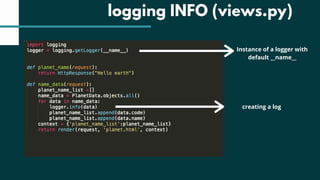
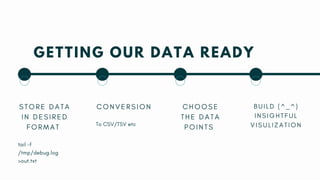
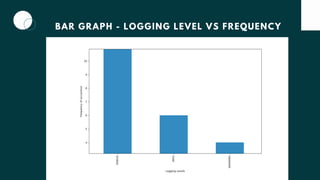
The document discusses debugging techniques in Django, focusing on the importance of logging for tracking events during code execution. It explains the differences between print statements and the logger module, emphasizing the structured capabilities of logger through filtering, log levels, and configuration. A step-by-step guide on configuring a logger in Django and visualizing logging data is also provided.