Civic Education Scheme of Work Summary for SSS1
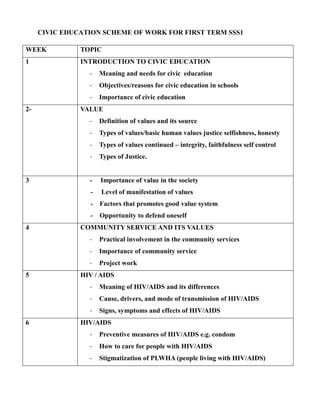
- 1. CIVIC EDUCATION SCHEME OF WORK FOR FIRST TERM SSS1 WEEK TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION TO CIVIC EDUCATION - Meaning and needs for civic education - Objectives/reasons for civic education in schools - Importance of civic education 2- VALUE - Definition of values and its source - Types of values/basic human values justice selfishness, honesty - Types of values continued – integrity, faithfulness self control - Types of Justice. 3 - Importance of value in the society - Level of manifestation of values - Factors that promotes good value system - Opportunity to defend oneself 4 COMMUNITY SERVICE AND ITS VALUES - Practical involvement in the community services - Importance of community service - Project work 5 HIV / AIDS - Meaning of HIV/AIDS and its differences - Cause, drivers, and mode of transmission of HIV/AIDS - Signs, symptoms and effects of HIV/AIDS 6 HIV/AIDS - Preventive measures of HIV/AIDS e.g. condom - How to care for people with HIV/AIDS - Stigmatization of PLWHA (people living with HIV/AIDS)
- 2. 7 YOUTH EMPOWERMENT - Definition of the concept of youth empowerment - Various youth empowerment skills, life coping manipulative skills intellectuals, other youth empowerment skills - Communicative skills - Artistic skills 8 IMPORTANCE AND BENEFITS OF YOUTH EMPOWERMENT SKILLS - Guiding students in acquiring a specific skill e.g. ICT, Capentry - Demonstrating or practicing a specific skill - Problems of youth empowerment 9 GOALS OF CITIZENSHIP EDUCATION (cont.) - Meaning of citizenship, acquisition of citizenship - Definition of goals of citizenship education, acquisition, knowledge, right attitude, values etc. 10 GOALS OF CITIZENSHIP EDUCATION (cont) - Meaning of government - Structure of government - Functions of government 11 NATIONALISM (Definition) - Different local/world civic problems - Effects of nationalism in Nigeria 12 – 13 REVISION AND EXAMINATION
- 3. THE CAVENDISH COLLEGE, KADUNA CIVIC EDUCATION WHITE BOARD SUMMARY CONTENT Meaning and needs for civic education Objectives/reasons for civic education in schools Importance of civic education Civic education is a social science subject. It teaches Nigeria youths their duties and right to become good followers and responsible future leaders. It indicates in them the right values, positive attitudes and behavior that are embraced in the society. Civic education expose students to necessary awareness of democratic values that will enable them make useful contribution to social – political development of their nation in particular and the world at large. NEEDS FOR CIVIC EDUCATION It inculcates in its scholars the relevance of nationalism and patriotism as well as solution to the multi – dimensional problems of Nigeria. It inculcates in them the consciousness and awareness of democratic values, social political institutions and citizens rights and duties to the society. To assist the governments in serving the citizens well by providing basic infrastructural facilities that will rise their standard of living. To re-orientates the citizens to imbibe positive values that will assist the economic growth and development throughout the nation TOPIC INTRODUCTION TO CIVIC EDUCATION TERM 1 WEEK 1 CLASS YEAR10 DATE
- 4. To educate citizens on how to fight for their right if any government goes contrary to the constitution. OBJECTIVES OF CIVIC EDUCATION IN SCHOOLS The school is a place where students come to acquire knowledge for potential actualization and self development. The following are the importance of civic education in schools: To receive instruction and learn about emergency of issues; so that student will be able to solve them. To emphasize the instruction of government, its functions and responsibilities to the people and vice-versa. To promote inter-relationship between man/woman, man/man, woman/woman, the government and the society. To assist the student in acquiring knowledge, attitudes, values and basic skills to become responsible and disciplined citizens. To enable student realize day to day societal living at their critical age of thinking and reasoning about the happenings around them. To enable student raise up and defend the course of justice when the government fails to perfume their duties. IMPORTANCE OF CIVIC EDUCATION TO NATION BUILDING Nation building involves promoting national unity, national integrity and national consciousness. Thereby enhancing national development for a country to develop, the citizens must know their rights and responsibilities and how to fight for those rights when violated by government or individual The following are the importance of citizen education It moves citizens to be particular in politics and social economic activities of the country.
