The document discusses considerations for doing business in India, including:
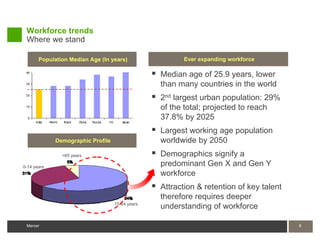
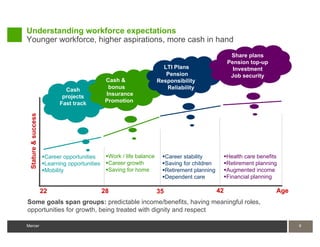
1) Attracting and retaining talent requires understanding expectations of India's young workforce and providing competitive compensation and career opportunities.
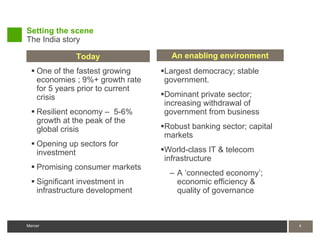
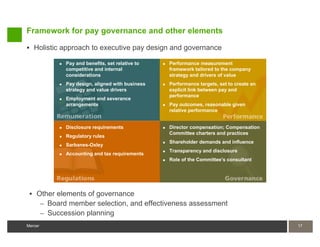
2) Governance requires compliance with India's regulatory environment on hiring, wages, and benefits as well as disclosure of executive pay.
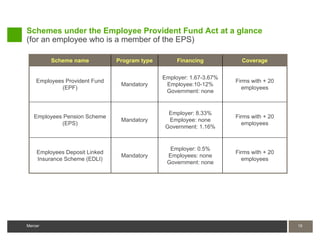
3) Statutory retirement benefits that are mandatory for employers in India include the Provident Fund and Gratuity plans.