Weekly Report of AACRA Practice site visit.docx
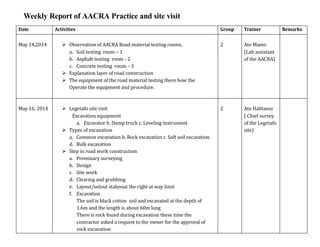
- 1. Weekly Report of AACRA Practice and site visit Date Activities Group Trainer Remarks May 14,2014 Observation of AACRA Road material testing rooms. a. Soil testing room – 1 b. Asphalt testing room - 2 c. Concrete testing room – 3 Explanation layer of road construction The equipment of the road material testing there how the Operate the equipment and procedure. 2 Ato Mamo (Lab assistant of the AACRA) May 16, 2014 Legetafo site visit Excavation equipment a. Excavator b. Dump truck c. Leveling instrument Types of excavation a. Common excavation b. Rock excavation c. Soft soil excavation d. Bulk excavation Step in road work construction a. Preminary surveying b. Design c. Site work d. Clearing and grubbing e. Layout/setout stakeout the right at way limit f. Excavation The soil is black cotton soil and excavated at the depth of 1.6m and the length is about 60m long There is rock found during excavation these time the contractor asked a request to the owner for the approval of rock excavation 2 Ato Habtamu ( Chief survey of the Legetafo site)
- 2. May 21, 2014 Site visit of around Balderas site i. The span of the road 20m and the length around 1km long. ii. Constructing of retaining wall iii. Segregating of water iv. Base course preparation by mixing of 00, 01, 02 aggregate size and the thickness is 25mm v. The moisture content of the base course 2 Engr. Tilahun
- 3. I. Trainees Name sign 1. Aregahegn Tilahun 2. Ashebir Mathewos 3. Asmera Taye 4. Awol Shengo 5. Ayele Mamo 6. Belaynesh Mekonnen 7. Belete Aweke 8. Bikila Asefa 9. Dawit Keba II. Checked By Ato Mamo (AACRA Lab Testing Assistant Representative) Ato Habtamu ( Chief survey of the Legetafo site) Engr. Tilaun (Contractor of the Balderas site) Engr. Ramil D.Henares (Instructor of Tunnels) Ato Tsegaye W/Tsedik (Dept. Head FTTI)
- 4. a. Soil testing room – 1 According to the soil foundation of the road classified in to three types. (i) Sand. Sand is a disintegrated rock whose particles vary in sizes from 6 mm to o.o5 mm. Sand is further classified as coarse or fine sand depending upon the grain size. The sand is a granular and non-cohesive material. (ii) Silt. This is very fine sand and is a granular material having particles of size smaller than 0.05 mm. It is a no cohesive material and has little or no strength, and compacts very poorly. (iii) Clay. Clay is a cohesive material having particles of microscopic size. Due to cohesiveness these have high strength when dry. These changes in volume considerably with the variation of moisture contents. The strength of these soils can be increased by blending with granular soils. b. Asphalt testing room – 2 Asphalt is a dark brown to black material cementations material in which the predominating constituents are bitumen that occur in nature or are obtained in petroleum processing. Asphalt is present in varying proportions in most crude petroleum. The crude petroleum is refined to separate the various fractions and recover asphalt. Similar process is occurring in nature have formed natural deposit of asphalt, some practically free from extraneous matter and some in which the asphalt has become mixed with variable quantities of mineral matter, water, and other substances. Natural deposits in which asphalt occurs within a porous rock structure are known as rock asphalts. Properties: Asphalt is strong cement, adhesive, highly waterproof, and durable. It is a plastic substance that imparts controllable flexibility to mixtures of mineral aggregates with which it is usually combined. It is moreover highly resistant to the action of most acids, alkalies and salts. Although a solid or semisolid at ordinary atmospheric temperatures, asphalt may be liquefied by the application of heat, or by dissolving it in petroleum solvents of varying volatility, or by emulsification. Almost all asphalt used in the world is refined from petroleum. Such asphalt is produced in a variety of types and grades ranging from hard brittle solids to almost water thin liquids. The semisolid form, known as asphalt cement, is the basic material. Cutting back or blending asphalts with petroleum distillates or by emulsifying them with water generally prepares liquid asphalt products. Recommendation: As the climatic condition of the city of Addis Ababa is cold to moderately cold for whole of the year, this manual therefore recommends the use of Asphalt Grade 85 – 100 for the heavily traffic roads.
- 5. Terms Related to Asphalt and its uses: Asphalt The term “asphalt” is usually interchangeable for bitumen. A dark brown to black cementicious material; solid, semisolid, or liquid in consistency; in which the predominating constituents are bitumen which occurs in nature as such or which are obtained as residue in refining petroleum”. (ASTM Designation D8) Asphalt, Catalytically Blown Air-blown asphalt produced by using a catalyst during blowing Process. Asphalt Cement Asphalt, which is refined to meet specifications, for paving or, other special purposes. Its Penetration is usually ranges from 40 to 300. The term is often abbreviated A.C. Asphalt Joint Filler An asphaltic product used for filling cracks and joints in pavement and other structures. Asphalt, Liquid an asphaltic material having a soft or fluid consistency that is beyond the range of measurement by the normal penetration test, the limit of which is 300 maximum. Asphalt Mineral filler Asphalt containing finely divided mineral matter passing No.200 sieve. Bitumen – A mixture of hydrocarbons of natural or pyrogenous origin, or a combination of both; frequently accompanied by non-metallic derivatives which may be gaseous, liquid, semi-solid, or solid; and which are completely soluble in carbon disulfide or carbon tetra-chloride. Asphalt Base Course A foundation course consisting of mineral aggregate, bound together with asphaltic material. Asphalt Concrete High quality, thoroughly controlled hot mixture of asphalt cement and well-graded, high quality aggregate, thoroughly compacted into a uniform dense, mass. Asphalt Pavements :- Pavements consisting of a surface course of 25 mm or more of mineral aggregate coated and cemented together with asphalt cement on supporting courses such as asphalt bases; crushed stone, slag or gravel; or on Portland cement concrete, brick or block pavement. Asphalt Prime coat Application of low viscosity liquid asphalt to an absorbent surface. It is used to prepare an untreated base for an asphalt surface. The prime penetrates into the base and plugs the voids, hardens the top and helps bind it to the overlying asphalt course. It also reduces the necessity of maintaining an untreated base course prior to placing the asphalt pavement.