- 5. It enables students to understand the government and as a result take part in the decision moving process of the country. It reminds the student that democracy is the best form of government and by this, citizens are able to form pillars of democracy across the Nation. It enables its scholars to acquire positive values that will assist them to be well behaved, courageous and responsible in their activities and relationship with members of the society. THE CAVENDISH COLLEGE, KADUNA CIVIC EDUCATION WHITE BOARD SUMMARY THE MEANING Of VALUES CONTENTS Meaning of value, Types of values, Types of Justice. INTRODUCTION: Values are related to the generally accepted standards of social behaviors. Values describe the sort of person we want to be; the manner in which we treat ourselves and others, and our interaction with the world around us. Definition of value Values are basic and fundamental beliefs that guide or motivate attitudes or actions. Values are important as they are related to the norms of a society, and so they guide the conduct of individuals, groups or the entire community. Types of value TOPIC VALUES TERM 1 WEEK 2 CLASS YEAR10 DATE
- 6. There are different types of values. They include; Honesty, Selflessness, Cooperation, Self-reliance, Integrity, Contentment, Discipline, Courage, Right altitude to work, Justice, etc. Honesty: honesty is about both speaking and acting truthfully. Selflessness: to have a great love for others. It also means giving- your time, money, and donated items you no longer use or need. It is also defines as as the act of caring for others more than yourself Discipline: is learning and applying intentional standards to achieve meaningful objectives. Courage: is the choice and willingness to confront agony, pain, danger, uncertainty, or intimidation. Justice: It refers to fairness in the way people are treated. Types of justice: there are so many types of justice but we are going to identify just five types. Retributive Justice, Social justice, Organizational justice,
- 7. Distributive justice, Restorative Justice, etc Evaluation Identify and explain at least five attributes of selflessness and four benefits of Selflessness. Explain The Following Types Of Values: Cooperation, Self-reliance, Integrity, Contentment, and Right altitude to work. READING ASSIGNMENT. Read page 8 to 10, and from page 13 to 20 of Bounty civic education for senior secondary school by A.A.ADEYINKA OLALEKAN ODETOLA. EVALUATION 1. Which One of the following is not an attribute of selflessness? (a)It breads true friendship (b) Humility (c) Love (d) Tolerance 2. The principle and structure that influence the behavior and culture of a particular people or community is known as ___________ (a) honesty (b) value (c) dishonesty (d) equity 3. One of the following is not a way of obtaining value: (a) family (b) School (c) religion (d) stealing.
- 8. 4. The human quality of communicating and acting truthfully in fairness and sincerity is known as ___________ (a) dishonesty (b) value (c) honesty (d) cultism. 5. __________ refers to fairness in the way people are treated (a) injustice (b) justice (c) cheating (d) stealing. THEORY 1. Explain the meaning of value 2. Identify and explain the attributes of justice 3. State three benefits of selflessness 4. Mention and explain the attribute of justice 5. Explain the level of manifestation of value in our society.
