safeguarding and child protection
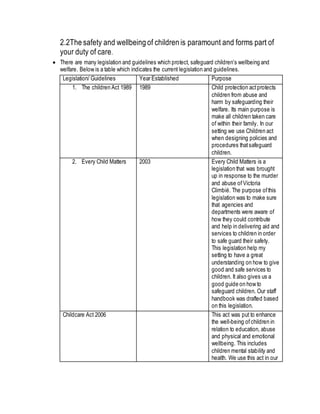
- 1. 2.2The safety and wellbeing of children is paramount and forms part of your duty of care. There are many legislation and guidelines which protect, safeguard children’s wellbeing and welfare. Below is a table which indicates the current legislation and guidelines. Legislation/ Guidelines Year Established Purpose 1. The children Act 1989 1989 Child protection actprotects children from abuse and harm by safeguarding their welfare. Its main purpose is make all children taken care of within their family. In our setting we use Children act when designing policies and procedures thatsafeguard children. 2. Every Child Matters 2003 Every Child Matters is a legislation that was brought up in response to the murder and abuse of Victoria Climbié. The purpose ofthis legislation was to make sure that agencies and departments were aware of how they could contribute and help in delivering aid and services to children in order to safe guard their safety. This legislation help my setting to have a great understanding on how to give good and safe services to children. It also gives us a good guide on how to safeguard children. Our staff handbook was drafted based on this legislation. Childcare Act 2006 This act was put to enhance the well-being ofchildren in relation to education, abuse and physical and emotional wellbeing. This includes children mental stability and health. We use this act in our
- 2. centre to manage children’s behaviour and their safety. EYFS 2008 Statutory Framework The framework was implemented to help children’s future through their early year’s experiences and social skills. We offer quality early years experiences in our nursery and give children opportunities to make choices. We take into consideration children’s happiness and achievements in order to enrich their developmentand their safety. Revised EYFS 2012, 2017 The framework was revised so as to strengthen cooperation and working together between parents and professionals. The revised EYFS states that unpleasant adult’s behaviour which might be abuse can be reported to safeguard the safety ofchildren. United Nations Convention on the Rights ofthe Child 1989 and the UAE joined in 1991 The Convention covers all aspects ofa child’s life .It set out all the rights that all children everywhere are entitled to. In the convection agencies and departments are recommended to fulfil children’s needs and protect them from violence, neglect and abuse. Italso explains how agencies and governments mustcooperate to ensure all children can enjoy all their rights. Every child has rights, whatever their race, gender, religion and abilities. The Convention also demonstrates how practitioners, families and governments should work
- 3. together to ensure that children enjoy their rights. Equality Act 2010 The act is a law that was put to safeguard children from ill- treated. It Protects children from indirect discrimination to those with disabilities and victimisation. Ministry ofInterior (MoI) established the Higher Committee for Child Protection 2009 and the MoI’s Child Protection Centre in 2011 The main purpose for the legislation was to keep children safe from violence, abuse and neglectfrom both schools and homes. The committee uplifts the safety of children since everyone is responsible for children’s safety and wellbeing. • Data Protection Act 1998 1998 It was put in place to protect personal data as well as improving confidentiality. It prevents people from unlawfully accessing other peoples information henceforth safeguarding children • Safeguarding Vulnerable Groups Act2006 2006 This act was passed to preventharm to children by restricting people who are not applicable to work with children. This involved people with criminal records. This act makes sure that people who are permitted to work with children are also being observed. 1.2 • Identify policies and procedures relating to the safeguarding, protection and welfare of children.
- 4. Policy Purpose Safeguarding Policy It is a child protection policy putto keep children safe from harm and also risk ofharm like negligence,violence and abuse. Accidentand IncidentPolicy It is a policy putup to preventaccidents from happening. It also provides the lines of reporting if harm or abuse are suspected. Allergy Policy This policy safeguards children who require special food diets or those with food allergies. Settings should work together with health departments and professionals so thatthey avoid the food they are allergic to. Anti-Bullying policy This policy protects and safeguards children from being bullied and harassed .Italso helps children to learn in a safe environmentwithout fear of being bullied or harassed.The policy provides medication and counselling to both children who are and notexperiencing bullying. Behaviour ManagementPolicy It promotes good child behaviour traits in children and show to ensure that they are learning on a safe environment. Drop off and Collection Policy The main purpose for this policy is to ensure that children are collected by the responsible person and make collection ofchildren smooth. This helps to ensure the safety and welfare of children as they are not collected by anyone else excepttheir parents or someone enlisted by their parentto collectthem thereby this policy promotes the safeguarding and protecting the welfare of children. Health and Safety Policy It is a policy that describes the roles and duties to help maintain safety at settings. This involves working ata safe environmentand also a safe environmentfor children to learn and play. LostChild Policy Children are distributed to members of staff. When a child is lost, people notify the person in charge oflooking after the child. If the child is not found then the police and parents ofthe child are informed. RiskAssessmentPolicy Thispolicywasput to inspectenvironments where childrenare fromharmand dangerto preventchildrenfromgettinghurt.
