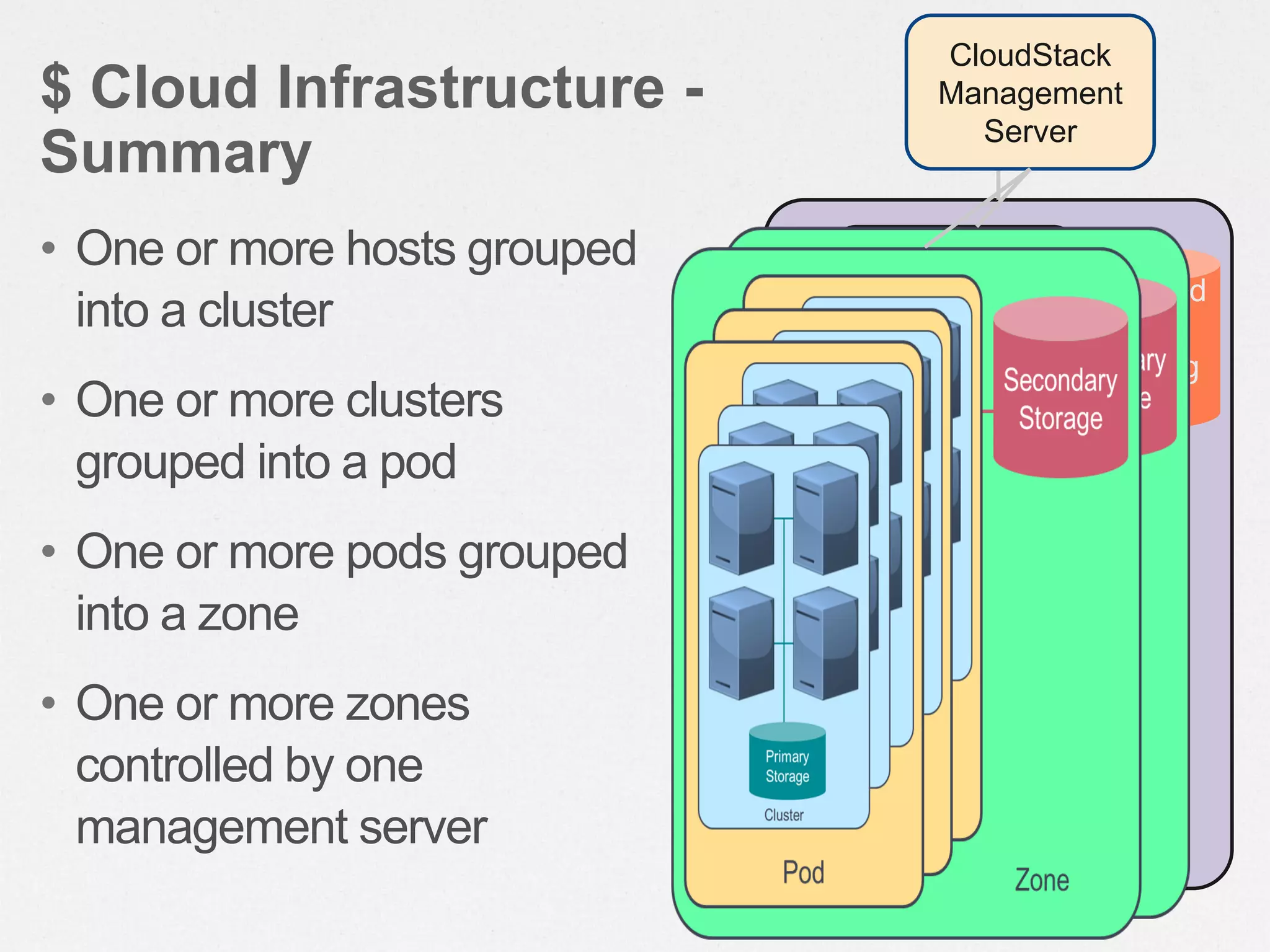
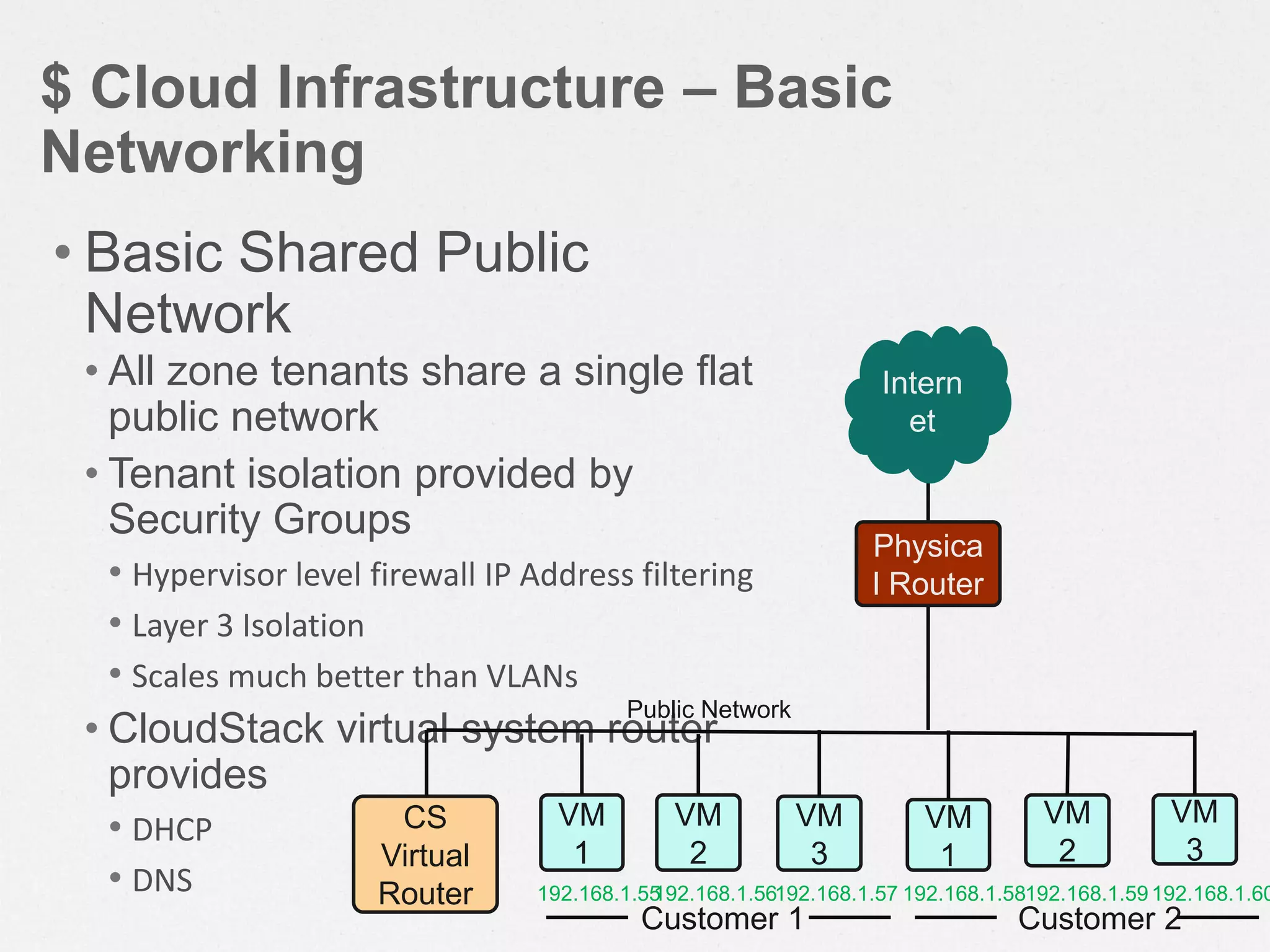
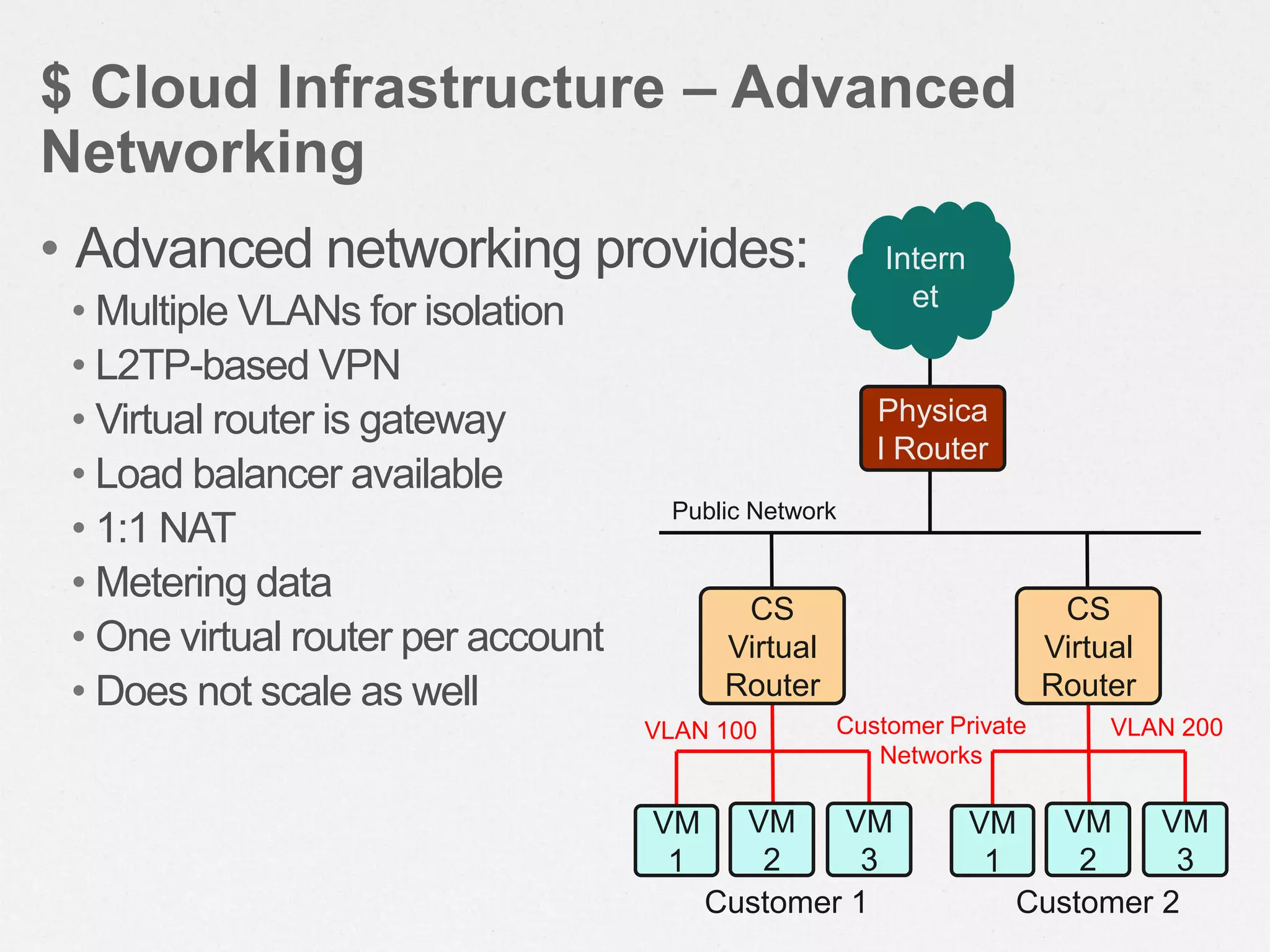
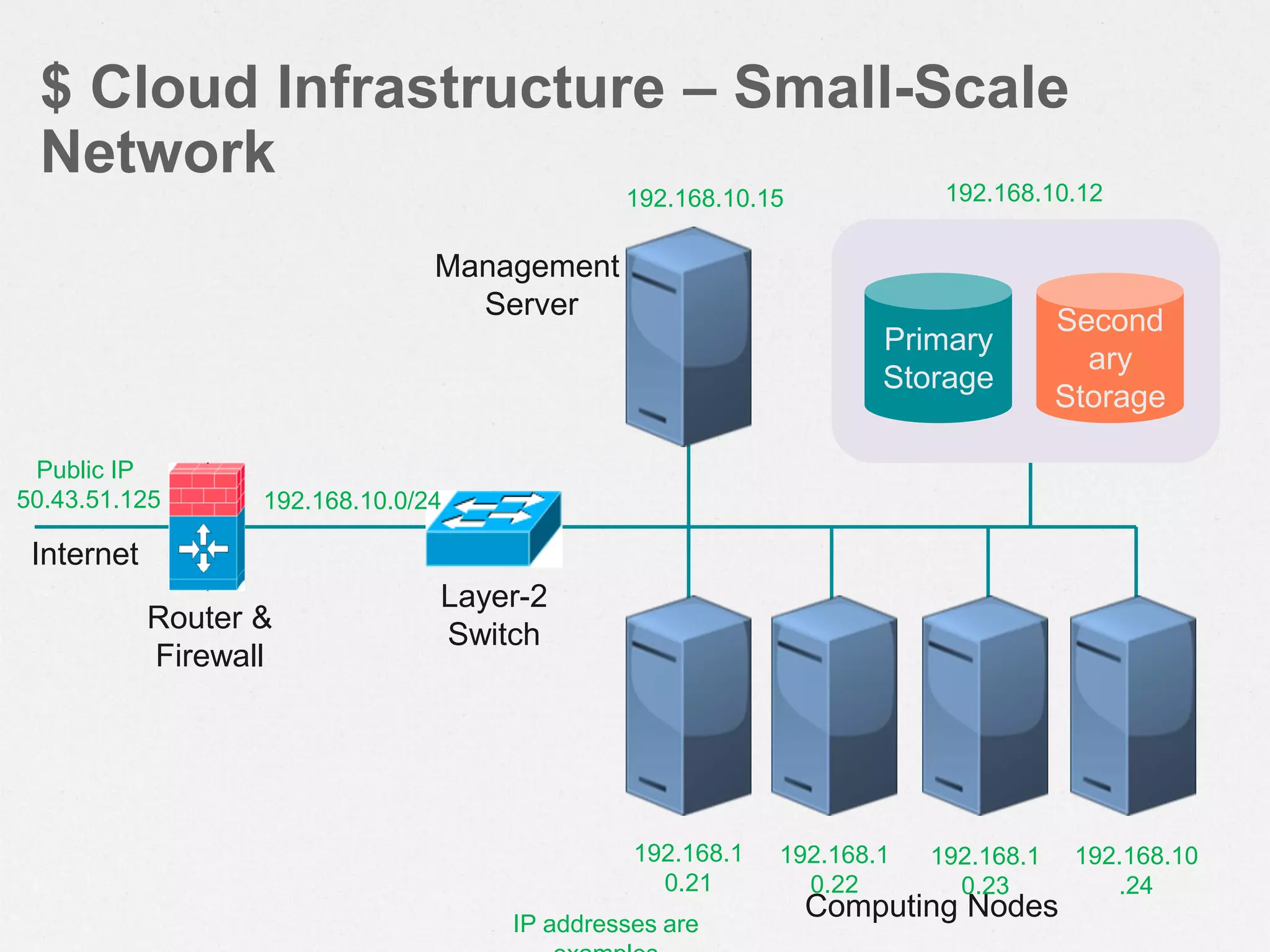
CloudStack is an open-source cloud computing platform that provides infrastructure as a service. It allows users to provision resources such as virtual servers and networking on demand through a self-service web portal. CloudStack can manage tens of thousands of servers across multiple geographically distributed datacenters and supports multiple hypervisors including XenServer, KVM, and vSphere. It provides high availability, scalability, and automation of infrastructure management.




![Server Virtualization++ Cloud
Built for traditional
enterprise apps & client-
server compute
• Enterprise arch for 100s of
hosts
• Scale-up (server clusters)
• Apps assume reliability
• IT Mgmt-centric [1:Dozens]
• Proprietary vendor stack
Designed around big data,
massive scale & next-gen
apps
• Cloud architecture for 1000s
of hosts
• Scale-out (multi-site server
farms)
• Apps assume failure
• Autonomic [1:1,000’s]
• Open, value-added stack
Think: vCloud Director Think: AWS, RAX, zCloud,
eBay, etc.