- 9. THE CAVENDISH COLLEGE, KADUNA CIVIC EDUCATION WHITE BOARD SUMMARY CONTENTS Importance of values in the society Factors that promotes good value systems The level of manifestation of value in the society Opportunity to defend oneself IMPORTANCE OF VALUES IN THE SOCIETY They help society to form thoughts, worlds and actions. Values help people grow and develop; It also create the future that people want to experience. The Importance Of Value in the society includes: Progress: Good values help each individual member achieve his or her particular goals. They manage the common actions of individuals in a society: They help to decide if preferences or events are good or bad, important or significant and correct or wrong. Expand the identity of a society and culture: Values have many social functions. Values that are derive from common experience unite families, tribes, TOPIC VALUES TERM 1 WEEK 3 CLASS YEAR10 DATE
- 10. societies and nations. They are the fabric that creates culture; If people lie, cheat and steal, the culture of society will not be healthy. Provide tools for self-realization: Values are needed to know how to react to difficult situations. Values are also needed to form lasting relationships with those around us. They make society and people work better: When values are well implemented, society can function in an orderly and functional way. This allows people to have an awareness of the purposes; Can solve quickly and satisfactorily the problems that are presented. Change human behavior: Values are an effective way of correcting and reforming negative behaviors in individuals and in a society. FACTORS THAT PROMOTES GOOD VALUE SYSTEMS The following are the factors that promote good value system in the society; Trust: When trust is established in society and even among individuals, progress and development can easily be attained. Tolerance: Tolerance brings about peace, harmony, unity and progress which transmit to the overall development of any society. Fairness: Fairness abhors partiality and favoritism thus promoting good values in our societies. Integrity: This is the attitude of doing what is right all the time and this has the tendency of promoting good moral values in the society. Consistency: This is the attitude of having confidence in someone in doing what is right. THE LEVEL OF MANIFESTATION OF VALUE IN THE SOCIETY
- 11. 1. Our life: even a mad man moves away for speedy vehicles on the road and other dangerous object to avoid death. 2. Good health: human beings and even the lower animals can exist and survive only with good health. Our life therefore depends on the sanitation habit, proper usage of drugs etc. 3. Being human being is a value: it is often said that ‘man is created in God’s image’. Human being can reason and manipulate his/her environment towards his satisfaction. Man and woman should therefore contribute positively towards making the society a better place to live. 4. One’s family is a value: family is where man originated from and the first agent of socialization. Nigerians are proud of their family’s name and hence, they do everything possible not to tarnish their family names. OPPORTUNITY TO DEFEND ONESELF Judging an individual without listening to his side of the story brings unfairness, partiality and injustice. Self – defence is protecting oneself against attack or something adverse. It is the use of force to protect oneself against someone attacking us. Every person should be security conscious in the society; hence, we will be protected against sudden adversities. BENEFITS OF OPPORTUNITY TO DEFEND ONESELF 1. It reduces conflict in the society: given the opportunity to defend oneself issues will be amicably resolved without deterioration. 2. It prevents injustice: judgement is passed based on content of parties’ defense. 3. It promotes peace in the society: the society is peaceful in justice and fairness. HOW TO DEFEND ONE’S SELF AGAINST BEING ATTACKED 1. Being careful about the type of people you keep as friends
- 12. 2. Avoid night clubbing apart from the fact that you can be vulnerable to physical and emotional attacks; you can be lured into hard drugs and other immoral acts which can jeopardize your future dreams and aspirations. 3. Do not use sexually attractive or provocative dresses especially in the public 4. Do not receive gift especially when you are in doubt of the source and motive behind such gift. EVALUATION 1. Which one of the following is not a level of manifestation of value in the society? (a) Life (b) family (c) health (d) being human (e) prostitution. 2. The following are the factors that promote good value except; (a) trust (b) Tolerance (c) integrity (d) Consistency (e)perjury 3. Members of a society are expected to adhere to societal values for the following reasons except? (a) Enhancement of development ( b )improvement of self dignity (c) Reduction of social vices (d) Relegation of morality. 4. An attribute of honesty is (a) tolerance (b) justice (C) compromise (d) liberty3 5. Discipline is describe as the (a) Ability to show hospitality (b) State or quality of being brave (c) Tendency to fight (d) Ability to behave in a controlled manner. THEORY (i) Explain five importance of defending one’s self (ii) Outline and explain the level of manifestation in the society, (iii) Explain the importance of value in the society.