- 5. DiaperChangingandToiletingPolicy Thispolicywasput so that childrenare alwayschangedina cleanand safe area. FoodHandlingpolicy Thispolicyprotectsfromcontamination.This helpsdistributehealthyandsafe foodto children. IllnessPolicy Thispolicyisput upto ensure thatif a child becomesunwellata settingtheyshouldbe treatedwithcautionandrespect.Italso helpstoprotectand preventotherchildren fromthe spreadof illness. MedicationAdministration Policy Thispolicyis to encourage communication betweenparents,the child’smedication providerandthe settingtoassure that the childisgiventhe right medication.This policypromotes the safeguardingof children’shealth. No SmokingPolicy Thispolicypromotesahealthyand tobacco free environmentforchildren.This policy safeguards children’s healthandalsoprotect themfromhealthrisks. VisitorsPolicy Thispolicydoesnotprotectvisitorsonlybut childrenalso.Thispolicysafeguardsand protectschildrenfromvisitorsorstrangers whomighthave a criminal record. Mobile Phone andCameras Policy Thispolicyhelpsinsafeguardingand protectingchildrenasmobile phonesor camerasmay cause risk to children.This policyavoidsstaff toignore children’ssafety because of mobile phonesandalsoto parents,mobile phonesandcamerasare not allowedatsettingsasa parentor guardian may mistakenlytake anotherchild’spicture hence the breakof confidentiality. 1.3 • Analyse how current legislation and guidelines for safeguarding inform policy and procedure. The Children Act2004 states that individuals should team up to protectand uplift the wellbeing and health of children based on The Children’s Act2004.It uplifts the notion that everyone is responsible for the protection and safety of children. Practitioners should work hand in glove and in partnership
- 6. with agencies and departments as well as the family of the child. The practitioners should work with departments like health department, education departmentand children’s social care justto mention a few. When making decisions they mustinvolve the departments and respectwhatthe child say and the parents’ views The role for this regulation is that practitioners caring for children must partner to protectand improve children’s lives. Everyone in the setting has a duty to meetthe safeguarding, protection and welfare requirements ofall children. • Practitioners need to be aware of the lines ofreporting and responsibility in their setting. • There will be designated people to reportto within the setting if there is a concern or problem. • Practitioners need to know who to go to if they have a concern or a question over the safeguarding, protection and welfare ofchildren. Lines of reporting and responsibility To ensure all staff and volunteers are aware of what they should do and who they should go to if they are concerned thata child/young person may be subjectto any form of abuse; To ensure any concerns abouta child/young person are acted on promptly,clearly recorded, referred on where necessary and, followed up to ensure the issues are addressed; To record any reported incidents in relation to a child/young person or breach ofChild Protection policies and procedures.This must be keptin a secure place and its contents must be confidential; To ensure any concerns aboutthe actions of any member ofstaff, volunteer, or person living or working on the premises are acted on promptly, clearly recorded,referred on where necessary and followed up to ensure the issues are addressed; To cooperate with the registered provider and make sure they are entirely aware of any significant concerns within the setting; To ensure information is shared when necessary, in line with Working Together to Safeguard Children guidance, and that information and records are passed on to the appropriate person ifthe child transfers to another setting or school. . 2.1 • Explain the roles and responsibilities ofthe early year’s practitioner in relation to the safeguarding, protection and welfare of children. . Practitioners should work hand in glove and in partnership with agencies and departments as well as the family ofthe child. The practitioners should work with departments like health department, education departmentand children’s social care justto mention a few. When making decisions they mustinvolve the departments and respectwhat the child say and the parents’ views .The role for this regulation is that practitioners caring for children must partner to protect and improve children’s lives 2.2 • Describe the lines ofreporting and responsibility to meetthe safeguarding, protection and welfare requirements ofchildren. Taff member: Studenton placement/ volunteer Responsibility: to follow policies or procedures and to summon further assistance in the eventof an accident, incidentor emergency. May need to reportto: whoever is acting as placementsupervisor or, in the eventofan emergency, any mem,ber ofstaff. Staff member: member ofstaff with a current paediatric first aid qualification.
