Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (12)
An Experimental Study on Stabilization of Loose Soil by Using Jute Fiber

An Experimental Study on Stabilization of Loose Soil by Using Jute Fiber
Effect of Compaction Moisture Content on Strength Parameters of Unsaturated C...

Effect of Compaction Moisture Content on Strength Parameters of Unsaturated C...
Similar to Anderson_Poster2_2015
Similar to Anderson_Poster2_2015 (9)
Stabilisation of Black cotton Soils by Using Groundnut Shell Ash

Stabilisation of Black cotton Soils by Using Groundnut Shell Ash
IRJET - Heave Reduction on Expansive Soil by using Geotextiles

IRJET - Heave Reduction on Expansive Soil by using Geotextiles
Improvement on the concrete cracks by using Bacillus pastuerii

Improvement on the concrete cracks by using Bacillus pastuerii
Physical Modelling Of Improving Bearing Capacity For Foundations By Geo Fabrics

Physical Modelling Of Improving Bearing Capacity For Foundations By Geo Fabrics
Research Inventy : International Journal of Engineering and Science

Research Inventy : International Journal of Engineering and Science
(httpwww.accessscience.com.ezproxy2.library.drexel.edu).docx

(httpwww.accessscience.com.ezproxy2.library.drexel.edu).docx
Review Paper on Study on Properties of Black Cotton Soil using Stone Dust and...

Review Paper on Study on Properties of Black Cotton Soil using Stone Dust and...
Effect of discrete_fiber_reinforcement_on_soil_ten

Effect of discrete_fiber_reinforcement_on_soil_ten
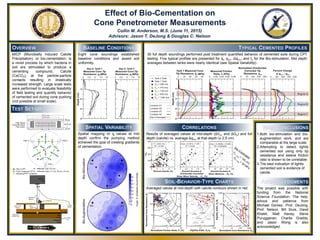
Anderson_Poster2_2015
- 1. Effect of Bio-Cementation on Cone Penetrometer Measurements Collin M. Anderson, M.S. (June 11, 2015) Advisors: Jason T. DeJong & Douglas C. Nelson 1.Both bio-stimulation and bio- augmentation work, and are comparable at the large scale. 2.Attempting to detect lightly cemented soil using only tip resistance and sleeve friction ratio is shown to be unreliable. 3.The best indication of lightly cemented soil is evidence of calcite. The project was possible with funding from the National Science Foundation. The help, advice and patience from Michael Gomez, Prof. DeJong, Prof. Nelson, Bill Sluis, Daret Khalet, Matt Havey, Steve Purugganan, Charlie Graddy, and Jason Wong is also acknowledged. MICP (Microbially Induced Calcite Precipitation), or bio-cementation, is a novel process by which bacteria in soil are stimulated to produce a cementing compound, Calcite (CaCO3), at the particle-particle contacts resulting in drastically increased strength. Large scale tests were performed to evaluate feasibility of field testing and quantify behavior of cemented soil during cone pushing (not possible at small scale). Eight cone soundings established baseline conditions and assed soil uniformity. Spatial mapping of qt values at mid depth confirm the pumping method achieved the goal of creating gradients of cementation. Results of averaged values at mid-depth (ΔVs1 and ΔGo) and full depth (calcite) vs. average Δqt1n at that depth (± 2.5 cm) 30 full depth soundings performed post treatment quantified behavior of cemented soils during CPT testing. Five typical profiles are presented for qt, qt1n. Δqt1n, and fs for the Bio-stimulation. Mid depth averages between tanks were nearly identical (see Spatial Variability). Averaged values at mid-depth with calcite contours shown in red Region B Region A Region C Yolo Loam Top Cap Concrete Sand String Pot To DAQ System Steel Cross Beams Mini- Cone Smooth Sleeve Waterproof Rubber Liner 2,000 lbs. Load Thin, Plastic Liner Bio-StimulationBio-Augmentation 3% 5% 1% 3% 5% 1% Measuredtipresistance,qt(MPa) W1 W2W3 W1 W2W3