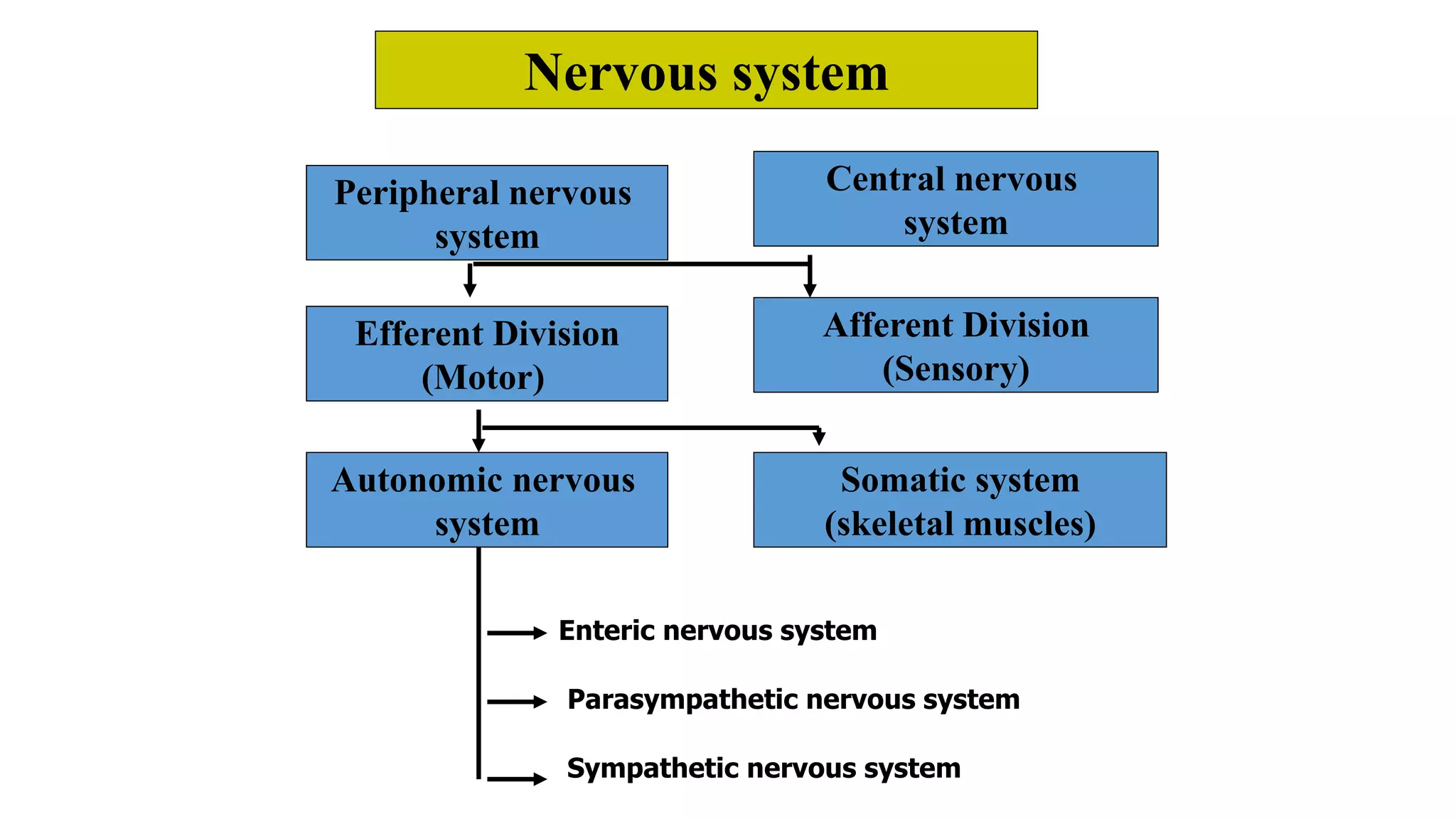
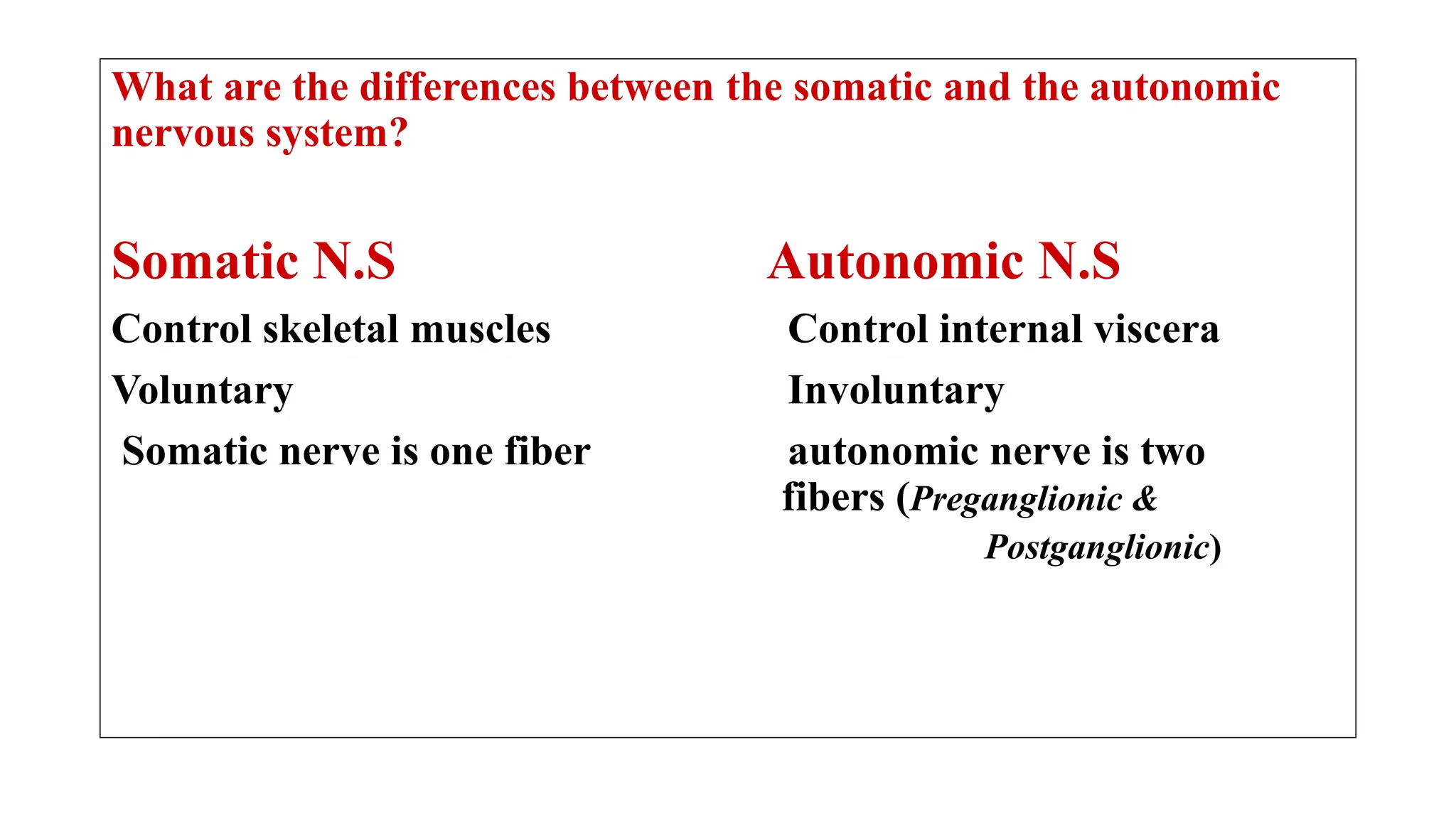
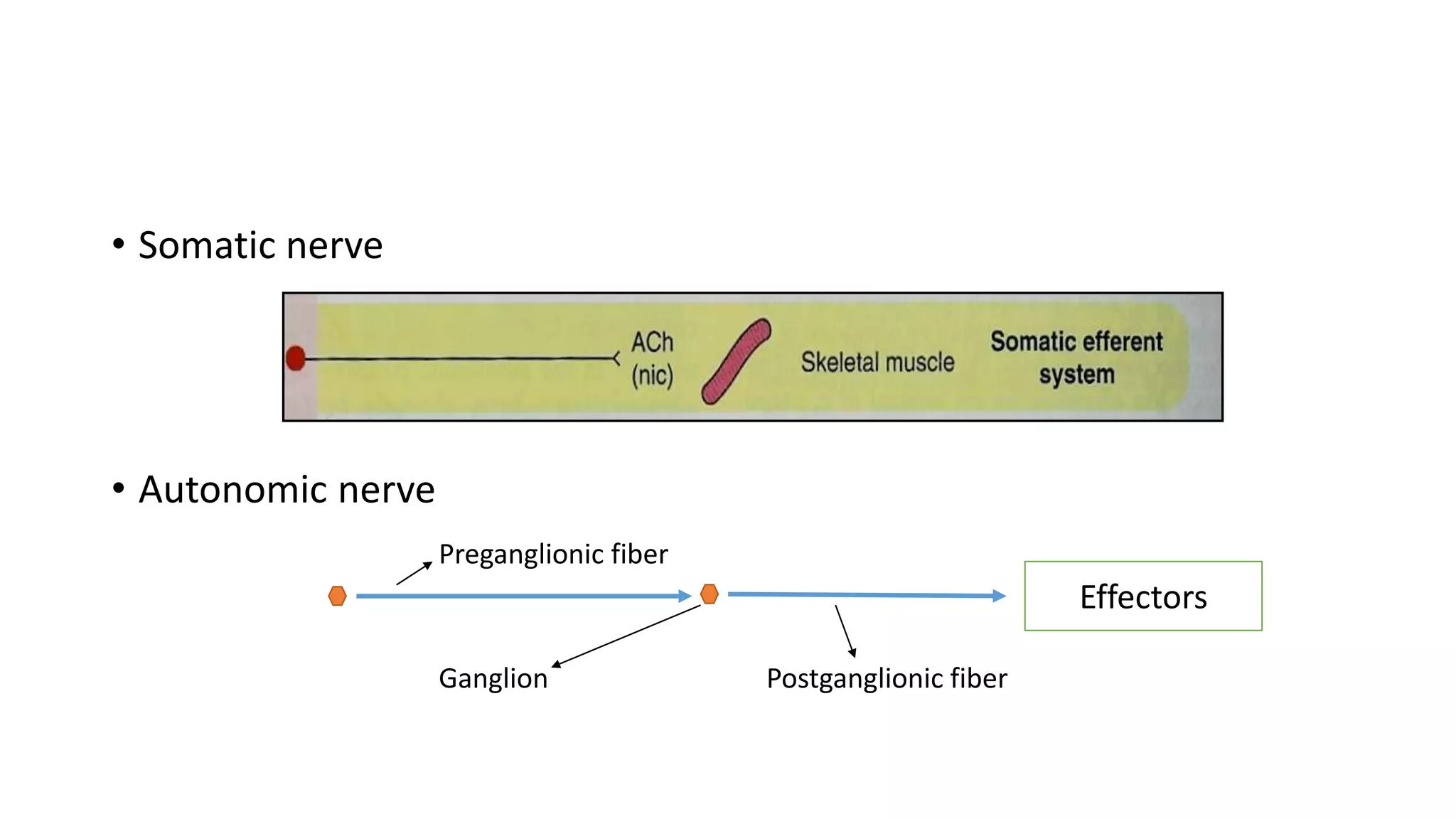
