final poster
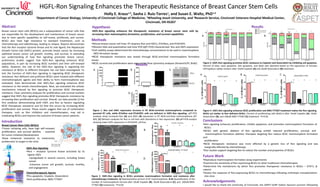
- 1. HGFL-Ron Signaling Enhances the Therapeutic Resistance of Breast Cancer Stem Cells Abstract Breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs) are a subpopulation of cancer cells that are responsible for the development and maintenance of breast cancer due to their specific capabilities to self-renew, proliferate, and survive. BCSCs also have high resistance to standard treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy, leading to relapse. Reports demonstrate that the Ron receptor tyrosine kinase and its sole ligand, the Hepatocyte Growth Factor-Like (HGFL) protein, promote breast cancer by increasing epithelial breast cancer cell growth, motility, and survival. In extending our understanding of how Ron signaling promotes breast cancer, preliminary studies suggest that HGFL-Ron signaling enhances BCSC populations, in part by increasing BCSC numbers and their self-renewal ability. However, the role of the HGFL-Ron signaling in regulating the resistance of BCSCs to different therapies has not been investigated. To test the function of HGFL-Ron signaling in regulating BCSC therapeutic resistance, Ron deficient and proficient BCSCs were treated with different chemotherapeutic agents and their ability to form mammospheres was evaluated. Data demonstrate that HGFL-Ron signaling enhances BCSC resistance to the tested chemotherapies. Next, we evaluated the cellular mechanisms induced by Ron signaling to promote BCSC therapeutic resistance. Flow cytometry analyses for proliferation and survival markers suggest that HGFL-Ron signaling promotes BCSC therapeutic resistance by increasing their proliferation and survival. Overall, our data provide (i) the first evidence demonstrating both HGFL and Ron as factors regulating BCSC therapeutic resistance and (ii) that this occurs by increasing BCSC proliferation and survival. These results suggest that use of combination therapies, such as Ron inhibitors and chemotherapies, may aid in eradicating BCSCs and improve the outcome of breast cancer patients. Methods •Mouse breast cancer cell lines: R7 (express Ron and HGFL), R7shRon, and R7shHGFL •Western Blot and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) characterized Ron and HGFL expression •Cell viability assays determined the chemotherapy concentrations to be used in mammosphere (MS) formation assays •BCSC therapeutic resistance was tested through BCSC-enriched mammosphere formation assays •BCSC survival and proliferation were assessed by flow cytometry analyses (AnnexinV/PI, BrdU) Holly E. Kraus1,2 , Sasha J. Ruiz-Torres1 , and Susan E. Waltz, PhD1,3 1 Department of Cancer Biology, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, 2 Wheeling Jesuit University, and 3 Research Service, Cincinnati Veterans Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH 45267 Results Figure 4. HGFL-Ron signaling enhances BCSC proliferation and BMS-777607 treatment makes the Ron signaling BCSCs act similar to Ron deficient BCSCs. Percent of proliferating cells (BrdU+) after 10uM Cisplatin (A), 10uM Doxorubicin (B), and 100uM BMS-777607 (C) treatment. *P<0.05 A B C Figure 2. HGFL-Ron signaling in BCSCs promotes mammosphere formation and resistance after chemotherapy treatment. A) Representative picture of R7 mammospheres. B-D) Quantification of the number of mammospheres formed after 10uM Cisplatin (B), 10uM Doxorubicin (C), and 100uM BMS- 777607 (D) treatments. *P<0.05 A B Hypothesis HGFL-Ron signaling enhances the therapeutic resistance of breast cancer stem cells by increasing their mammosphere formation, proliferation, and survival capabilities Conclusions •Ron signaling enhances proliferation, inhibits apoptosis, and promotes mammosphere formation of BCSCs •BCSCs with genetic ablation of Ron signaling exhibit reduced proliferation, survival, and mammosphere formation abilities; therapies targeting Ron reduce BCSC mammosphere formation and proliferation •BCSC therapeutic resistance was more affected by a genetic loss of Ron signaling and was marginally affected by chemotherapy •Our studies support targeting Ron to reduce the number and properties of BCSCs Future Work •Reproduce mammosphere formation assay experiments •Examine the sensitivity of Ron expressing BCSCs to other traditional chemotherapies •Determine the mechanisms by which Ron promotes therapeutic resistance in BCSCs – STAT1, β- catenin •Assess the response of Ron-expressing BCSCs to chemotherapy following orthotopic transplantation into mice Acknowledgements I would like to thank the University of Cincinnati, the ASPET-SURF Dalton Zannoni summer fellowship A A C D C B Figure 3. HGFL-Ron signaling promotes BCSC resistance to Cisplatin and Doxorubicin by inhibiting cell apoptosis. Percent of alive, early apoptotic, late apoptotic, and dead cells obtained based on the expression of Annexin V/Propidium Iodide markers after 10uM Cisplatin (A) and 10uM Doxorubicin (B) treatment. Introduction Breast Cancer Stem Cells (BCSCs) •Tumor initiating cells, have high self-renewal, proliferation, and survival abilities - essential for tumor initiation/development •Have enhanced resistance to treatments, problematic to target in the clinic * * D HGFL-Ron Signaling •Ron – receptor tyrosine kinase activated by its ligand, HGFL -Upregulated in several cancers, including breast cancer -Enhances tumor cell growth, survival, motility, and angiogenesis Chemotherapeutic Agents •Pro-apoptotic: Cisplatin, Doxorubicin •Anti-proliferative: BMS-777607 B Results Figure 1. Ron and HGFL expression increase in R7 BCSC-enriched mammospheres compared to parental R7 cells, while R7shRon and R7shHGFL cells are deficient in HGFL-Ron signaling. qRT-PCR analyses show increased Ron (A) and HGFL (B) expression in R7 BCSC-enriched mammospheres (R7 MS). (C) Western analyses for Ron in cell lines with alterations in Ron expression. (D) qRT-PCR analysis showing lower HGFL expression in R7shHGFL cell line.
Editor's Notes
- You can talk a little bit about how Ron signaling occurs (walk thru the Ron figure on the Introduction) I changed figures 1D and 3B.