Bhupendra Jain
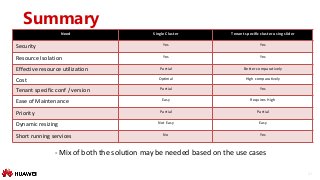
In a multi tenant scenario the biggest challenge is to achieve the QoS for each tenant without impacting the other tenants workload. This session will talk about the multi tenancy use cases and challenges present in HBase. Session will talk in detail about
a) Achieving Multi tenancy with Single HBase cluster - Solutions, Pros and cons (RS Group, RPC Throttling, Quota etc.)
b) Achieving Multi tenancy with multiple HBase cluster - Solutions, Pros and cons.
hbaseconasia2017 hbasecon hbase https://www.eventbrite.com/e/hbasecon-asia-2017-tickets-34935546159#
















![18
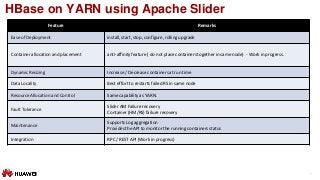
HBase on YARN using Apache Slider
Slider is a YARN application to deploy non-YARN-enabled applications in a YARN cluster
Slider client: Communicates with YARN and the Slider AM via remote procedure calls and/or REST requests
Slider AM: Application master to manage containers( actual application)
Slider Agent: Communicate with AM and mange one container instance.
Component : HBase application component. [ HM,RS etc.]
https://slider.incubator.apache.org/
http://events.linuxfoundation.org/sites/events/files/slides/apachecon-slider-2015.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/track1-2-170807123820/85/hbaseconasia2017-HBase-Multi-tenancy-use-cases-and-various-solution-18-320.jpg?cb=1502114990)