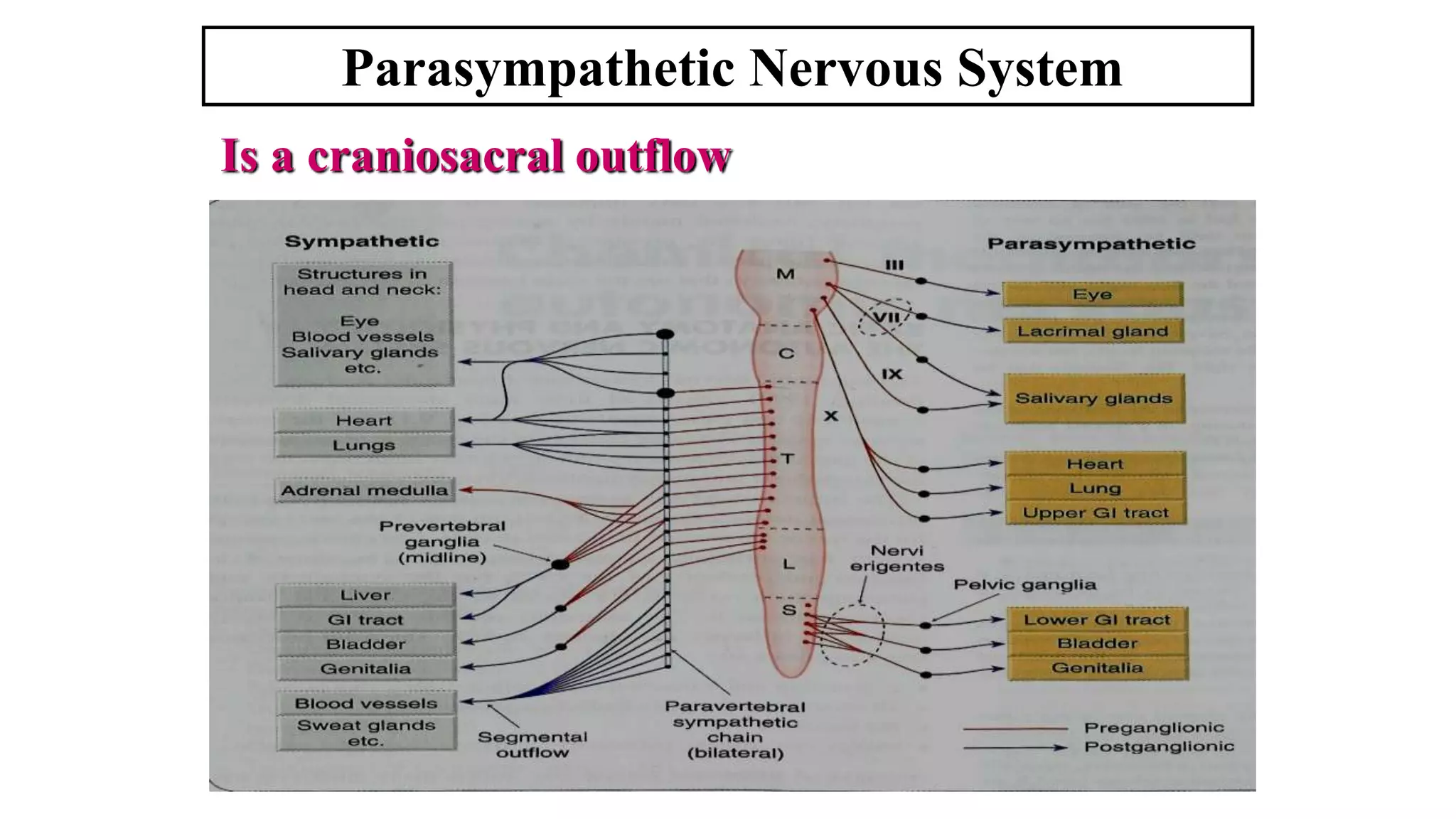
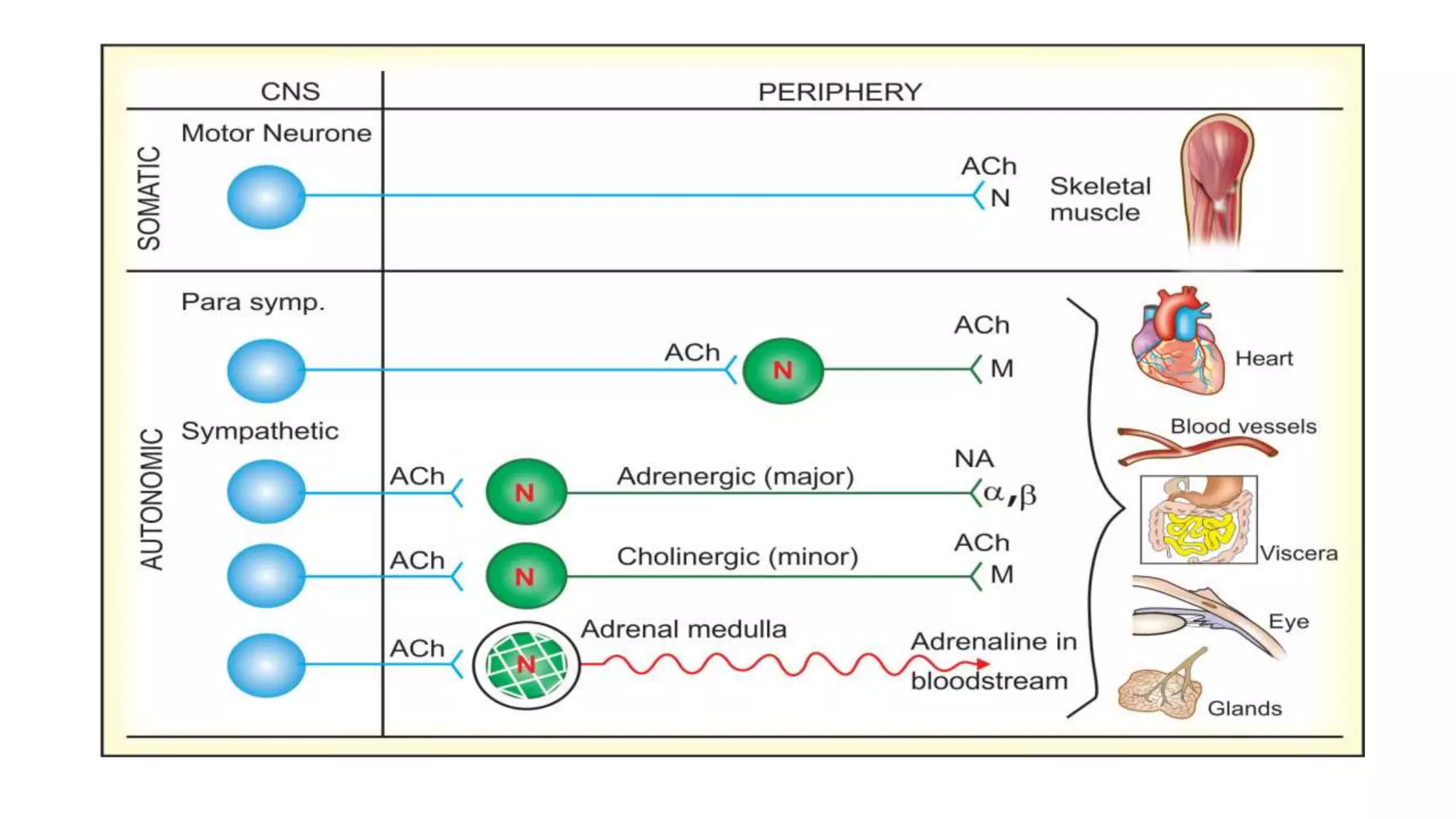
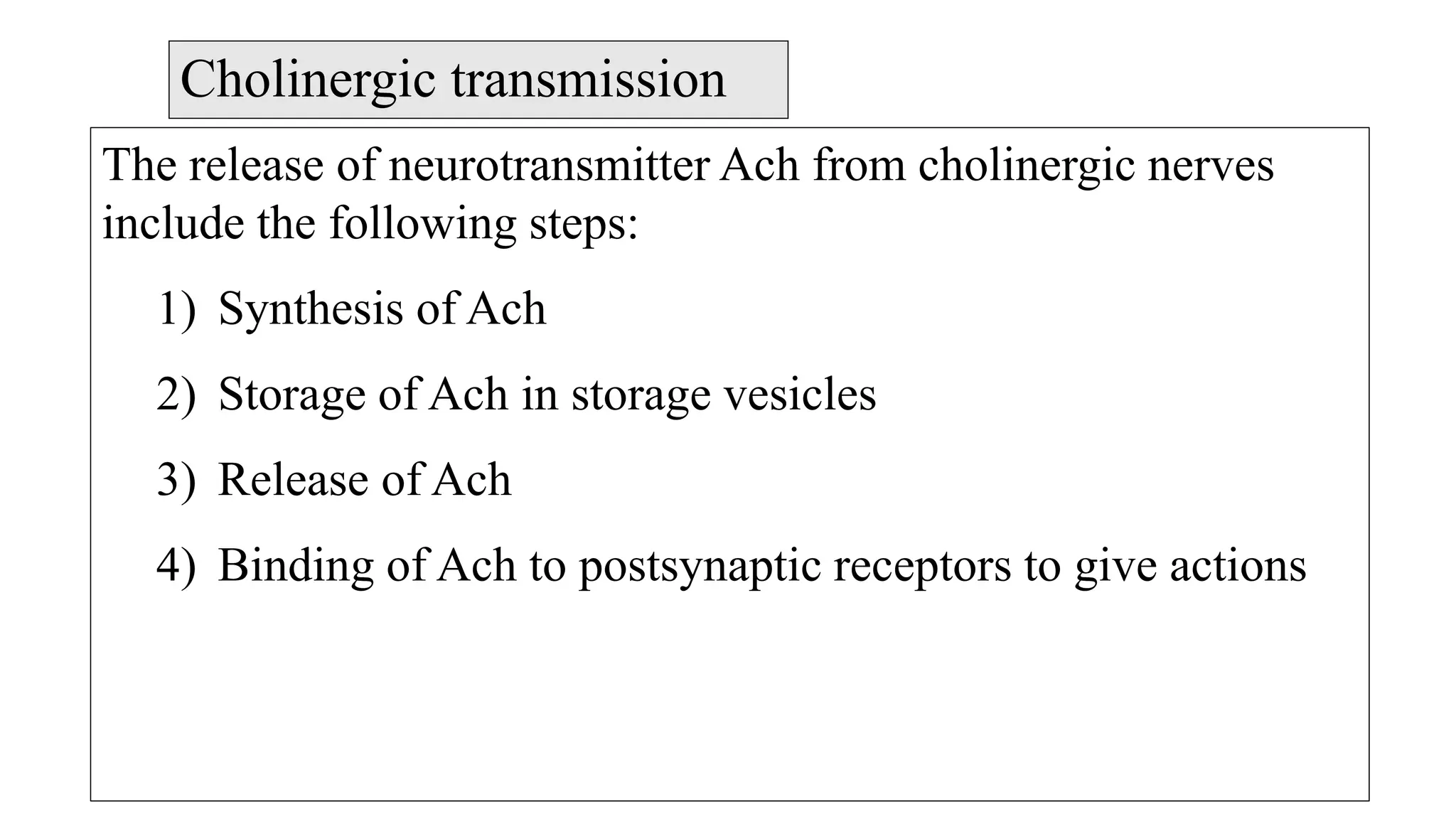