…but adoption of new
cloud architecture is the
future
Enterprises should, and
will, make SV 1.0 more
cloud-like…
• 10x more
scaleable
• 2-5x lower
cost
• 100% more
open](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudstackforbeginners-131120220046-phpapp01-151103125819-lva1-app6891/75/Cloudstack-for-beginners-7-2048.jpg)

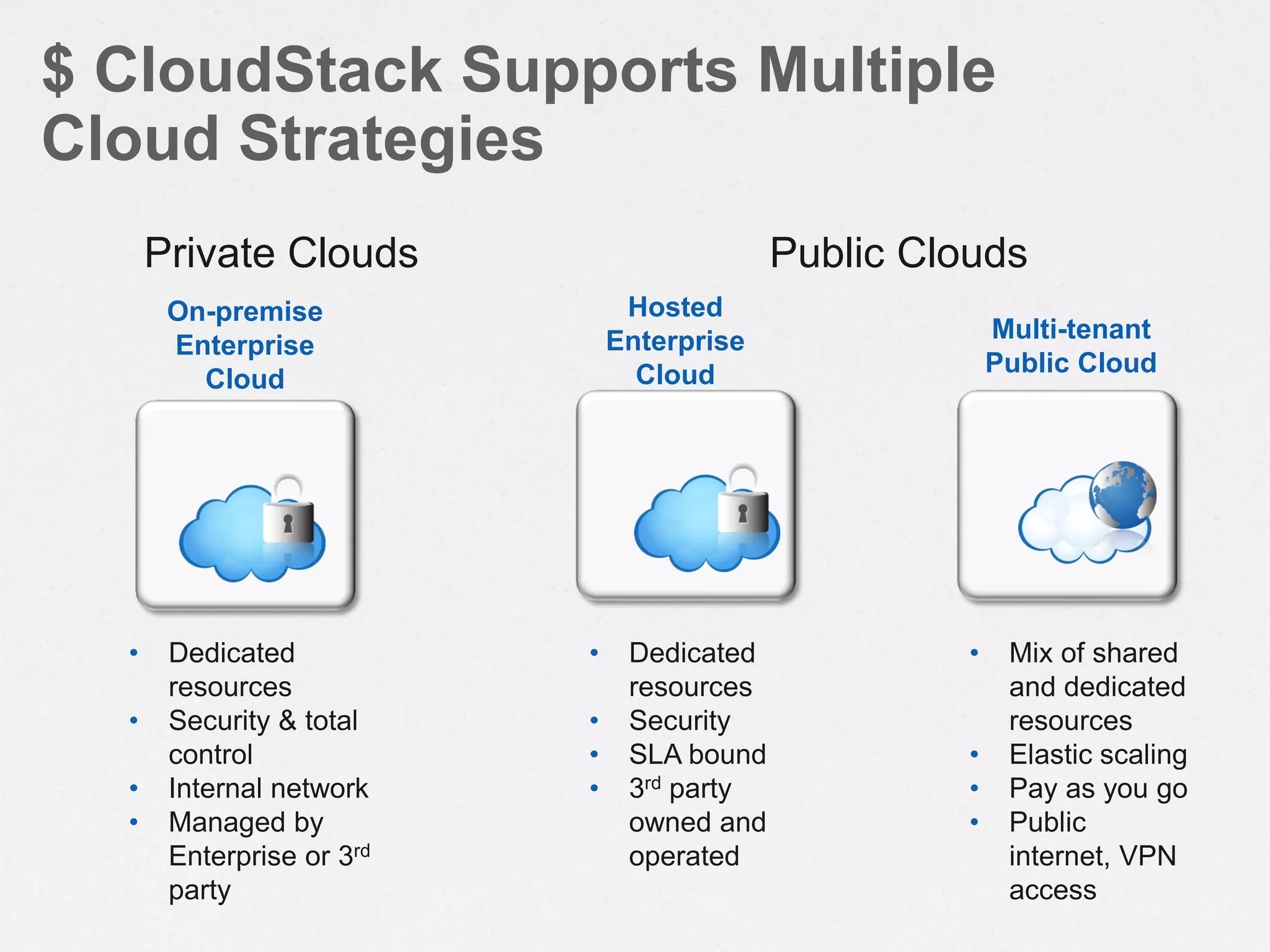
















![$ Configure the YUM repo
vi /etc/yum.repos.d/cloudstack.repo
[cloudstack]
name=cloudstack
baseurl=http://cloudstack.apt-get.eu/rhel/4.1/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudstackforbeginners-131120220046-phpapp01-151103125819-lva1-app6891/75/Cloudstack-for-beginners-54-2048.jpg)