- 6. c. Concrete testing room – 3 Properties of Portland cement: Most specifications for Portland cement place limits on its chemical composition and certain physical properties. An understanding of the significance of some of these properties is helpful in interpreting results of cement tests. In general, tests of the physical properties of the cement should be used merely to evaluate the properties of the cement rather than the concrete. 8-2.1 Fineness: Fineness of cement affects the rate of hydration. Greater cement fineness increases the rate at which cement hydrates and thus accelerates strength development. The effects of greater fineness on strength are manifested principally during the first seven days. 8-2.2 Soundness: Soundness refers to the ability of a hardened paste to retain its volume after setting. Lack of soundness or delayed destructive expansion is caused by excessive amounts of hard-burned free lime or magnesia. Most specifications for Portland cement limit the magnesia content and the autoclave expansion. Since the adoption of the autoclave expansion test by ASTM in 1943, there have been exceedingly few cases of abnormal expansion attributed to unsound cement. Consistency: Consistency refers to the relative mobility of a fresh mixture, or its ability to flow. During cement testing, pastes are mixed to normal consistency as defined by a penetration of 10±1mm of the Vicat plunger, while mortars are mixed to obtain either a fixed water-cement ratio or to yield a flow within a prescribed range. Both the normal consistency method and the flow test are used to regulate water contents of pastes and mortars; both allow comparing dissimilar ingredients with the same penetrability of flow. During concrete testing, the consistency of concrete is measured by the slump test. Setting Time: To determine if a cement paste undergoes setting and hardening during the first few hours, setting-time tests are performed using either the Vicat apparatus or a Gillmore needle. Initial set of cement paste must not occur too early; final set must not occur too late. The setting times indicate that the paste is or is not undergoing normal hydration reactions. Setting times of concretes do not correlate directly with setting times of pastes because of water loss to air or substrate and because of temperature differences. Compressive Strength: Compressive strength of Portland cement as specified by ASTM C150 is that obtained from tests of standard 50mm mortar cubes. These cubes are made and cured in a prescribed manner using standard sand. Compressive strength is influenced by the cement type, or more accurately, the compound composition and fineness of the cement. Typically, cement strengths exceed the ASTM minimum requirements by significant but different amounts. When early strengths with blended cements are important, concrete mixes should be proportioned for early age and not 28- day strengths.
- 7. The road construction there is seven layers and testing 1. Sub-Grade:- (1) The top layer of specified thickness of embankment or excavated areas on which the pavement structure including shoulders is constructed. (2) The top of a roadbed upon which the pavement structure and shoulders are constructed. The taking test as following Classification of soil a. Silt b. sand c. clay PI; Plastic index = LL(liquid limit) – PL( Plastic limit) California Bearing Ratio (CBR):- (CBR) The ratio of the force required to penetrate a soil mass with a circular piston of 50 mm diameter to the force required to penetrate a mass of high quality crushed stone with the same piston. The rate of penetration in both cases is 1.27 mm per minute Shrinkage test :- a type of test which is that putting a soil in tube like metal put on the oven Proctor test a. Compaction b. Modify c. Standard d. Mechanical compaction 2. Capping:- Under the capping there are three type of test a. PI test b. Proctor test c. CBR test 3. Sub-Base:- The layer or layers of specified or selected material of designed thickness placed on a sub-grade to support the base course Under the sub base there are three type of test a. PI test b. Proctor test c. Gradations test 4. Base Course:- The layer or layers of specified or selected material of designed thickness placed on a sub base or sub grade to support a surface course Under the base course there are three type of test a. PI test b. Proctor test c. Gradations test or sieve analysis d. Flakiness index e. CBR test
- 8. f. LAA – Los anjles ape ration 5. Prime Coat:- The application of a low viscosity liquid bituminous material to an absorbent surface, preparatory to any subsequent treatment, for the purpose of hardening or toughening the surface and promoting adhesion between it and the superimposed construction. 6. Base Asphalt:-One or more layers of a pavement structure designed to accommodate the traffic load, the top layer of which resists skidding, traffic abrasion, and the disintegrating effects of climate. The top layer is top layer is sometimes called Wearing Course. The mixing size of the aggregate 00, 01, 02 and bitumen. Under the base Asphalt there are three type of test Bitumen test a. Quality test b. Safety test c. Grade test 7. Surface Asphalt: - An application of bituminous material and cover aggregate the mixing size of the aggregate 00, 01 and bitumen. Under the surface Asphalt there are three type of test Bitumen test a. Quality test b. Safety test c. Grade test