- 13. THE CAVENDISH COLLEGE, KADUNA CIVIC EDUCATION WHITE BOARD SUMMARY CONTENTS - Practical involvement in the community services - Importance of community service - Project work COMMUNITY SERVICE Community Service helps us to connect to the Community. Thus, it teaches us how significant it is to help the ones in need, the ones who are less fortunate than us. It can also be defined as a volunteered service or activity that is performed by an individual, group or organization for the benefit of the public without any compensation. There are a lot of areas in the community that requires the involvement of citizens. They include the following: Creating awareness campaign about HIV/AIDS and its consequences, Road drainage construction; Donating drugs and other useful materials to health centers and hospitals; Donating instructional materials such a books, computers and stationeries to schools; Cleaning the market and Motor Park; TOPIC COMMUNITY SERVICE AND ITS VALUES TERM 1 WEEK 4 CLASS YEAR10 DATE
- 14. Helping to control traffic on the road, Teaching children with learning disability. IMPORTANCE OF COMMUNITY SERVICE Community service is an important social development factor, it helps in building the society by improving the structure of the community and also impacts positively on the individuals who carried out the work. 1. Learn New Skills Community service offers numerous options for personal and professional development, with one of the most valuable advantages being the potential to learn new skills. 2. Community Service Raises Social Awareness Community service broadens your horizons by helping you understand the needs of the society and the population you are trying to help through the project you are volunteering on. 3. Helps in Socialization Introverted students sometimes have problems meeting people and making friends, but volunteering might help shy and quiet individuals with this issue as it offers lots of opportunities to meet and work with various people. Thus, it is a valuable experience for improving and practicing how to socialize in diverse surroundings. 4. Society Development Community Service helps in the building and development of society especially when there is a problem to solve that requires financial aid, such problem(s) can be solved by the volunteers, 5. Impact on student’s life It’s also proven to increase a student’s self-esteem and help them meet other people and develop connections with their community.
- 15. THE CAVENDISH COLLEGE, KADUNA CIVIC EDUCATION WHITE BOARD SUMMARY CONTENTS Meaning of HIV/AIDS and its differences Cause, drivers, and mode of transmission of HIV/AIDS Signs, symptoms and effects of HIV/AIDS INTRODUCTION Human beings are protected against diseases- causing microorganisms by the immune system of the body. The human immune system through a series of steps called immune response, attacks infectious organisms and other substances that invade the body system and causes diseases. But, when the body system is affected, then the body will be exposed to various infections. MEANING OF HIV HIV stands for Human Immune- deficiency Virus. It is one of a group of viruses known as Retroviruses. After getting into the body, the virus damages the cell of the body’s immune system thereby paving way for life threatening opportunistic infections to thrive. MEANING OF AIDS AIDS stands for Acquired immune deficiency syndrome. It is caused by HIV and occurs when the HIV virus ha destroyed much of the body’s defenses. Making it very easy for people with AIDS to be affected by virus that might not ordinarily affect people when their immune system is functioning well. TOPIC HIV/AIDS TERM 1 WEEK 5 CLASS YEAR10 DATE
- 16. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HIV AND AIDS HIV AIDS HIV infects humans and weakens the immune system. AIDS is the disease that results from HIV. A person can have HIV and never develop AIDS, Anyone Who has been Diagnosed With AIDS Has HIV. Antiretroviral drugs can be used to suppress HIV particles within the blood. AIDS Can Not Be Controlled HIV is not a death sentence it can be managed AIDS cannot be managed it is life threatening CAUSE OF HIV/AIDS To become infected with HIV/AIDS, infected blood, semen or vaginal secretions must enter your body. This can happen in several ways. By having sex. You may become infected if you have vaginal, anal or oral sex with an infected partner whose blood, semen or vaginal secretions enter your body. By sharing needles. Sharing contaminated injection drug paraphernalia (needles and syringes) puts you at high risk of HIV and other infectious diseases, such as hepatitis. From blood transfusions. In some cases, the virus may be transmitted through blood transfusions. During pregnancy or delivery or through breastfeeding. Infected mothers can pass the virus on to their babies.
