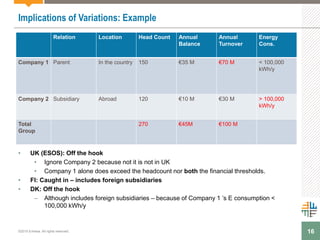
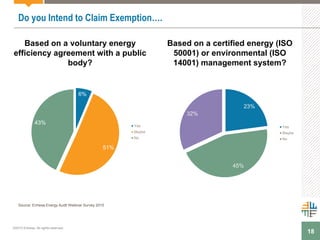
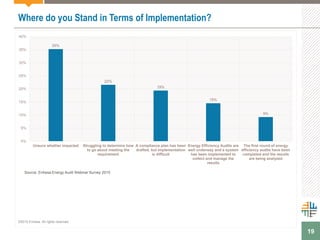
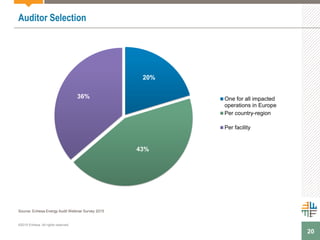
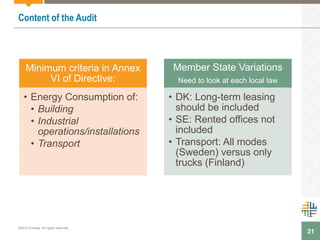
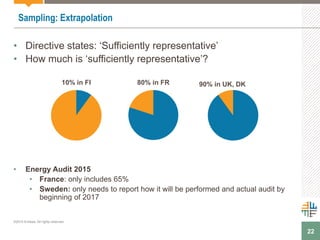
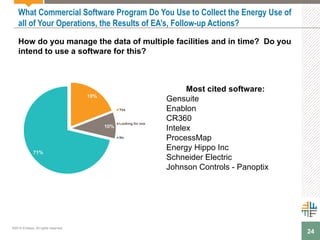
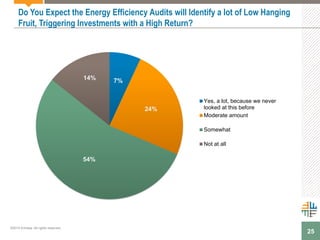
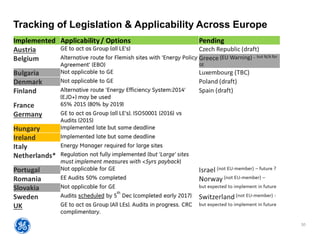
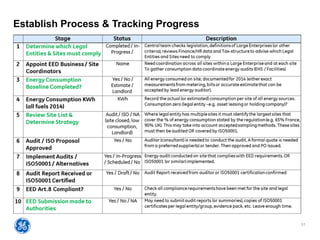
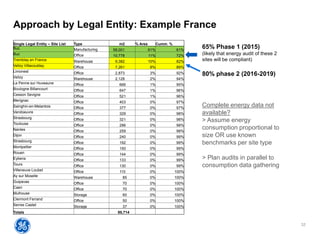
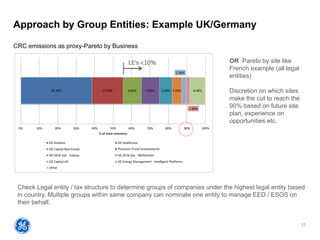
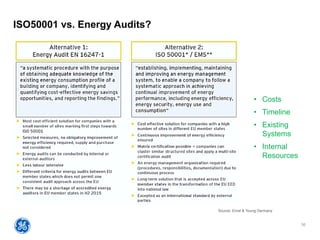
The document outlines a webinar presented by Enhesa regarding the compulsory energy efficiency audits mandated for large enterprises in Europe, in accordance with the EU Energy Efficiency Directive. It details the requirements for conducting these audits, including deadlines, necessary qualifications for auditors, and the reporting obligations for organizations. The presentation also highlights the varying interpretations and implementations of these directives across different EU member states, alongside a case study from General Electric.