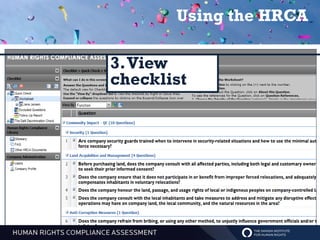
The Human Rights Compliance Assessment (HRCA) is an online tool designed for businesses to measure and enhance their adherence to international human rights principles. It provides a comprehensive checklist, assesses risks, benchmarks performance, and aids companies in preventing human rights violations while managing legal and reputational risks. The HRCA has been developed through extensive consultations and can be customized for different industries and operational contexts.








































![The HRCA in
Practice
Self-Application
The company conducts its own site visits and interviews,
with DIHR assisting in initial scoping and final data analysis
Novartis Indonesia tested a draft version of the HRCA tool for pharmaceutical
companies […] Testing the tool particularly improves the methodology and the
integration into existing management systems of pharmaceutical companies
— Novartis Communication on Progress, 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hrcapresentation-websiteversion-mba-020710-100708042500-phpapp02/85/Human-Rights-Compliance-Assessment-Presentation-43-320.jpg)