- 17. SYMPTOMS OF HIV/AIDS Some people infected by HIV develop a flu-like illness within 2 to 4 weeks after the virus enters the body. This illness, known as primary (acute) HIV infection, may last for a few weeks. Possible signs and symptoms include: Fever Headache Muscle aches and joint pain Rash Sore throat and painful mouth sores Swollen lymph glands, mainly on the neck Diarrhea Weight loss Cough Night sweats EFFECTS OF HIV/AIDS ON THE BODY HIV primarily affects the body by targeting and damaging cells in the immune system. The immune system protects the body against viruses, bacteria, and fungi. It damages the CD4T cells, which are responsible for keeping people healthy and protecting them from diseases and infections. It causes sores in and around the body It causes rapid loss of soft tissue and jaw bone,
- 18. It causes weight loss and ulcers all over the body, It leads to a decrease in the ability to think properly and process information, It leads to brain tumor, It leads to premature death. EVALUATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS. HIV is a retrovirus that infects and colonizes cells in the ______. 1. immune system (b)immune system and the central nervous system (c) endocrine system (d) immune system and endocrine system (e) the cell 2. In 2015, the global prevalence of HIV infection was ______. a. 0.2% (b) 0.4% (c) 0.6% (d) 0.8% (e) 0.5% 3. The most common cause of inpatient admission to hospital for those living with HIV is ______. a. tuberculosis and other Micro bacterial infections (b)cardiovascular disorders ( c) bacterial infections (d) none of these (e)flu 4. ______ who needs combination antiretroviral therapy receives it. a. Two in ten (b) One in five ( C) Four in ten (d) Three in five (e) five in ten 5. According to Crepaz, Hart and Marks (2004), people’s ______ and viral load may promote unprotected sex. (a) Beliefs about ART ,(b) Knowledge of risk, (c) Beliefs about transmission, (d) Level of health literacy, (e) knowledge.
- 19. THEORY QUESTIONS 1. Outline at least five symptoms of HIV/AIDS? 2. Which is the most effective way to control the spread of HIV? 3. What are the latest inventions in the prevention of HIV? 4. Where did the AIDS pandemic begin? Is AIDS an epidemic or a pandemic disease? 5. What are the differences between HIV and AID?
- 20. THE CAVENDISH COLLEGE, KADUNA CIVIC EDUCATION WHITE BOARD SUMMARY CONTENTS Preventive measures of HIV/AIDS e.g. condom How to care for people with HIV/AIDS Stigmatization of PLWHA (people living with HIV/AIDS) PREVENTIVE MEASURES OF HIV/AIDS Know the Risks HIV prevention starts by getting the facts straight—understanding the various modes of transmission and identifying which activities place you, as an individual, at risk. E.g HIV/AIDS is spread through breast milk, anal sex, vaginal sex, and shared needles, etc. Take Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PREP) Is a prevention strategy in which a daily dose of HIV medications, known as antiretroviral can reduce your risk of getting HIV by as much as 99%. PREP can be used by anyone at risk of HIV who wants to reduce their odds of infection Get and Stay Undetectable Undetectable = untransmissible (U=U) is an evidence-based strategy in which people with an undetectable viral load cannot pass the virus to others. Undetectable means that no virus was detected in the blood sample, which is defined as having under 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood. A viral load is a measurement of the amount of virus in a sample of blood. TOPIC HIV/AIDS TERM 1 WEEK 6 CLASS YEAR10 DATE
- 21. Use Condoms: There is no reason to be lax when it comes to condoms. Short of abstinence, internal and external condoms are still the most reliable means of preventing pregnancy, HIV, and other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). No other preventive strategy can do all three Conceive Safely: In nearly half of all couples living with HIV, one partner is HIV-positive and the other is HIV-negative. couples today have a greater opportunity than ever to conceive—enabling pregnancy while minimizing the risk of transmission to a partner without HIV. Avoid Mother-to-Child Transmission: By placing the mother on antiretroviral therapy early in the pregnancy, the risk of transmission is extremely low. Even if treatment is started later in the pregnancy, the overall risk is still less than 2%. Avoid Sharing Needles: The rate of HIV among people who inject drugs (PWIDs) is high. Studies suggest that anywhere from 20% to 40% of PWIDs are infected due to the shared use of needles or syringes. Their sexual partners may also be at risk, particularly if they are unaware of their partner's drug use. Prevent HIV After an Exposure: If you believe you have been exposed to HIV, either through condom less sex or other high-risk activities, you can take a 28-day course of HIV drugs to potentially avert the infection. Called post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), the strategy works best if started soon after exposure to the virus. How to care for people with HIV/AIDS Listen to them: Being diagnosed with HIV is a life-changing news. Listen to them and offer your support. Be available to have open and honest conversations with them about HIV. Learn: Educate yourself about HIV: what it is, how it is and is not transmitted, how it is treated, and how people can stay healthy with HIV.