- 7. Responsibility: to provide immediate assistance in the eventofa medical emergency. They may provide direction to others – for example, ask them to call for an ambulance. May need to reportto: medical teams in the eventof a child needing medical attention. Staff member: health and safety/ fire officer Responsibility: to ensure thatthe health and safety/ fire policy is being followed and to advise the manager as to how to make improvements. Should acton reports by members ofstaff aboutfaulty equipmentand potential hazards. May need to reportto: depends on setting butusual;ly deputy, manager or head teacher Staff member: deputy Responsibility: to take on the responsibilities oin the absence ofthe manager. To take specific 7ssential7lities for health and safety in some roles. May need to reportto: mananger Staff member: Manager/head teacher Responsibility: to ensure the smooth running ofthe setting. To ensure that all policies relating to health and safety are being followed. May need to reportto: Parents in the eventofa serious injury, incidentor emergency Staff member: director/owner/governors Responsibility: to take on the legal responsibility in the eventthat an accident, incidentor emergency is the fault of the setting May need to reportto: Healthy and Safety Executive , Ofsted 2.3 Explain the boundaries ofconfidentiality in relation to the safeguarding, protection and welfare of children. Remember to include GDPR. The principles and boundaries ofconfidentiality are to do with safeguarding children and young people. The principle – or main reason for having confidentiality in settings is to maintain positive, supportive, respectful relationships with children and young people thatrecognises each individual’s rightto privacy, their right to protection and their right to free expression. This could be done by finding quietless public areas for discussing information, ensuring information given within a setting isn’t repeated outside ofthe setting for less professional reasons, everyone connected with a setting understands how sharing information relating to safeguarding is valued and welcomed.A boundary ofconfidentiality is that it isn’t always appropriate/safe to keep information confidential where there may be a risk of harm to a child or young person. The boundaries ofconfidentiality are in place to keep the information of children, parents, carers and the members ofstaff confidential. It is the responsibility ofall the members ofstaff to keep the records ofchildren and staff members, which contains personal information safe and confidential. This information should notbe shared with other agencies and people unless itis 7ssential. If sharing personal information is needed in order to protecta child then it should be shared on ‘need to know’ basis. This means that the
- 8. information should only be shared with people or agencies who are supposed to know itand who can play an important role in protection ofchildren. All the computerized records should be secured and have password on it. Contactnumbers of the parents of children and the photographs ofchildren should notbe kepton personal mobile phone. Schools, nurseries and early years settings have policies and procedures in place which mustbe followed to keep children and other people safe. Sometimes some unsuitable and unsafe people getinto the childcare profession and cause harm to children. Like the case ofVanessa George, who was a nursery nurse and she abused children by taking their inappropriate pictures, while changing their nappies and sentthem to pedophiles.Ifthe nursery’s policies ofmobile phone and intimate care had been followed then this would not have happene In general, itis essential that early years and childcare childcare workers respectconfidentiality and keep all sensitive information confidential. This is essential whether in a early years setting, a care setting, school, the home and any other organisation dealing with children and their families/carers. Publishing personal information aboutchildren without due care may cause parents/carers to feel vulnerable and at risk of harm. As a result, they may be reluctant to share information with members of staff in case it is disseminated to others. Ifchildcare workers gather personal information about children, their privacy needs to be respected.Others trust childcare workers to keep such information confidential. In dealing with personal information, the needs ofeveryone have to be considered carefully. Information about a child or young person should notbe collected or retained without the permission of the parents/carers and they should have open access to itif they wish. Information should only be shared with professionals with the formal permission ofparents/carers, by signature. The only exceptions are the small number ofcases where a child may be at risk of directand substantial harm if information is shared with a parent/carer. It is necessary to be aware ofprofessional rules ofconfidentiality. Unfortunately, situations arise when childcare workers are expected to share information in order to protectthe welfare of the child. They have a duty to do so. Any matters involving the safeguarding ofchildren must be referred to a line manager or senior member ofstaff. It may be necessary to share some information with other professionals such as: the social services, the police or the National Society for the Prevention ofCruelty to Children (NSPCC). Only information essential for professionals to be able to offer a service for the benefitand welfare of the child and the parents/carers should be shared. If parents/carers discuss confidential matters with childcare workers, itis important that they have been informed ofthe setting’s confidentiality and child protection policy. They need to know that information they share may be shared with a line manager if the childcare worker feels that they should do so. Parents/carers need to know that childcare workers are entitled to breach confidentiality as they have a responsibility to consider the health and welfare of the child primarily. A copy ofthe All Wales Child Protection Procedures should be available in the setting for parents/carers to view and staff to refer to.