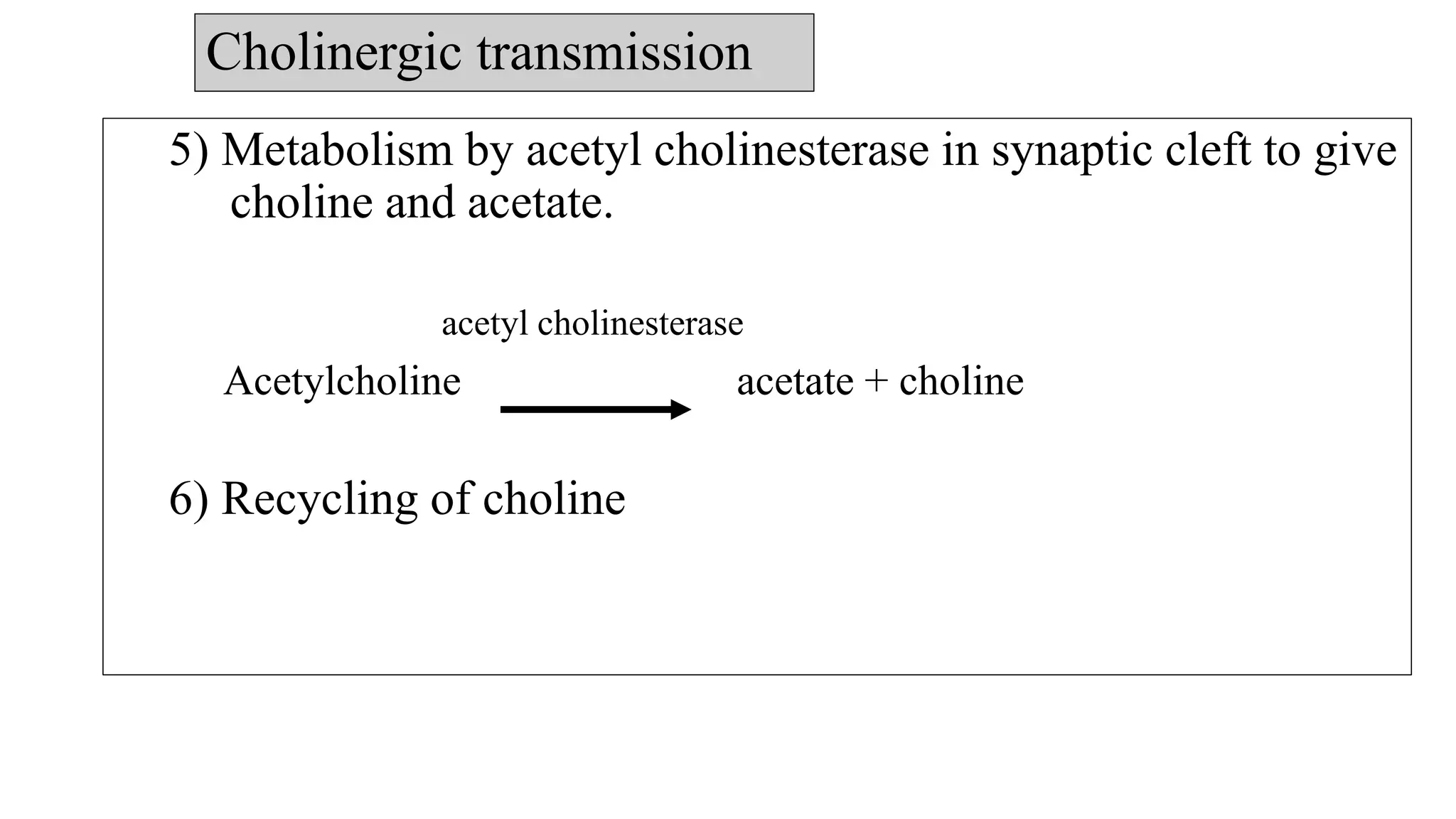
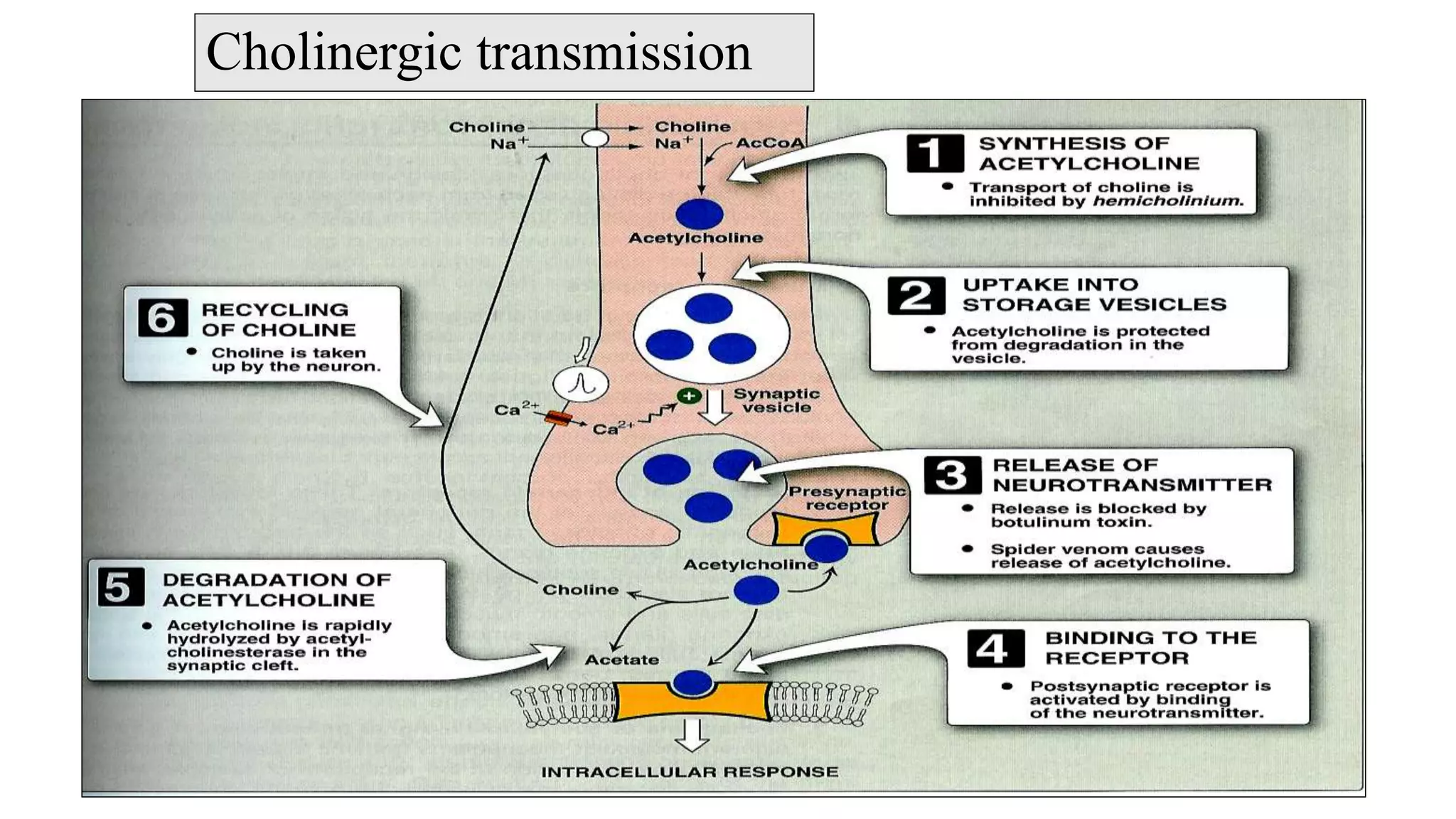
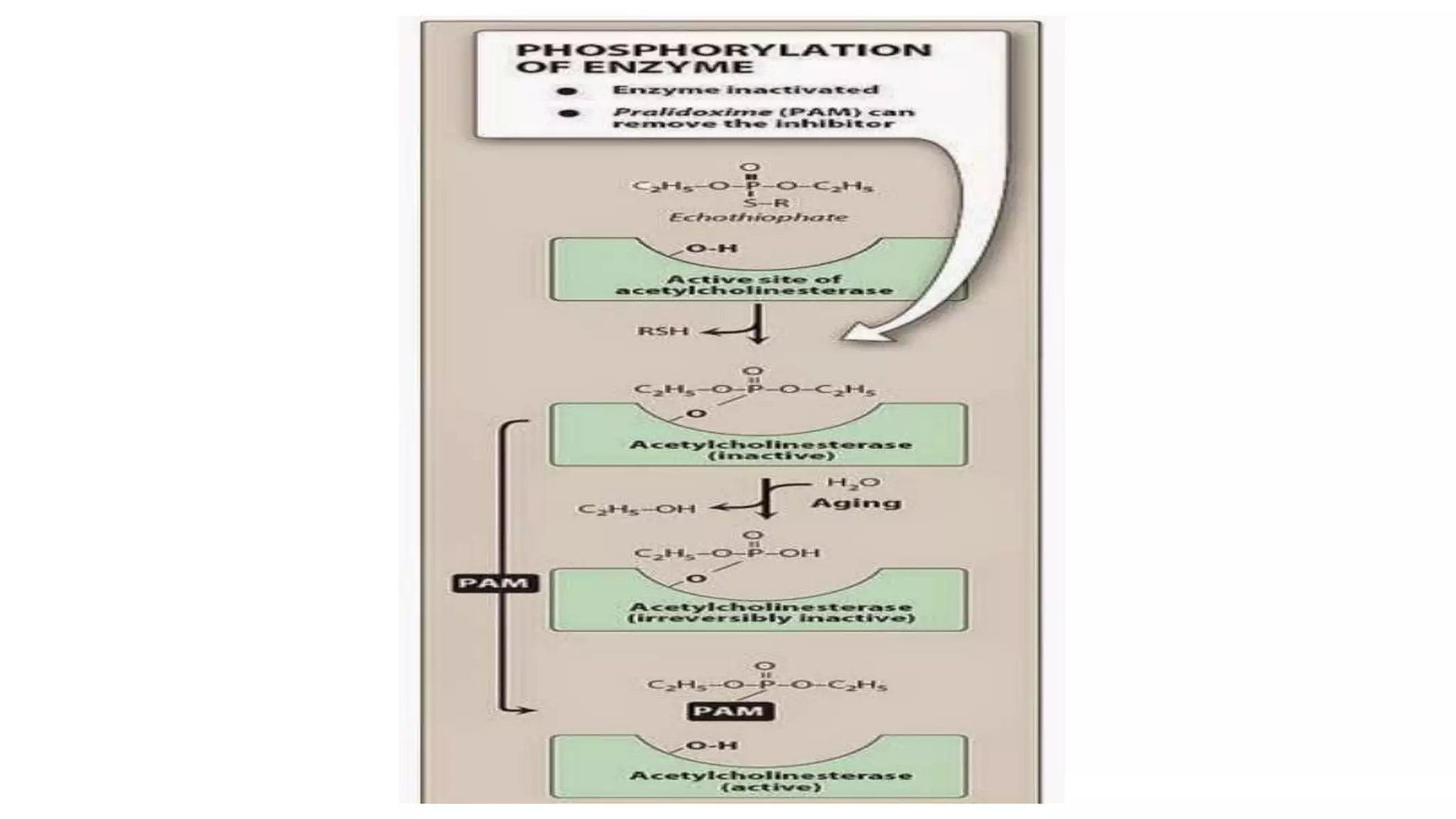
The somatic nervous system controls skeletal muscles voluntarily, while the autonomic nervous system involuntarily controls internal viscera. The autonomic nervous system consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Acetylcholine is the primary neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system and some parts of the sympathetic nervous system. Cholinergic transmission can be stimulated by direct-acting cholinergic agonists that mimic acetylcholine or indirect-acting anticholinesterase inhibitors that prevent the breakdown of acetylcholine.