- 22. Having a solid understanding of HIV is a big step forward in supporting your loved one and reassuring them that HIV is a manageable health condition. Encourage treatment. Some people who are recently diagnosed may find it hard to take that first step to HIV treatment. Encourage your them to see a doctor and start HIV treatment as soon as possible. Support medication adherence. It’s important for people with HIV to take their HIV medicine exactly as prescribed. Ask them what you can do to support them in establishing a medication routine and sticking to it. Get support. Take care of yourself and get support if you need it. Turn to others for any questions, concerns, or anxieties you may have, so that the person who is diagnosed can focus on taking care of their own health. STIGMATIZATION OF PLWHA (PEOPLE LIVING WITH HIV/AIDS) Stigmatization is a mark of disgrace associated with a particular circumstances, quality or person. HIV stigma is negative attitudes and beliefs about people with HIV. It is the prejudice that comes with labeling an individual as part of a group that is believed to be socially unacceptable. The stigma can also be based on gender. The way people of a particular ethnic group are perceived can also be a basis for stigmatization; people can also be stigmatized base on their social class, the epidemic has been characterized by the assumption about the rich, and HIV/AIDS has been associated with affluent lifestyle. People living with HIV/AIDS are openly abused and maltreated due to their status. The consequences are not palatable and include the following: Rejection by family Rejection by friends and peer groups Poor treatment at healthcare facilities
- 23. Poor treatment in education settings Denial of rights, Psychological damage. As a result of all the above mentioned consequences of stigmatization, many people are afraid to visit the hospital to know their HIV/AIDS status or seek treatment if they have the disease EVALUATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS. 1. Who said that stigma is ‘an attribute that is deeply discrediting’ and that reduces the bearer ‘from a whole and usual person to a tainted, discounted one’. a. Foucault (b)Moscovici (c)Vygotsky (d) Goff man (e) ploto 2. One in ten people ______ believed HIV infection can be transmitted through routes such as ______. a. incorrectly; kissing and spitting (b) correctly; kissing and spitting (c) incorrectly; needle sharing (d)none of these (e) hugging 3. Studies suggest that fear of stigmatization is especially strong among migrants. This is ______ which occurs when there is more than one type of difference. a. stigma enlargement (b) stigma multiplication (c ) stigma amplification (d) stigma magnification (e)none of the above 4. Golub et al. (2010) surveyed 180 HIV-negative high-risk MSM and found that around 70% of participants reported that they would be likely to use PREP if it were
- 24. at least 80% effective in preventing HIV. Of those, over ______ reported that they would be likely to decrease condom use while on PREP a. 15% (b) 25% (c) 35% (d) 45% (e) 30% 5. Scott-Sheldon et al. (2013) found that ______ mediated the association between HIV status and alcohol use. a. Depression (b) stress (c) income(d) social support (e) rejection THEORY 1. what is the meaning of HIV/AIDS 2. what are the causes of HIV/AIDS 3. list five symptoms of HIV/AIDS 4. outline and explain at least five ways we can care for those living with HIV/AIDS 5. discuss HIV/AIDS stigmatization