- 9. If parents/carers want to ask advice on a matter, it is suggested thatthey are referred to other workers. If they give certain types ofprivate information, it will be necessary to explain that it cannot be keptconfidential and that the information must be shared. A childcare worker may have noticed signs ofunexplained physical harm or is concerned abouta significant change in a child’s behaviour. They may receive a valid explanation from the parents/carers but discussions should not be held with parents/carers ifthis could endanger the child in any way. The advice ofsocial services must be soughtin the case ofany uncertainty. Childcare workers must reconsider the rules relating to confidentiality if a child ‘discloses’ thatthey are being abused or have been abused in the past. The situation is the same whether sensitive information is received from children or parents/carers. This information must be shared with the line manager, and then with other agencies such as social services, the police or the National Society for the Prevention ofCruelty to Children (NSPCC). If a child shares information with a childcare worker, itmust be explained thatthe information cannot be keptconfidential. It might to tempting to allow the child to talk, without explaining the situation on confidentiality. Unfortunately, this would be poor practice as itmisleads the child into thinking that the childcare worker is going to keep something confidential when they are unable to do so. Childcare workers have a duty to reportany concerns aboutpossible harm, abuse or neglect. In doing so they: protectthe health and welfare ofthe child justify that children are entitled to be protected by adults protectthe health and welfare ofparents/carers deal with information appropriately and as quickly as possible show the employee’s concern for the child show the child that the childcare worker believes his disclosure builds up the trust of the child displays the courage to be able to protectthe child; the child will remember this ensures that the correctagencies supportthe child safeguards and protects the child from further abuse ensures that actions do notinterfere with any legal process againstthe abuser ensures that a person who has abused in the pastdoes notwork with children behaves in a professional manner – takes the matter seriously and treats the situation carefully and fairly is able to refer the child to specific agencies to enable them to receive help and supportto recover from the trauma The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is an EU law that came into effect on 25 May 2018.
- 10. It replaced the currentData Protection Act1998 and the changes remain in place even though the UK has left the EU. GDPR gives individuals greater control over their own personal data. Your nursery or early years setting may already have a data protection policy in place butGDPR introduces some significantchanges in what is needed. Early years providers need to be aware ofthese changes and make changes in order to be compliant You must have a lawful reason for collecting personal data and must do it in a fair and transparent way. You must only use the data for the reason it is initially obtained. You must not collectany more data than is necessary. It has to be accurate and there must be mechanisms in place to keep itup to date. You cannot keep itany longer than needed. You must protectthe personal data. 2.4. Analyse the benefits of partnership working in the contextofsafeguarding, protection and welfare of children . Responding to evidence or concerns a child may have been abused or suffered some harm needs your full understanding. Through researching the above legislation and looking into your setting policies and procedures complete the following points: 33.1 Explain child protection in relation to safeguarding. 3.2 Describe signs, symptoms, indicators and behaviours thatmay cause concern relating to domestic abuse neglect physical abuse
- 11. emotional abuse Sexual abuse. 3.3 Describe actions to take if harm or abuse is suspected and/or disclosed. 3.4Explain the rights ofchildren and parents/carers in situations where harm or abuse is suspected or alleged. • 3.5Explain the responsibilities ofthe early year’s practitioner in relation to whistleblowing. Through reading pastserious case reviews like Baby P or Victoria Climbie you will then be able to complete the following points: Whistleblowing is an important aspectofsafeguarding . 4.1 Explain why serious case reviews are required. When a child dies or is seriously harmed as a resultofabuse or neglect, a review may be conducted to identify ways that professionals and organisations can improve the way they work together to safeguard children and preventsimilar incidents from occurring. Each UK nation has its own terminology and guidance for carrying outand sharing the learning from the reviews. Cases that meetthe criteria setout in the relevantguidance are reviewed by multi-agency panels 4.2 Analyse how serious case reviews inform practice.